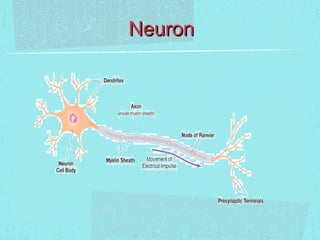
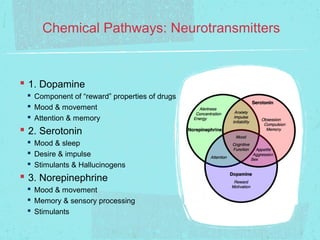
The document discusses the components of the nervous system, including glial cells which provide structure and nutrients, and neurons which analyze and transmit information. It then focuses on the 7 main neurotransmitters - dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, GABA, endorphins, glutamate, and acetylcholine - and their roles in mood, movement, memory, and other processes. Finally, it explains how psychoactive substances can impact neurotransmission by increasing or reducing neurotransmitter activity, or blocking reuptake.