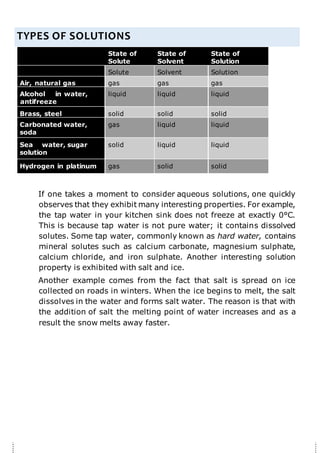
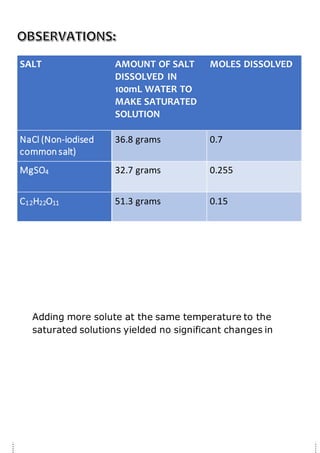
This document describes a student project measuring the solubility of common chemicals like table salt, Epsom salts, and sugar in water. The student followed an experimental procedure that involved adding incremental amounts of each chemical to water until saturation was reached. Key results were that table salt had the highest solubility due to its small ionic components, while sugar had the lowest solubility due to its large molecular size. Increasing the temperature increased the solubility of all chemicals by providing more kinetic energy to molecules. The student's results and conclusions agreed with chemical theories of solubility.