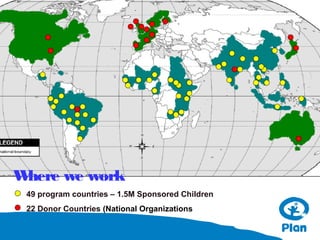
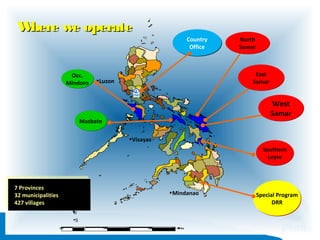
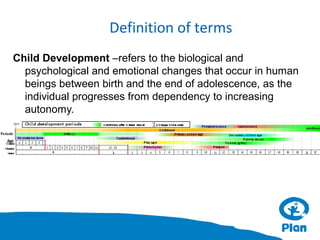
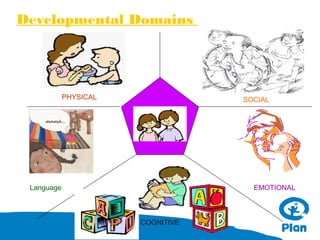
The document provides information about understanding child development and their needs. It discusses Plan International's identity as a child-centered NGO and their impact programs that focus on economic security, health, education, water and sanitation, and protection. It also outlines the methodology and duration of a training module on understanding children, their development domains of physical, cognitive, language, social and emotional. Key principles of child development are presented, including that development is holistic, multi-determined, and children are active participants. The training emphasizes understanding children in their context and building relationships through communication and comprehension.