This document provides an overview of child psychology and its theories and applications. It discusses:
- Definitions of psychology and child psychology.
- The importance of understanding child psychology for dental care.
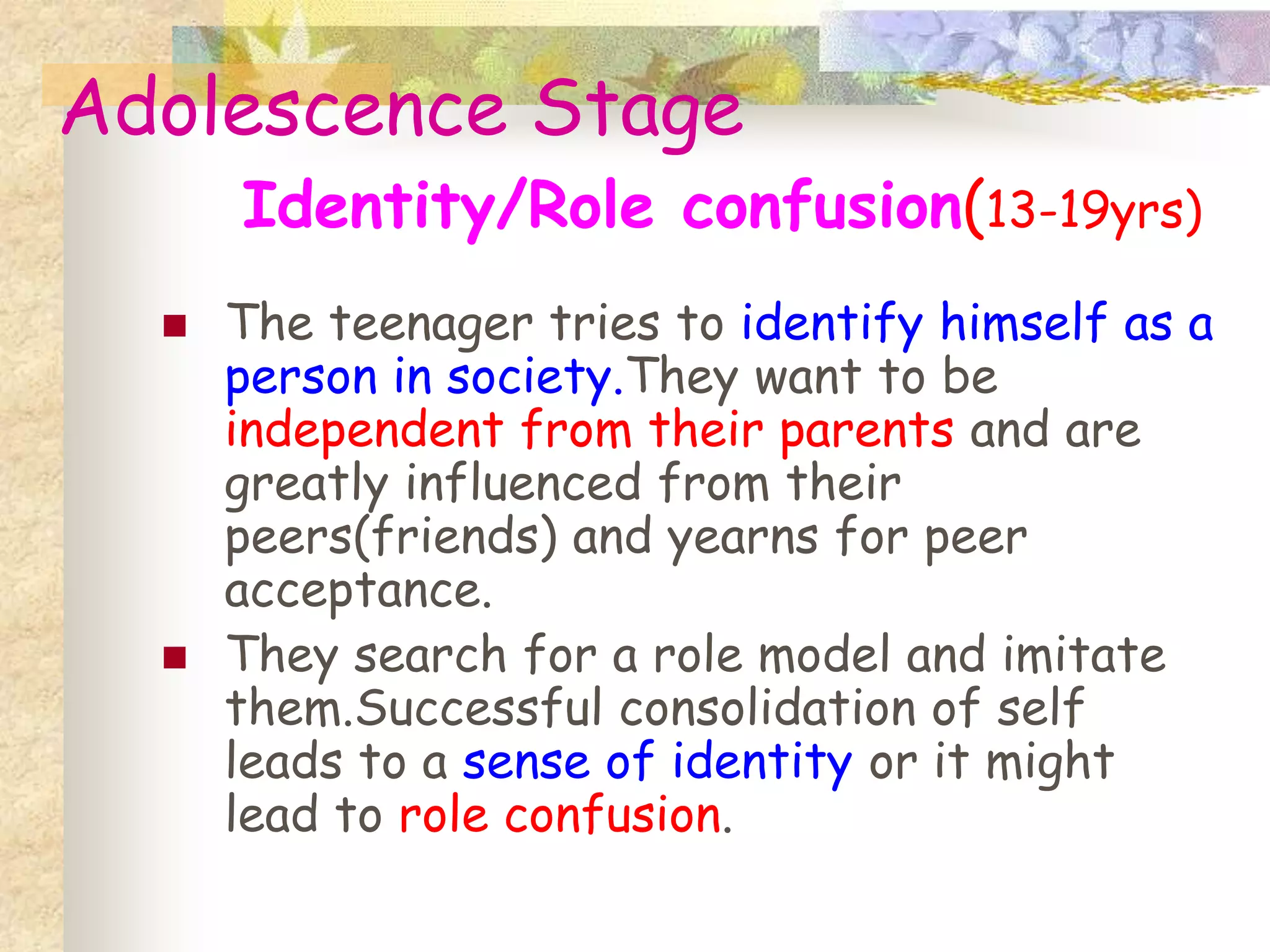
- Major theories of child psychology including psychodynamic theories by Freud and Erickson, learning theories by Pavlov, Skinner and Piaget.
- Key concepts in each theory like the psychosexual stages, psychosocial stages, classical and operant conditioning, cognitive development stages.
- Applications of these theories in understanding child behavior and development and providing effective dental care.