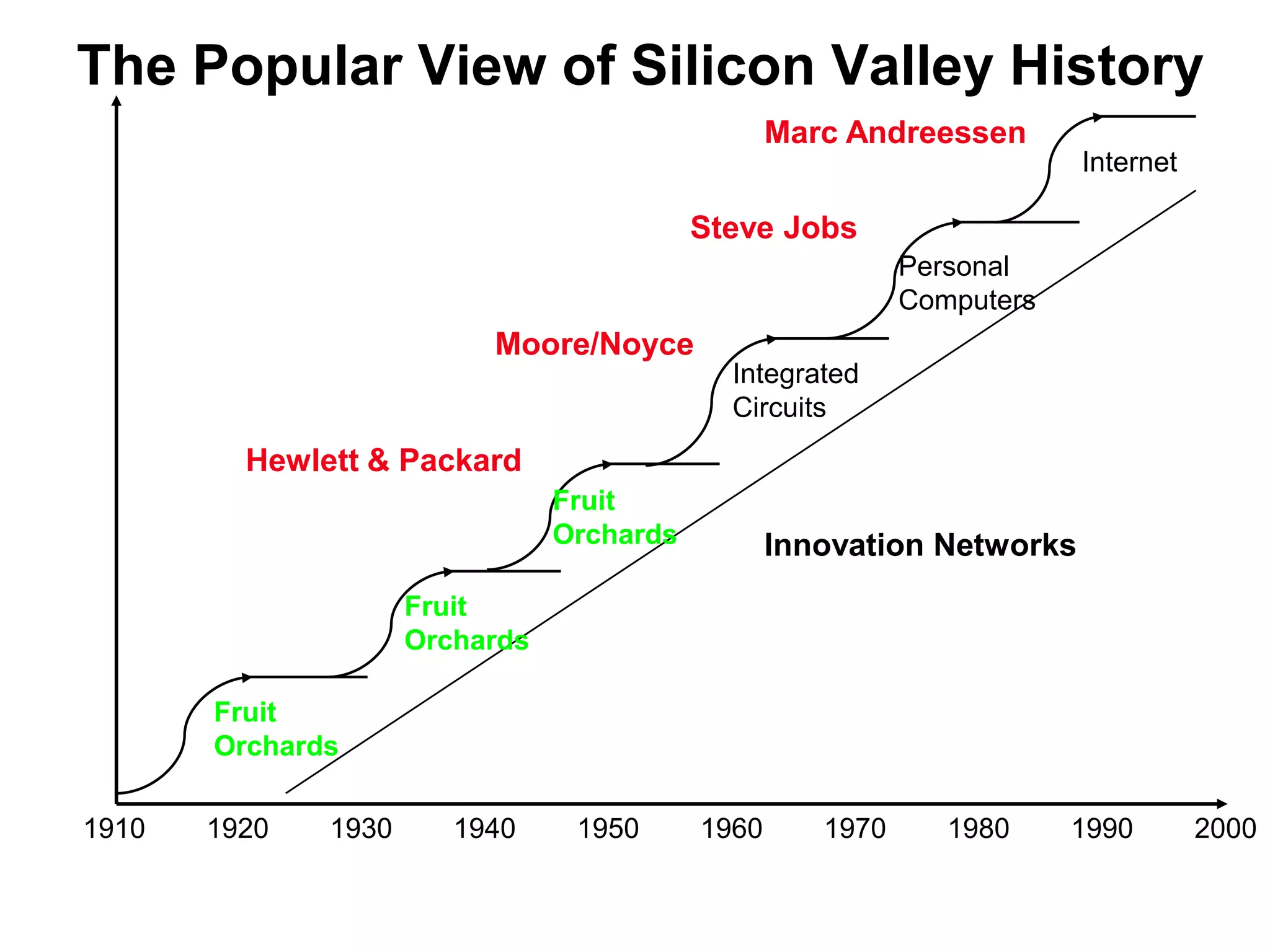
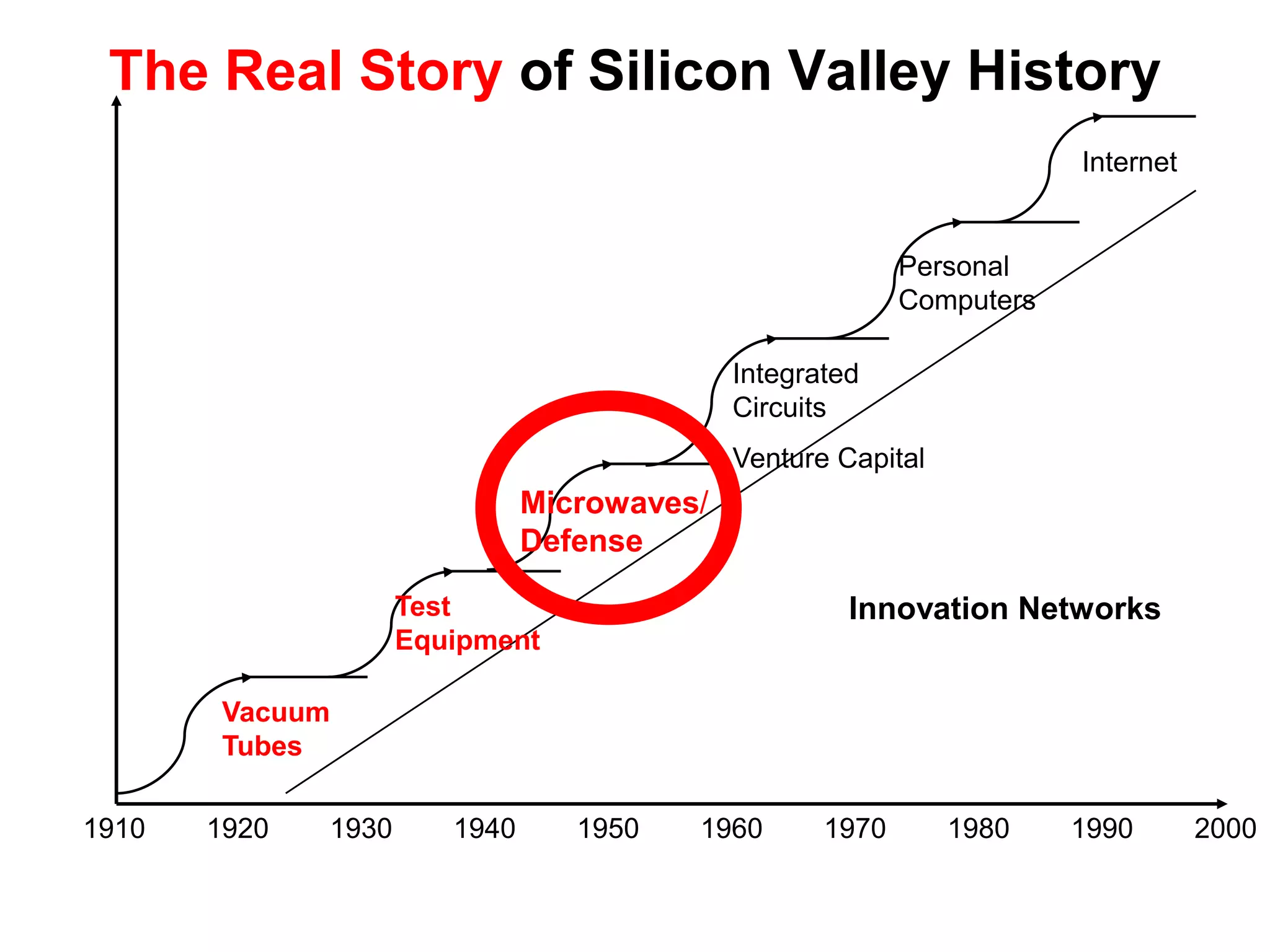
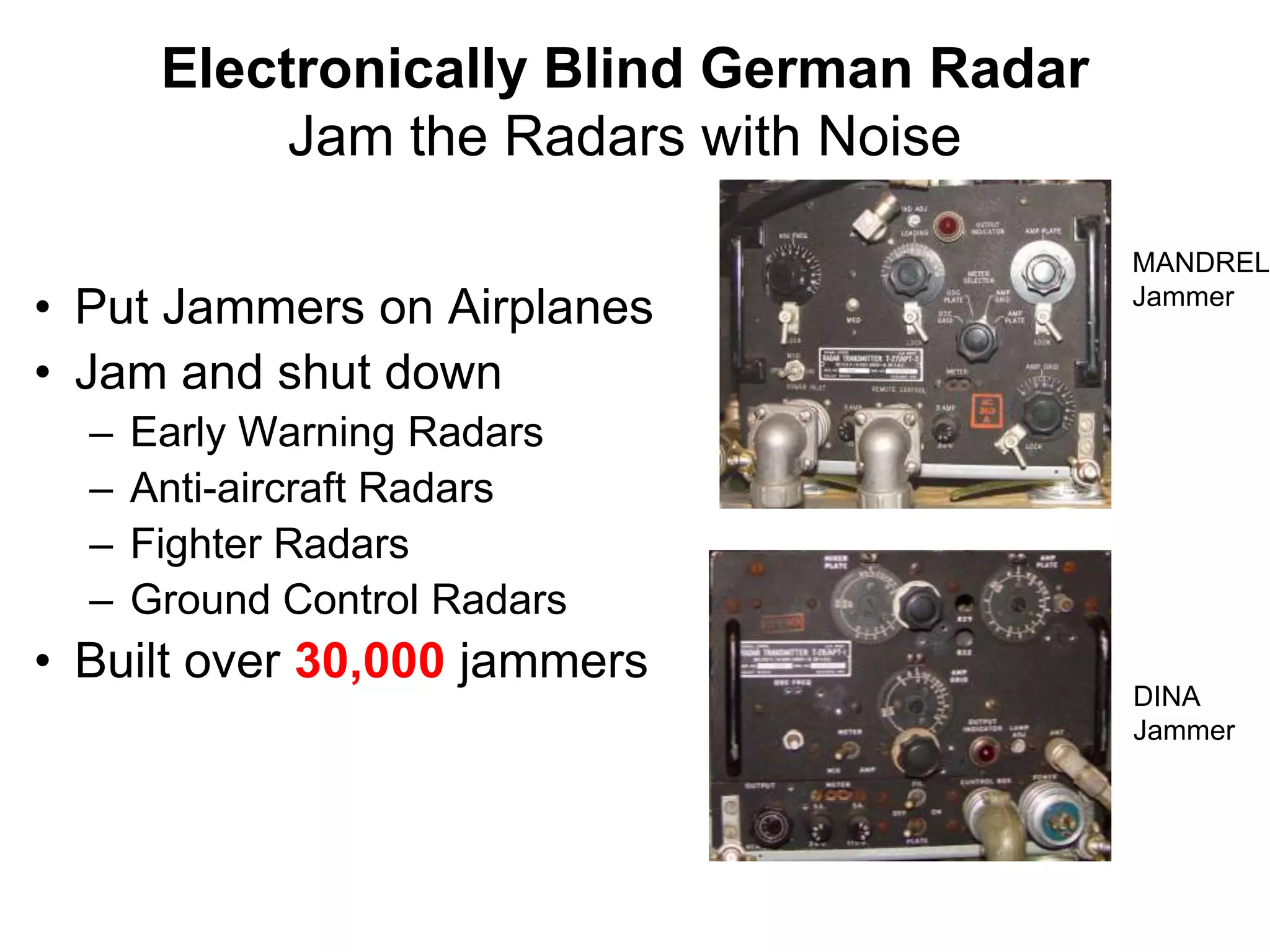
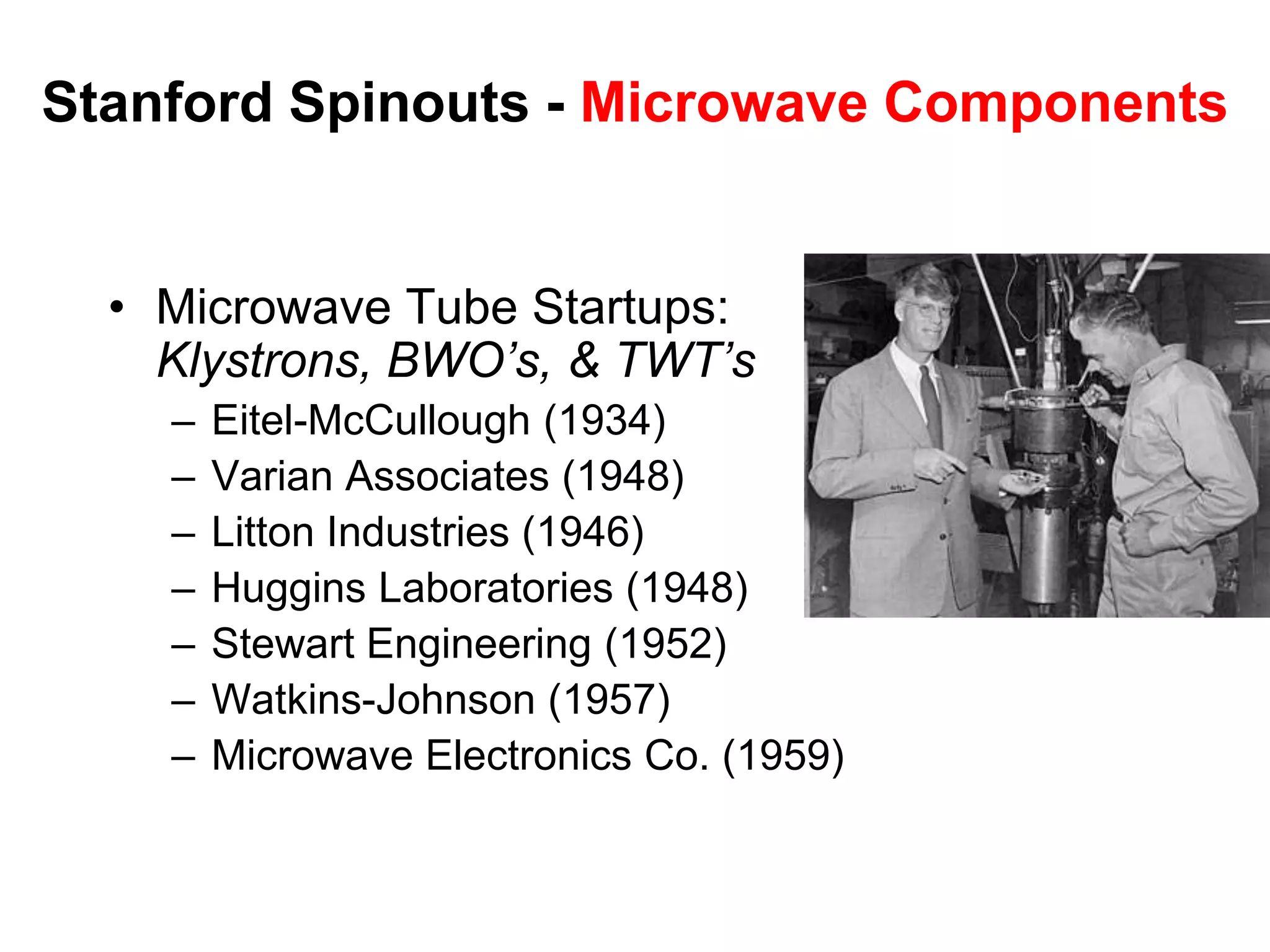
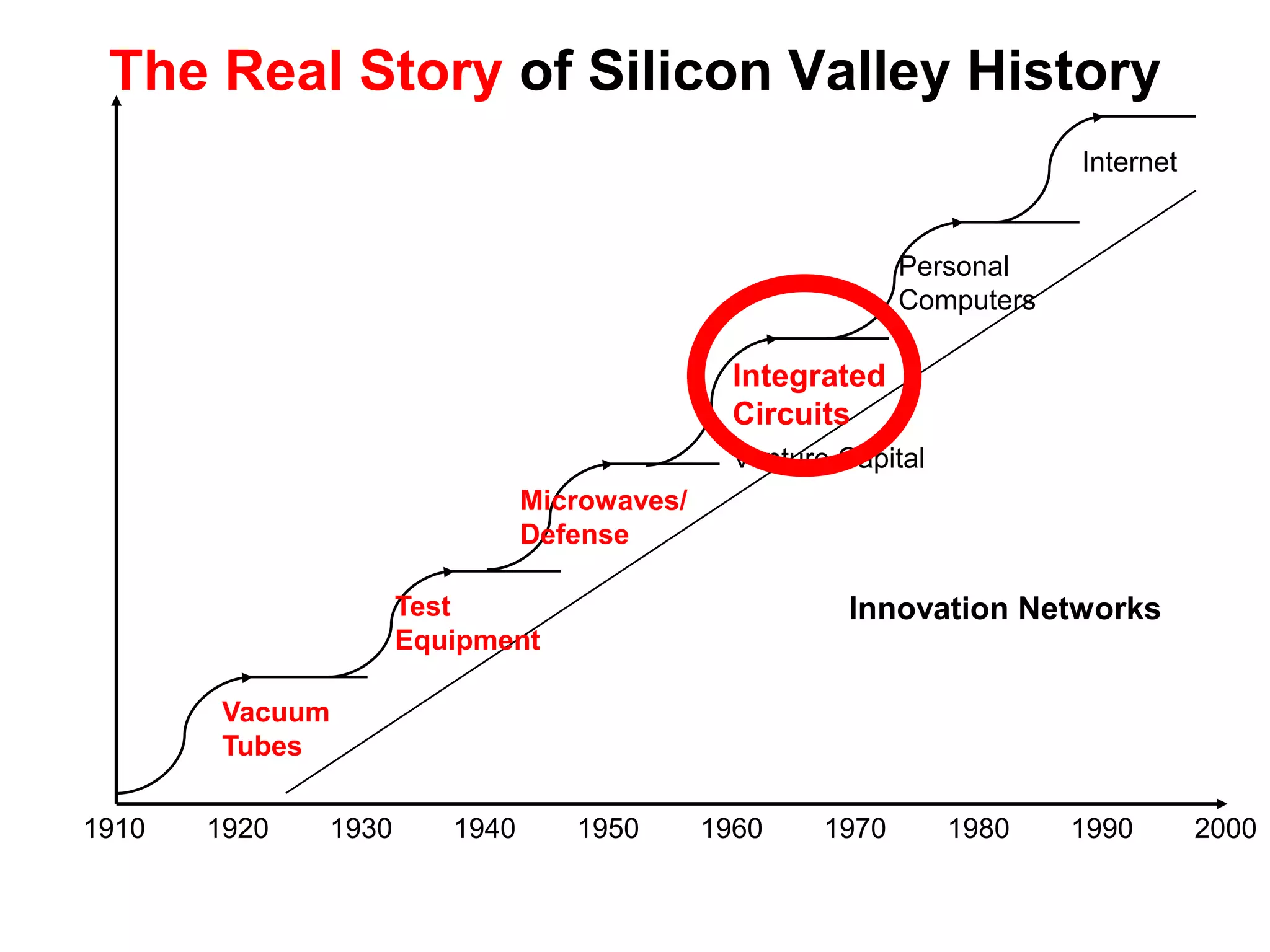
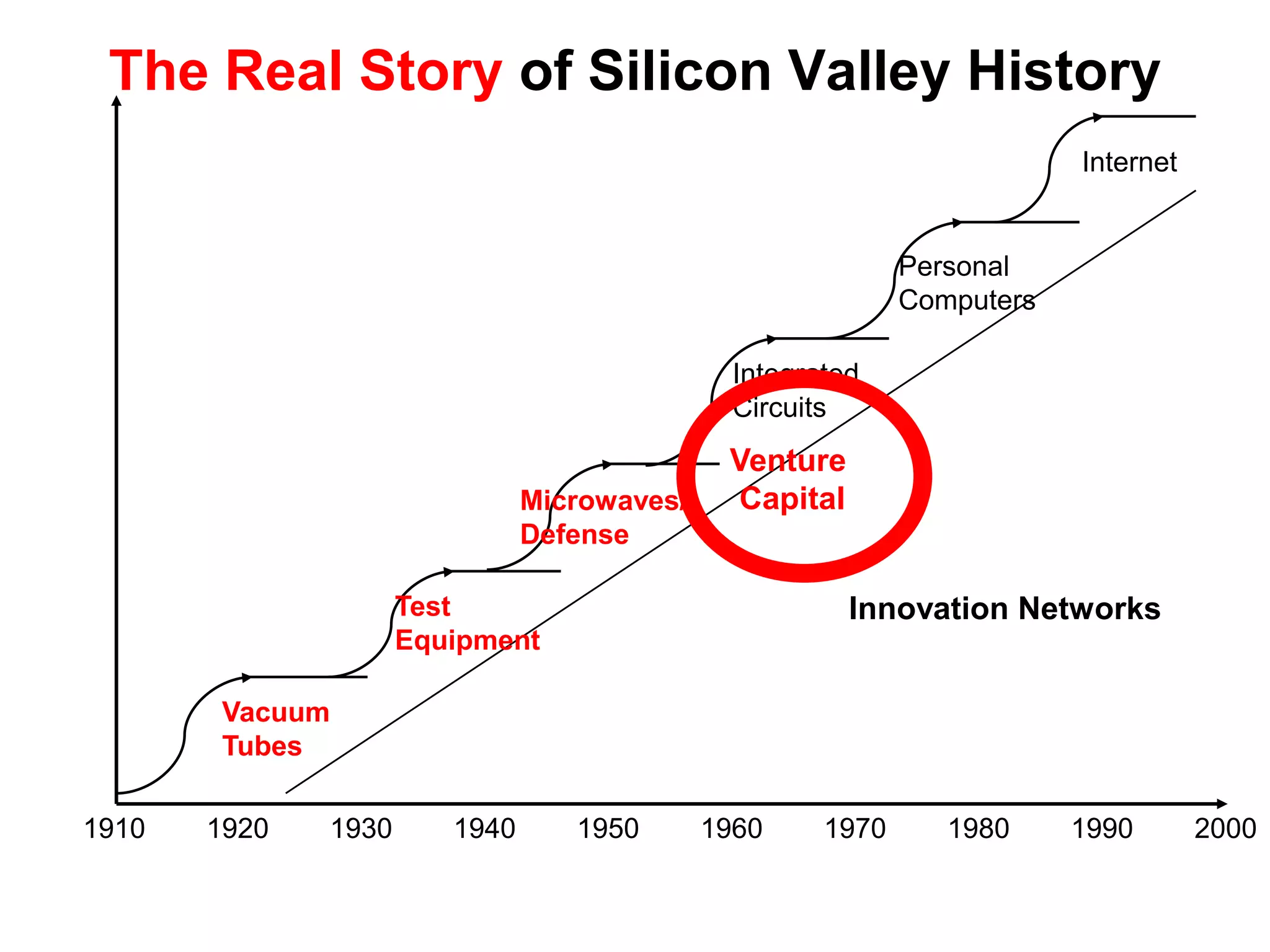
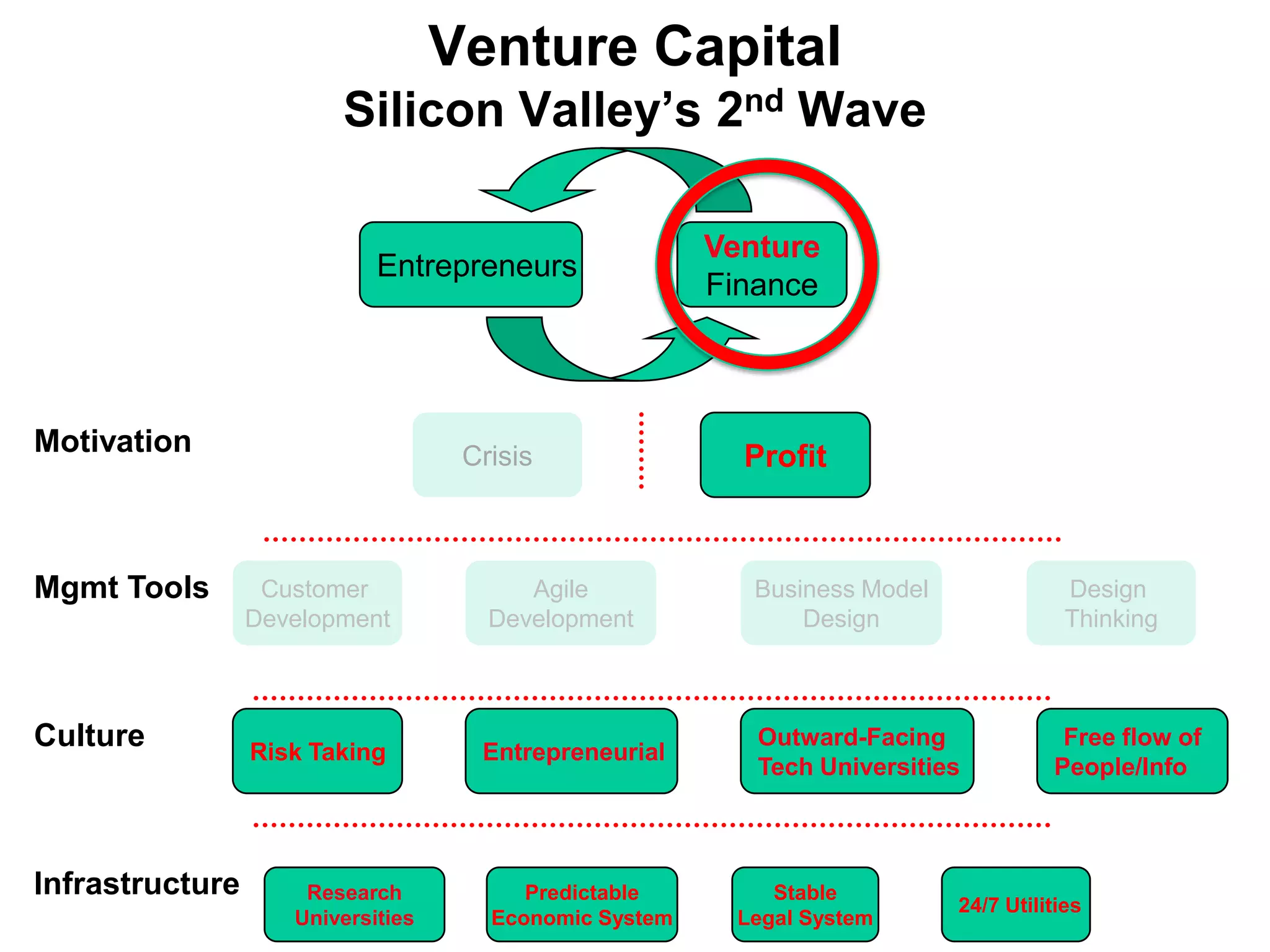
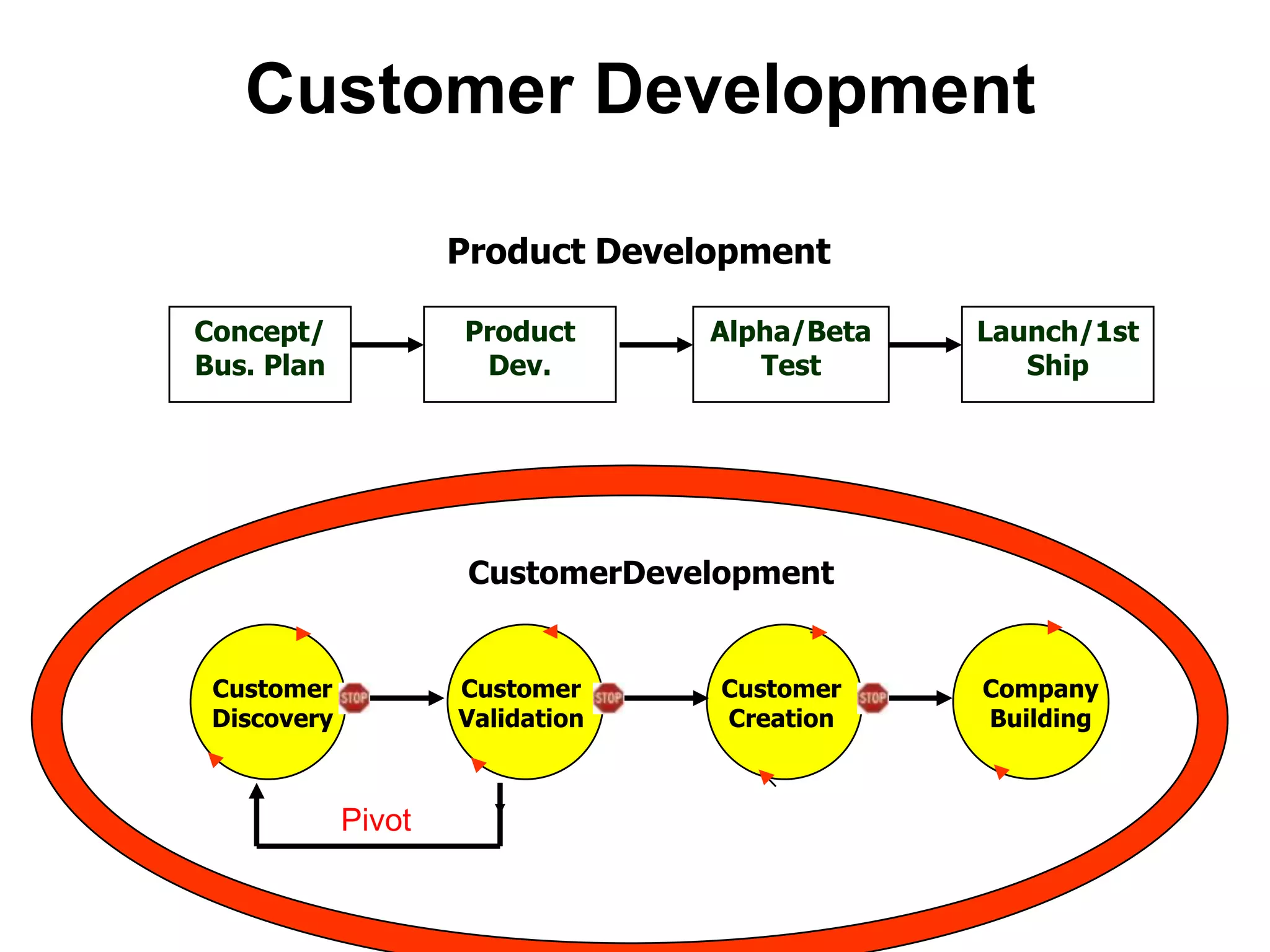
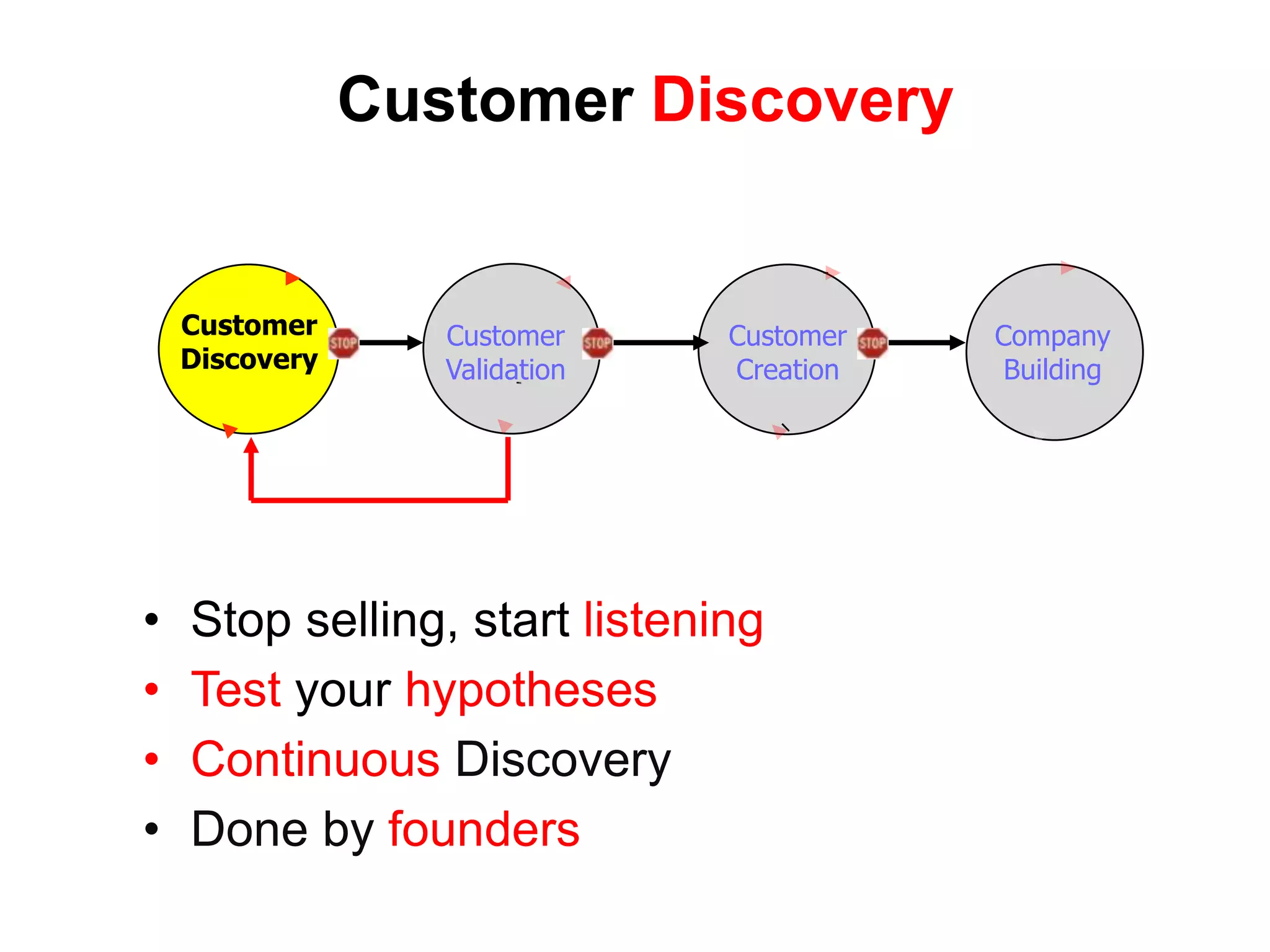
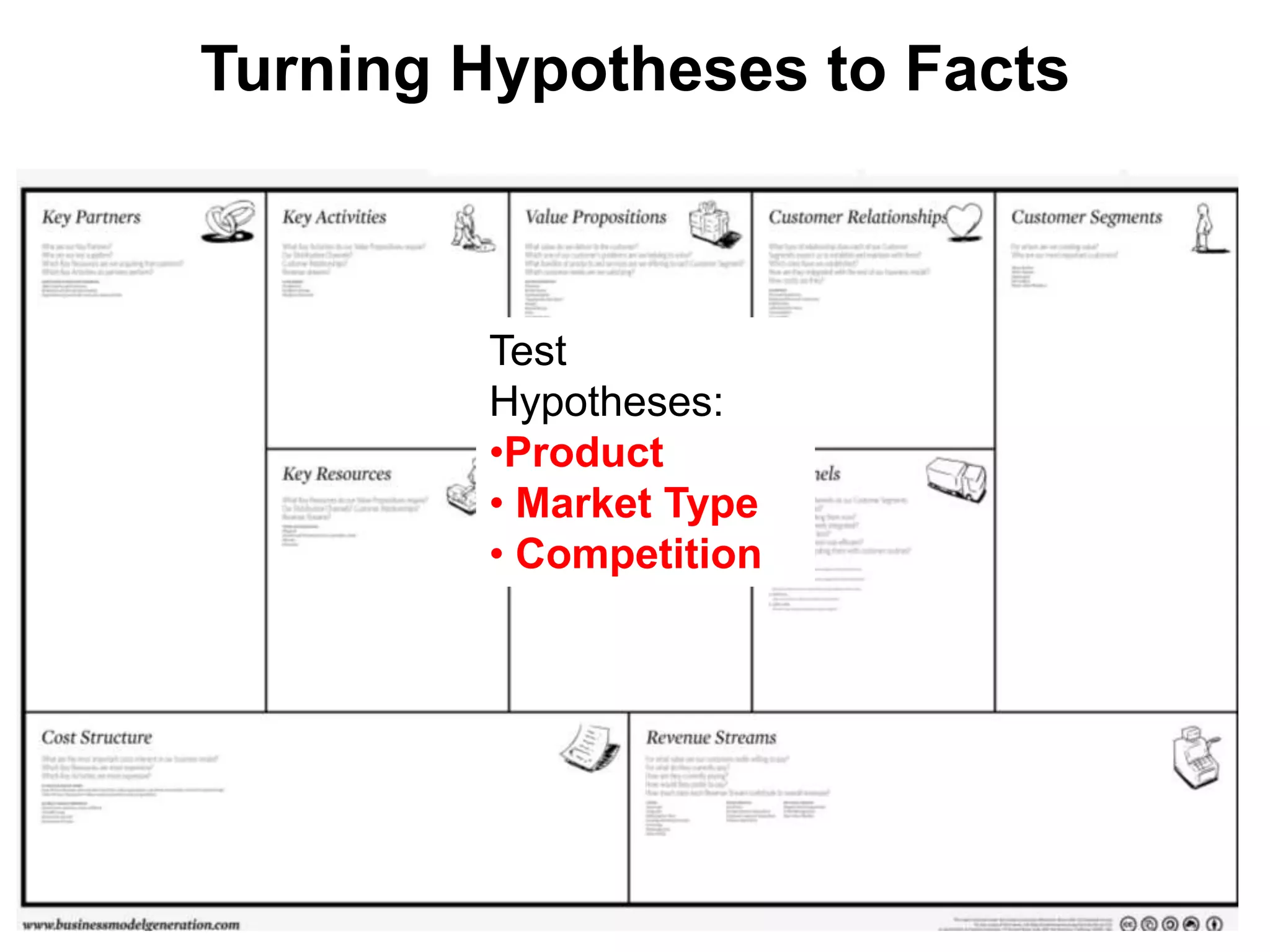
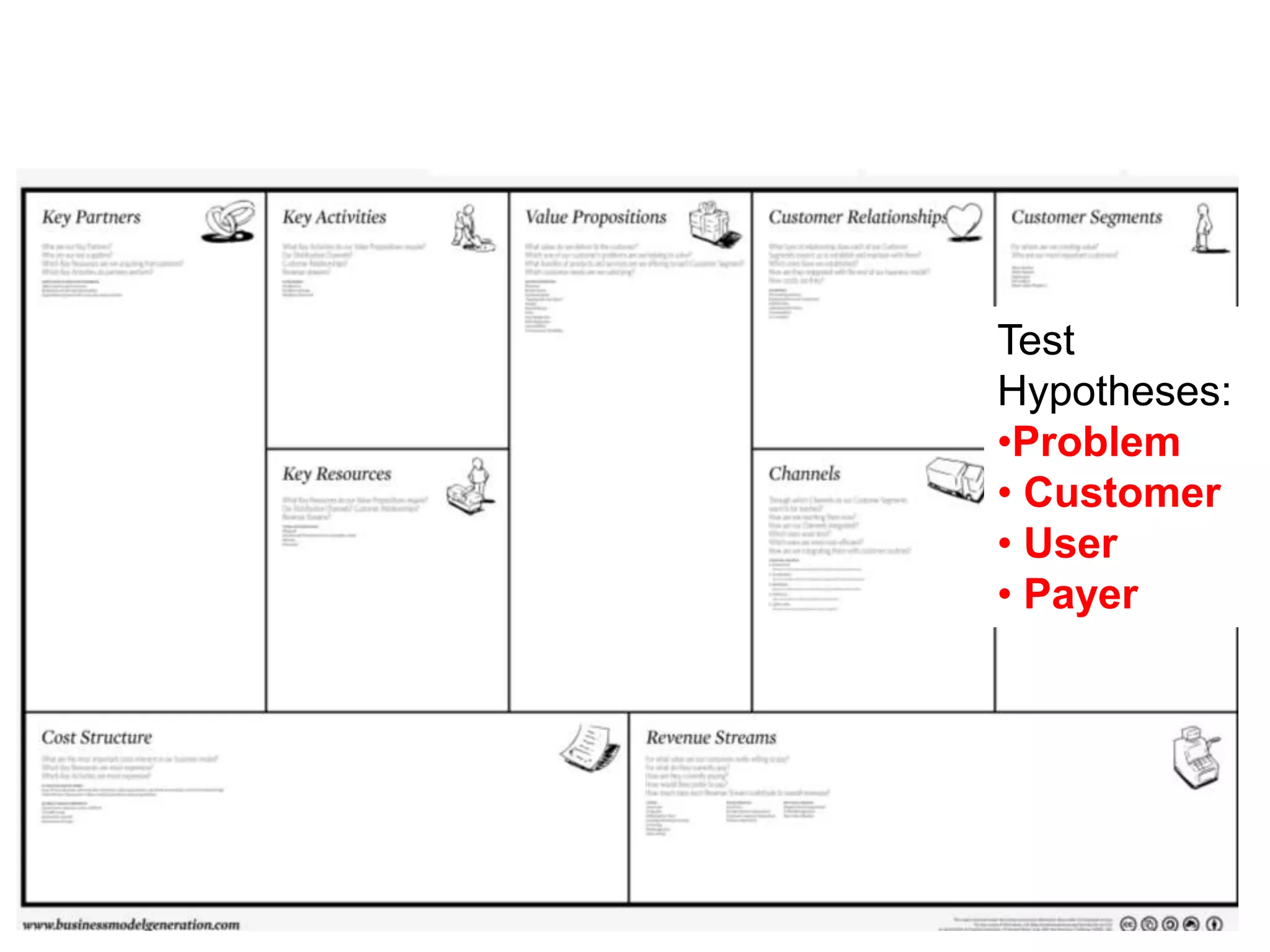
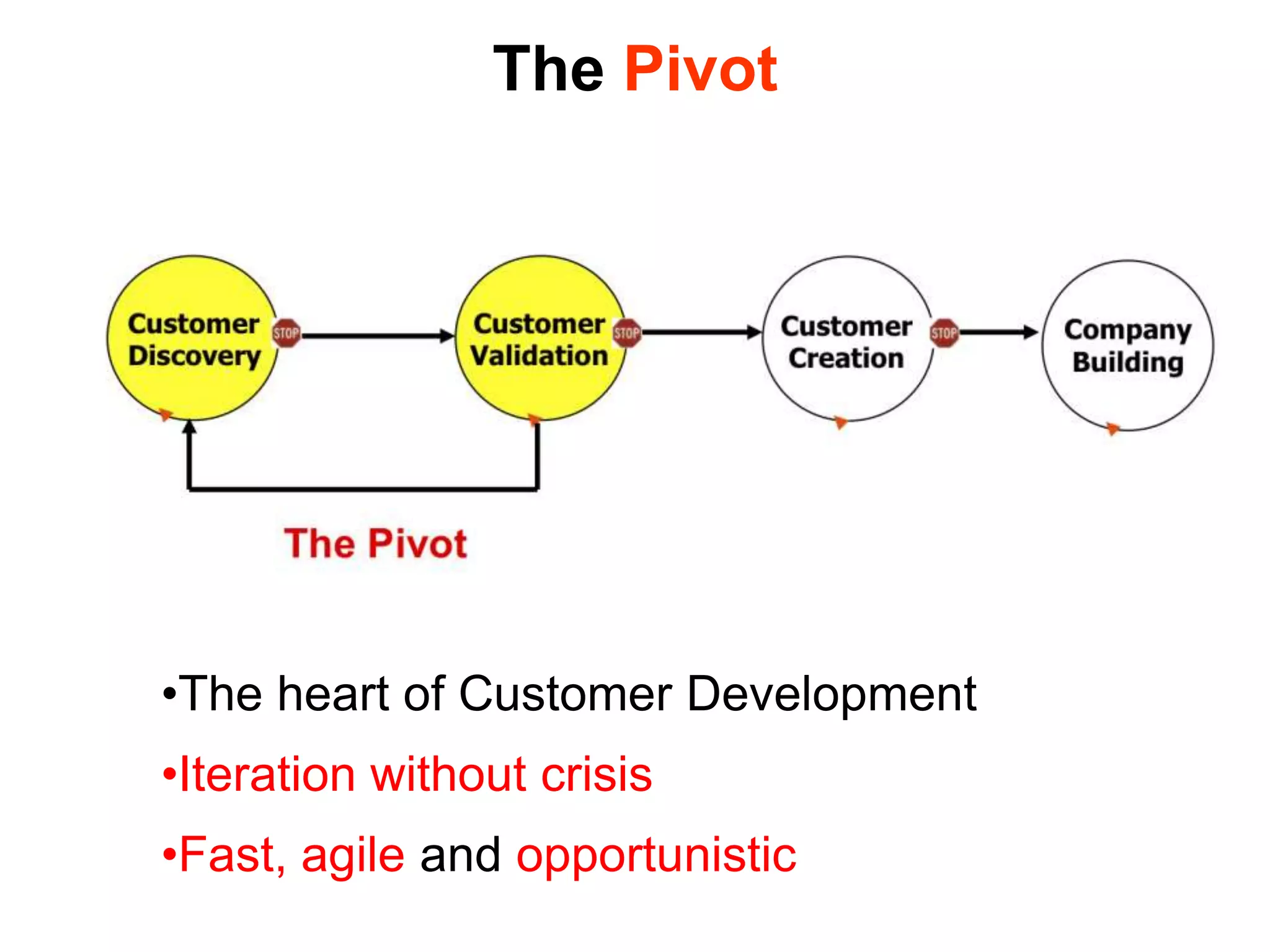
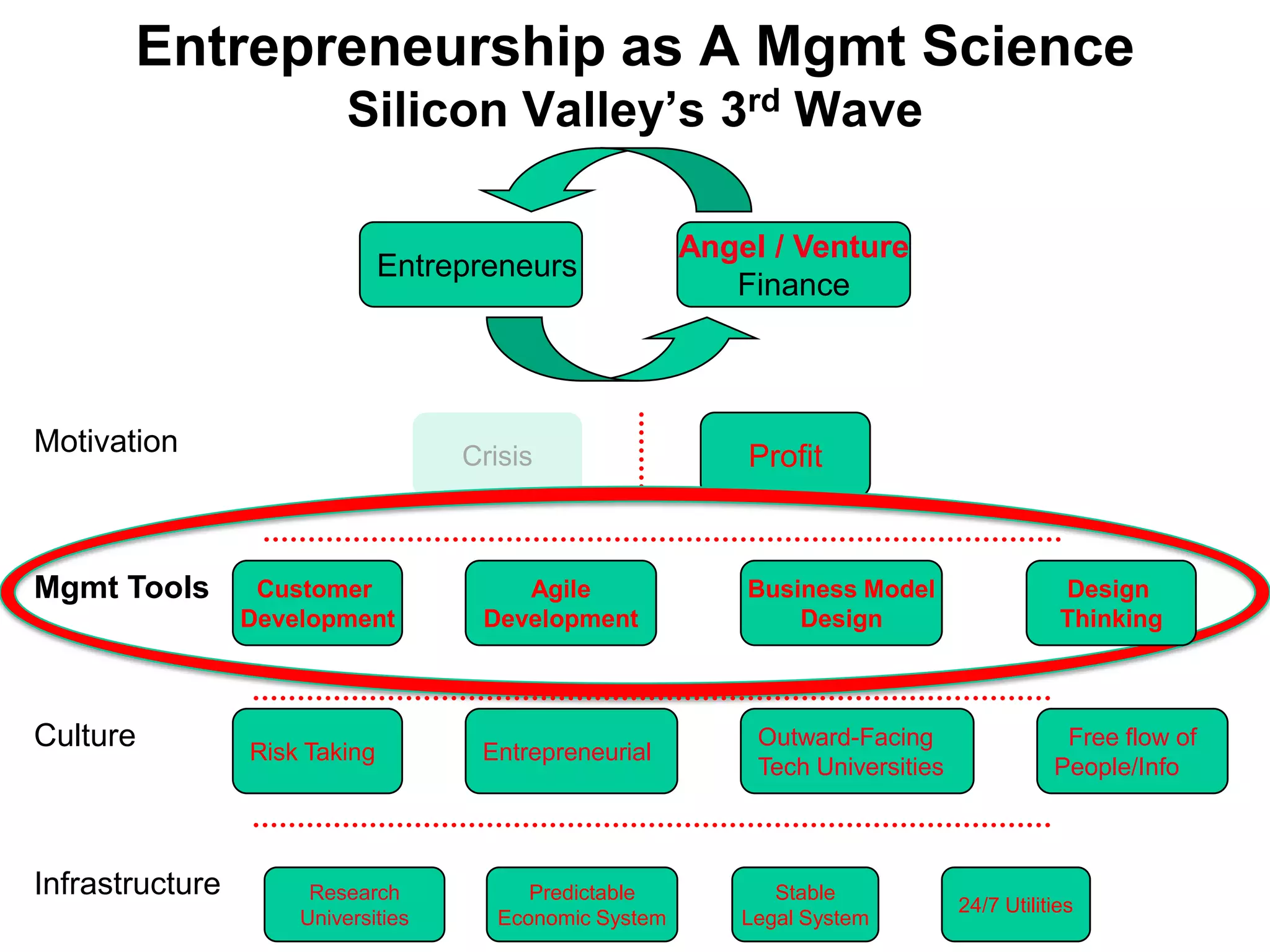
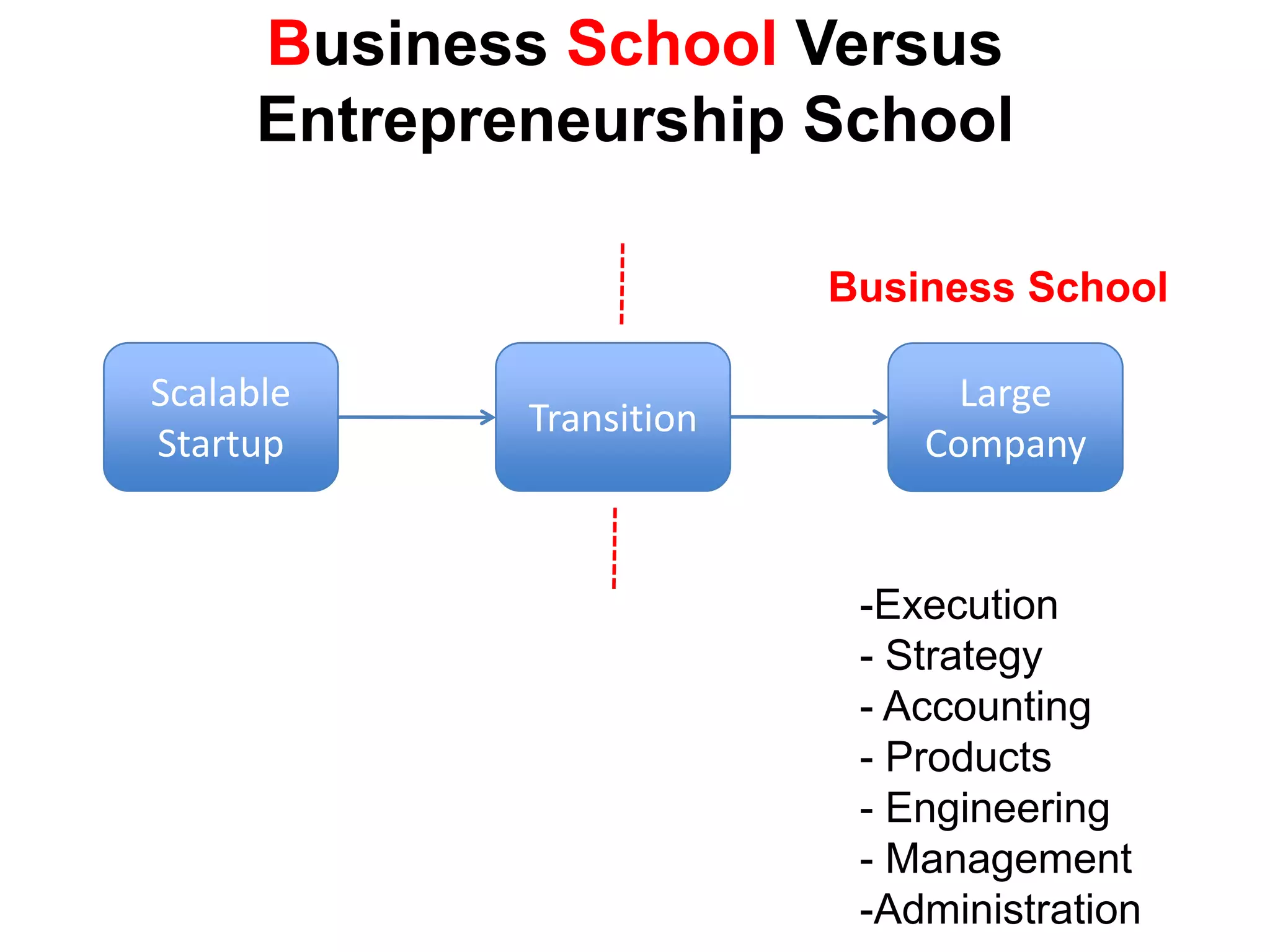
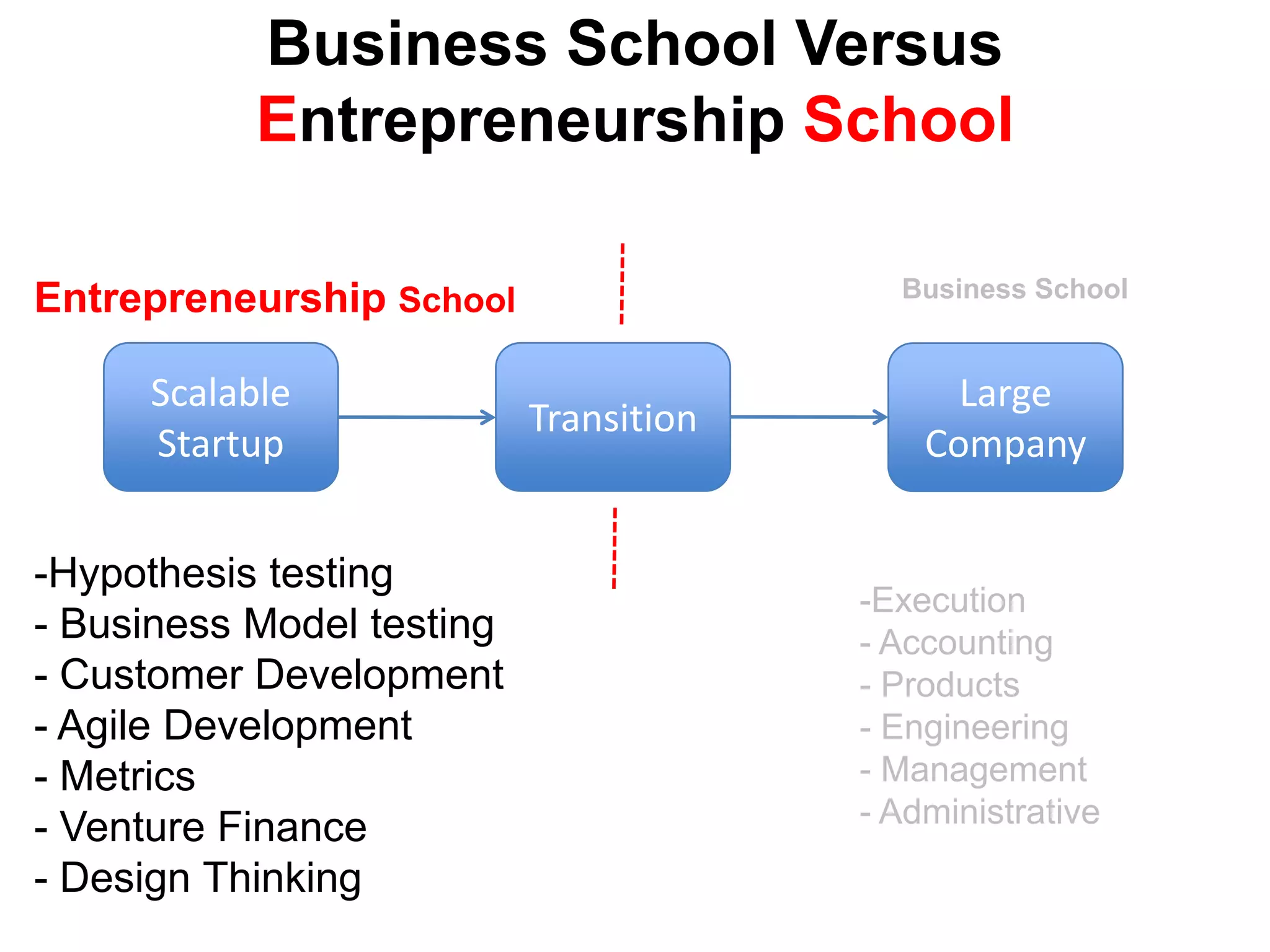
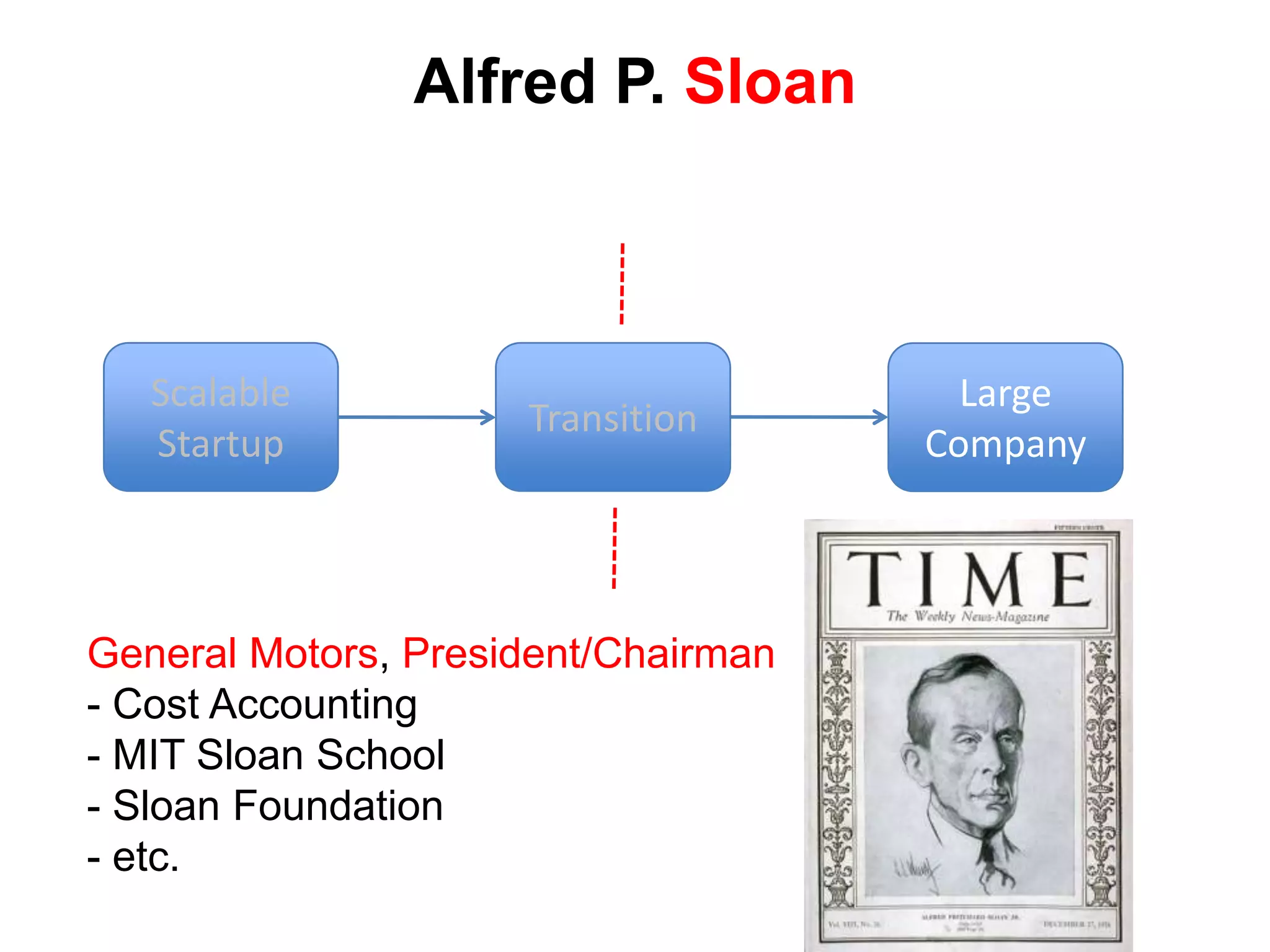
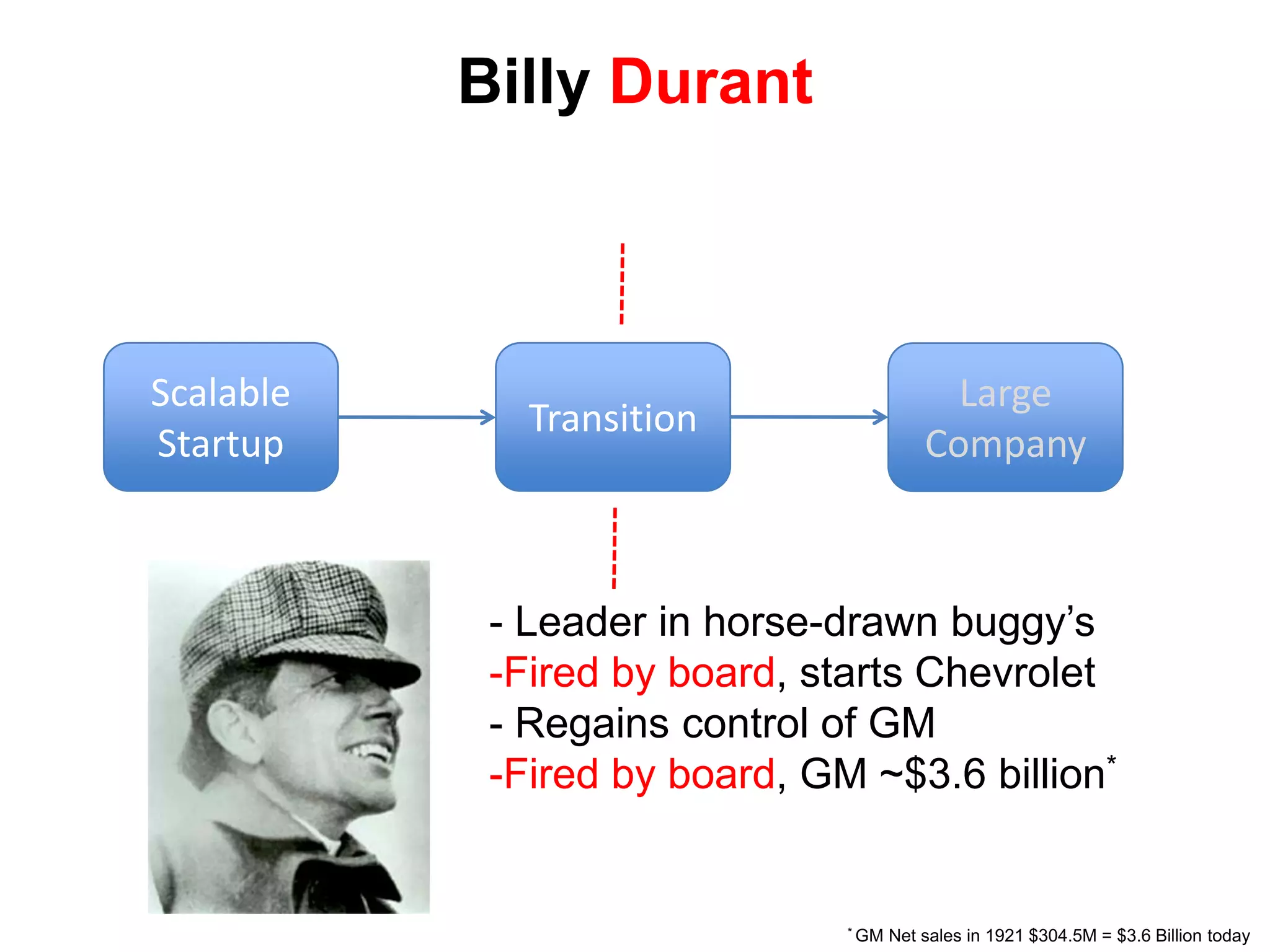
The document provides a summary of the history of Silicon Valley and the factors that contributed to its emergence as a major hub of innovation. It discusses several key events and individuals:
1) Frederick Terman's role as Stanford professor and provost in encouraging collaboration between academia and industry, including supporting HP's founding.
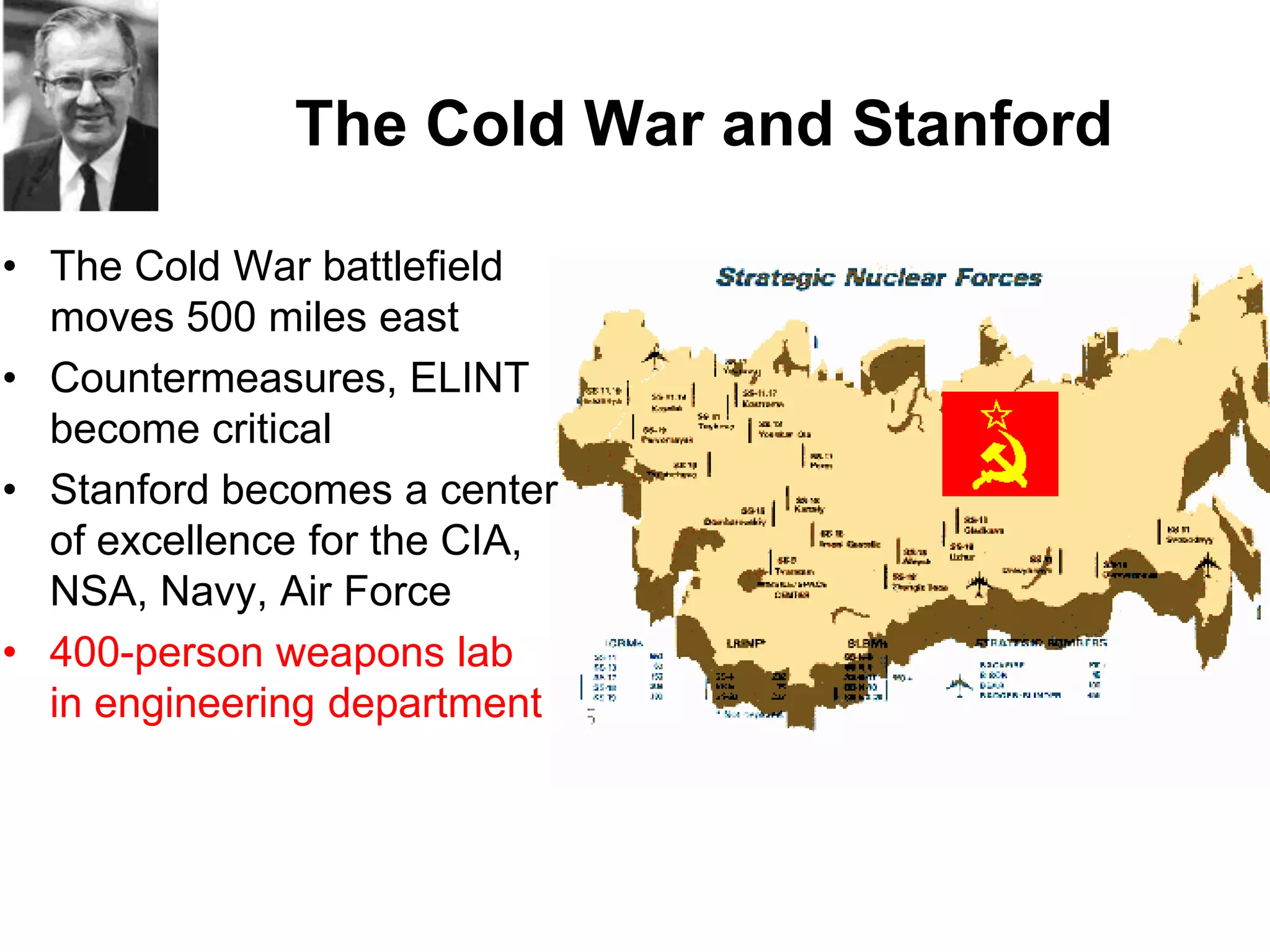
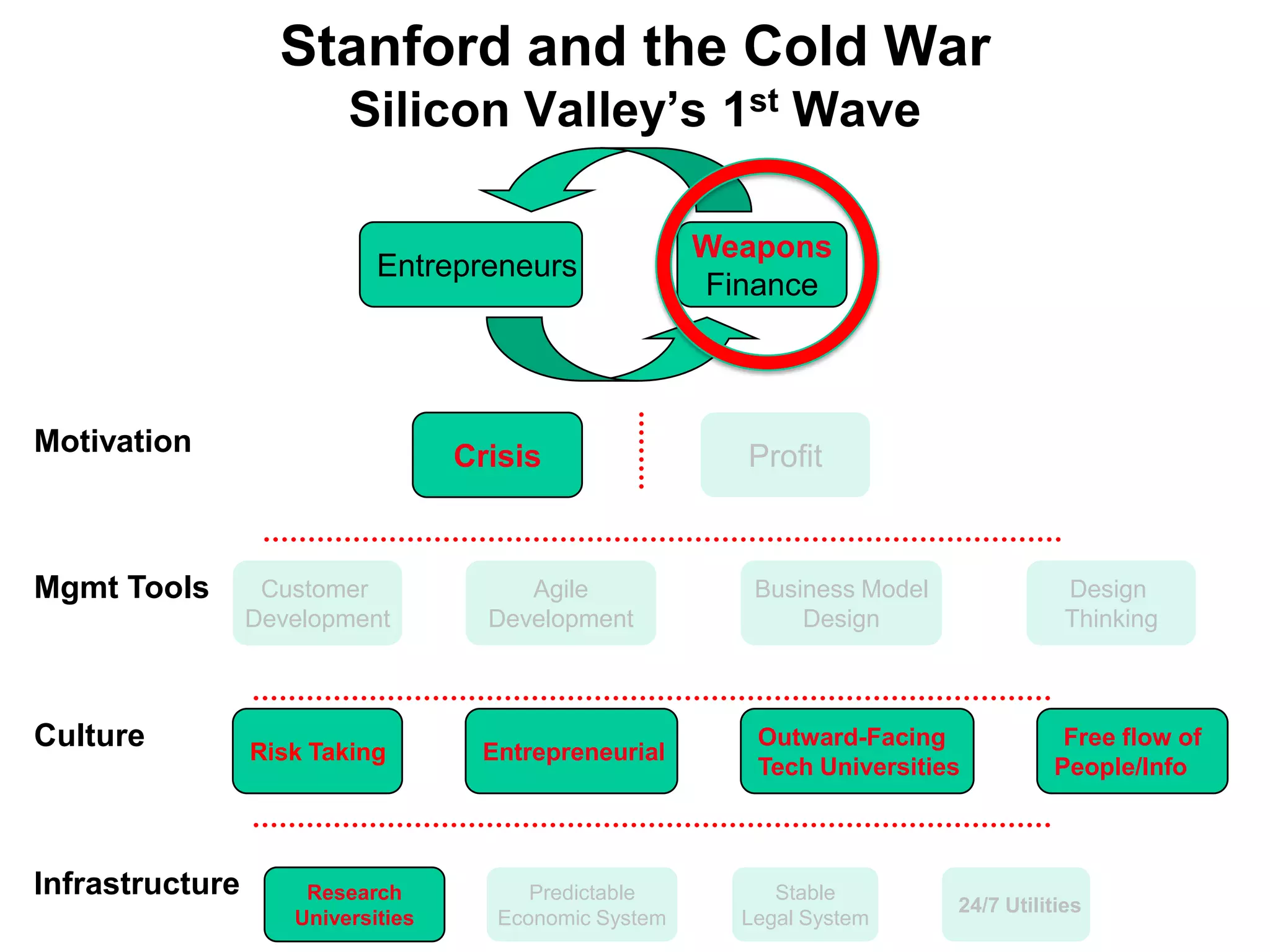
2) Stanford's focus on electronics during WWII and the Cold War, bringing defense funding and spinouts like Varian Associates.
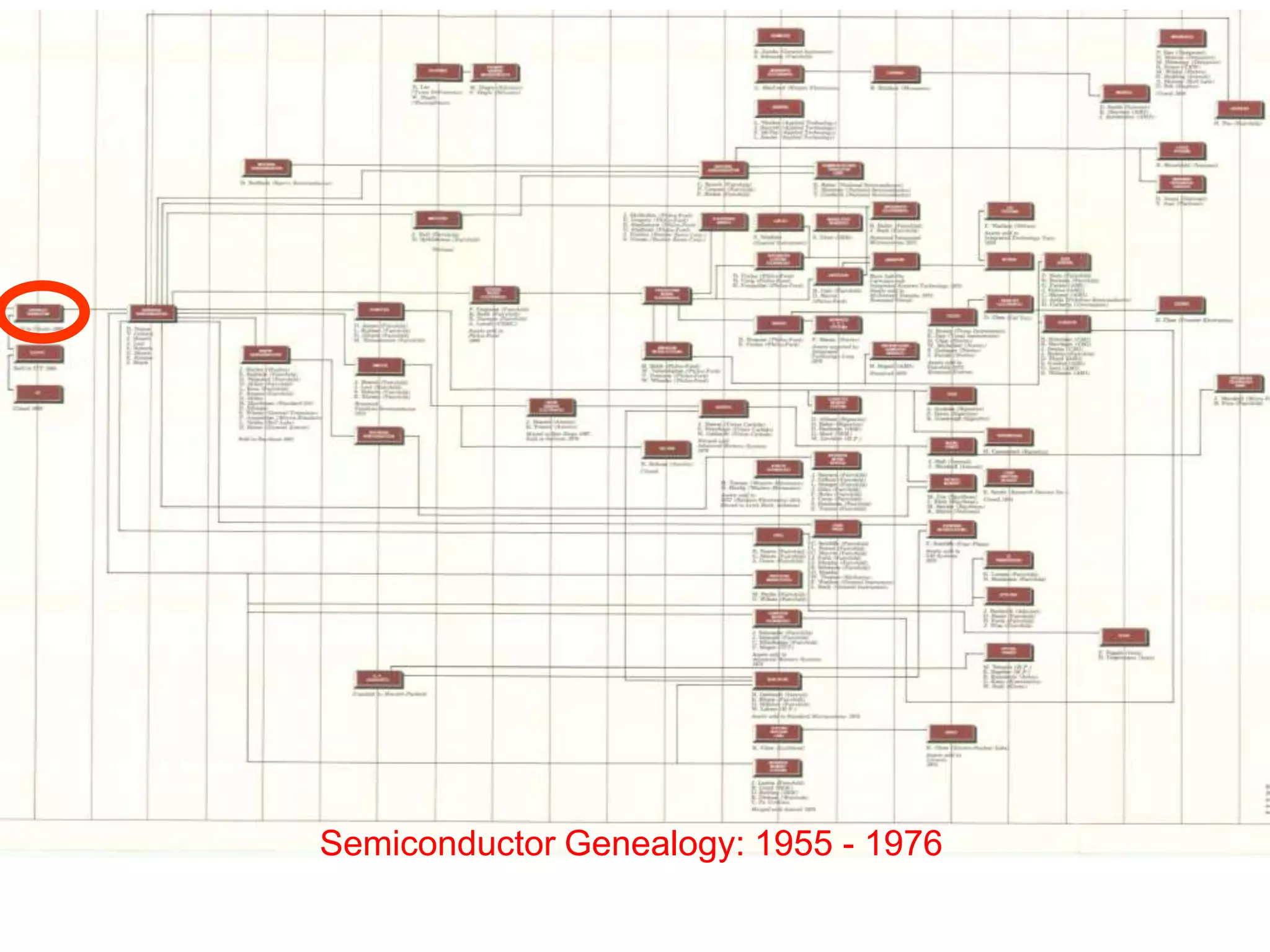
3) William Shockley founding Shockley Semiconductor which led to the "Traitorous 8" founding Fairchild Semiconductor and initiating the chip industry.
4) The rise of venture capital firms like Draper Gaither & Anderson and later Kleiner Per