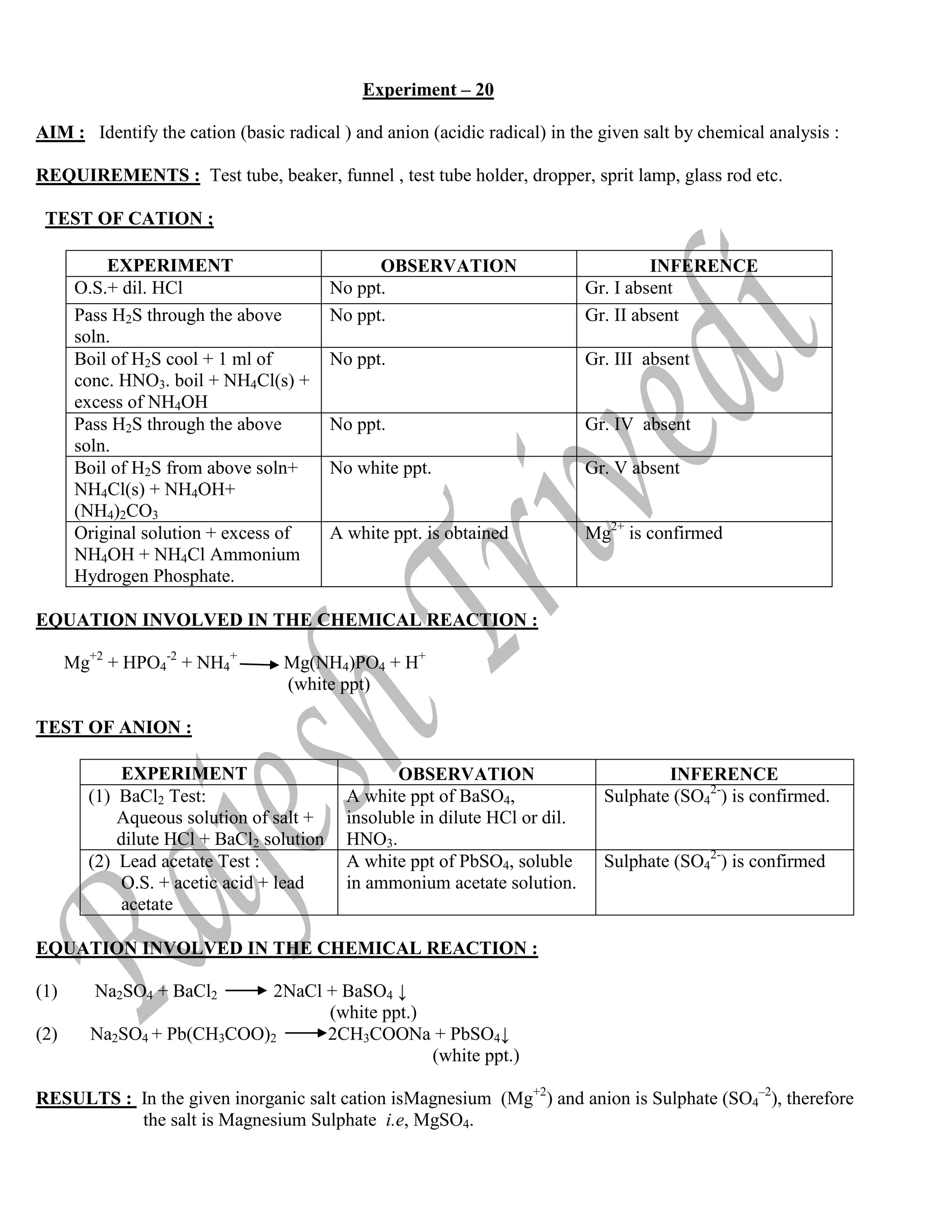
The document outlines the syllabus for a chemistry practical exam according to CBSE guidelines. It includes:
1. Volumetric analysis (titration) experiments to determine the concentration of a given potassium permanganate solution using standard Mohr's salt or oxalic acid solutions.
2. Qualitative analysis of inorganic salts.
3. Experiments to test functional groups in organic compounds.
4. An investigatory project on topics like studying ripening of fruits, milk composition, food preservatives etc.
5. Evaluation of practical records and viva.
The document also provides details of sample experiments to determine concentration of potassium permanganate using titration with Mohr's salt at different
![Experiment – 1
AIM: Prepare 0.1 M Mohr’s salt solution . Using this solution determine the molarity and strength of the
given potassium permanganate solution.
CHEMICAL EQUATION :
MnO4
–
+ 8H+
+ 5e–
Mn+2
+ 4H2O
Fe+2
Fe+3
+ e–
] × 5
MnO4
–
+ 8H+
+ 5Fe+2
5Fe+3
+ Mn+2
+ 4H2O
INDICATOR : KmnO4 is a self- indicator
END POINT: Colourless to permanent pink colour . (KMnO4in burette)
OBSERVATION TABLE :
CALCULATION :
Preparation of 0.1 M solution of Mohr’s salt
In fact Mohr’s salt is ferrous ammonium sulphate.
Molecular wt. of Mohr’s salt [FeSO4.(NH4)2SO4.6H2O] = 392
As we know w =
w = = 9.8
9.8 gm Mohr’s salt needed to prepare 250 ml of 0.1 M solution .
From the balanced ionic equation , it is clear that1 mole of KMnO4 reacts with 5 mole of Mohr’s salt.
=
M1 = Molarity of KMnO4
M2 = Molarity of Mohr’s salt
V1 = Volume of KMnO4
V2 = Volume of Mohr’s salt
=
S.No. Reading of pipette
(ml)(FAS)
Initial reading of
burette (ml) (KMnO4)
Final reading of
burette (ml) (KMnO4)
Volume of KMnO4
used (ml)
1 10 0.00 10 10
2 10 0.00 9.8 9.8
3 10 0.00 10 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempracticalpdf-220526153021-fe01c010/75/chemistry-Practical-Class-12th-CBSE-2-2048.jpg)

![Experiment – 2
AIM: Prepare 0.25 M Mohr’s salt solution . Using this solution determine the molarity and strength of the
given potassium permanganate solution.
CHEMICAL EQUATION :
MnO4
–
+ 8H+
+ 5e–
Mn+2
+ 4H2O
Fe+2
Fe+3
+ e–
] × 5
MnO4
–
+ 8H+
+ 5Fe+2
5Fe+3
+ Mn+2
+ 4H2O
INDICATOR : KmnO4 is a self- indicator
END POINT: Colourless to permanent pink colour . (KMnO4in burette)
OBSERVATION TABLE :
CALCULATION :
Preparation of 0.25 M solution of Mohr’s salt
In fact Mohr’s salt is ferrous ammonium sulphate.
Molecular wt. of Mohr’s salt [FeSO4.(NH4)2SO4.6H2O] = 392
As we know w =
w = = 24.5
24.5 gm Mohr’s salt needed to prepare 250 ml of 0.25 M solution .
From the balanced ionic equation , it is clear that 1 mole of KMnO4 reacts with 5 mole of Mohr’s salt.
=
M1 = Molarity of KMnO4
M2 = Molarity of Mohr’s salt
V1 = Volume of KMnO4
V2 = Volume of Mohr’s salt
=
S.No. Reading of pipette
(ml)(FAS)
Initial reading of
burette (ml) (KMnO4)
Final reading of
burette (ml) (KMnO4)
Volume of KMnO4
used (ml)
1 10 0.00 25 25
2 10 0.00 24.8 24.8
3 10 0.00 25 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempracticalpdf-220526153021-fe01c010/75/chemistry-Practical-Class-12th-CBSE-4-2048.jpg)

![Experiment – 3
AIM: Prepare 0.2 M Mohr’s salt solution . Using this solution determine the molarity and strength of the
given potassium permanganate solution.
CHEMICAL EQUATION :
MnO4
–
+ 8H+
+ 5e–
Mn+2
+ 4H2O
Fe+2
Fe+3
+ e–
] × 5
MnO4
–
+ 8H+
+ 5Fe+2
5Fe+3
+ Mn+2
+ 4H2O
INDICATOR : KmnO4 is a self- indicator
END POINT: Colourless to permanent pink colour . (KMnO4in burette)
OBSERVATION TABLE :
CALCULATION :
Preparation of 0.2 M solution of Mohr’s salt
In fact Mohr’s salt is ferrous ammonium sulphate.
Molecular wt. of Mohr’s salt [FeSO4.(NH4)2SO4.6H2O] = 392
As we know w =
w = = 19.6
19.6 gm Mohr’s salt needed to prepare 250 ml of 0.2 M solution .
From the balanced ionic equation , it is clear that 1 mole of KMnO4 reacts with 5 mole of Mohr’s salt.
=
M1 = Molarity of KMnO4
M2 = Molarity of Mohr’s salt
V1 = Volume of KMnO4
V2 = Volume of Mohr’s salt
=
S.No. Reading of pipette (ml)
(FAS)
Initial reading of
burette (ml) (KMnO4)
Final reading of
burette (ml) (KMnO4)
Volume of
KMnO4 used (ml)
1 10 0.00 20 20
2 10 0.00 19.8 19.8
3 10 0.00 20 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempracticalpdf-220526153021-fe01c010/75/chemistry-Practical-Class-12th-CBSE-6-2048.jpg)

![Experiment – 4
AIM: Prepare 0.15 M Mohr’s salt solution . Using this solution determine the molarity and strength of the
given potassium permanganate solution.
CHEMICAL EQUATION :
MnO4
–
+ 8H+
+ 5e–
Mn+2
+ 4H2O
Fe+2
Fe+3
+ e–
] × 5
MnO4
–
+ 8H+
+ 5Fe+2
5Fe+3
+ Mn+2
+ 4H2O
INDICATOR : KmnO4 is a self- indicator
END POINT: Colourless to permanent pink colour . (KMnO4in burette)
OBSERVATION TABLE :
CALCULATION :
Preparation of 0.2 M solution of Mohr’s salt
In fact Mohr’s salt is ferrous ammonium sulphate.
Molecular wt. of Mohr’s salt [FeSO4.(NH4)2SO4.6H2O] = 392
As we know w =
w = = 14.7
14.7 gm Mohr’s salt needed to prepare 250 ml of 0.15 M solution .
From the balanced ionic equation , it is clear that 1 mole of KMnO4 reacts with 5 mole of Mohr’s salt.
=
M1 = Molarity of KMnO4
M2 = Molarity of Mohr’s salt
V1 = Volume of KMnO4
V2 = Volume of Mohr’s salt
=
S.No. Reading of pipette (ml)
(FAS)
Initial reading of
burette (ml) (KMnO4)
Final reading of
burette (ml) (KMnO4)
Volume of
KMnO4 used (ml)
1 10 0.00 15 15
2 10 0.00 14.8 14.8
3 10 0.00 15 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempracticalpdf-220526153021-fe01c010/75/chemistry-Practical-Class-12th-CBSE-8-2048.jpg)

![Experiment – 5
AIM: Prepare 0.1 M solution of Oxalic acid . Using this solution determine the molarity and strength of
the given potassium permanganate solution.
CHEMICAL EQUATION :
MnO4
–
+ 8H+
+ 5e–
Mn+2
+ 4H2O] × 2
C2O4
–2
2CO2 + 2e–
] × 5
2MnO4
–
+ 16H+
+ 5C2O4
–2
2Mn+2
+ 10CO2 + 8H2O
INDICATOR : KmnO4 is a self- indicator
END POINT: Colourless to permanent pink colour . (KMnO4in burette)
OBSERVATION TABLE :
CALCULATION :
Preparation of 0.1 M Oxalic acid solution
Molecular wt. of Oxalic acid [H2C2O4.2H2O] = 126
As we know w =
w = = 3.15
3.15 gm Oxalic acid needed to prepare 250 ml of 0.1 M solution .
From the balanced ionic equation , it is clear that 2 mole of KMnO4 reacts with 5 mole of Oxalic acid.
=
M1 = Molarity of KMnO4
M2 = Molarity of Oxalic acid
V1 = Volume of KMnO4
V2 = Volume of Oxalic acid
=
S.No. Reading of pipette (ml)
(Oxalic acid)
Initial reading of burette
(ml) (KMnO4)
Final reading of burette
(ml) (KMnO4)
Volume of KMnO4 used
(ml)
1 10 0.00 20 20
2 10 0.00 19.8 19.8
3 10 0.00 20 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempracticalpdf-220526153021-fe01c010/75/chemistry-Practical-Class-12th-CBSE-10-2048.jpg)

![Experiment – 6
AIM: Prepare 0.15 M solution of Oxalic acid . Using this solution determine the molarity and strength of
the given potassium permanganate solution.
CHEMICAL EQUATION :
MnO4
–
+ 8H+
+ 5e–
Mn+2
+ 4H2O] × 2
C2O4
–2
2CO2 + 2e–
] × 5
2MnO4
–
+ 16H+
+ 5C2O4
–2
2Mn+2
+ 10CO2 + 8H2O
INDICATOR : KmnO4 is a self- indicator
END POINT: Colourless to permanent pink colour . (KMnO4in burette)
OBSERVATION TABLE :
CALCULATION :
Preparation of 0.15 M Oxalic acid solution
Molecular wt. of Oxalic acid [H2C2O4.2H2O] = 126
As we know w =
w = = 4.725
4.725 gm Oxalic acid needed to prepare 250 ml of 0.15 M solution .
From the balanced ionic equation , it is clear that 2 mole of KMnO4 reacts with 5 mole of Oxalic acid.
=
M1 = Molarity of KMnO4
M2 = Molarity of Oxalic acid
V1 = Volume of KMnO4
V2 = Volume of Oxalic acid
=
S.No. Reading of pipette (ml)
(Oxalic acid)
Initial reading of burette
(ml) (KMnO4)
Final reading of burette
(ml) (KMnO4)
Volume of KMnO4 used
(ml)
1 10 0.00 30 30
2 10 0.00 29.8 29.8
3 10 0.00 30 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempracticalpdf-220526153021-fe01c010/75/chemistry-Practical-Class-12th-CBSE-12-2048.jpg)

![Experiment – 7
AIM: Prepare 0.2 M solution of Oxalic acid . Using this solution determine the molarity and strength of
the given potassium permanganate solution.
CHEMICAL EQUATION :
MnO4
–
+ 8H+
+ 5e–
Mn+2
+ 4H2O] × 2
C2O4
–2
2CO2 + 2e–
] × 5
2MnO4
–
+ 16H+
+ 5C2O4
–2
2Mn+2
+ 10CO2 + 8H2O
INDICATOR : KmnO4 is a self- indicator
END POINT: Colourless to permanent pink colour . (KMnO4in burette)
OBSERVATION TABLE :
CALCULATION :
Preparation of 0.2 M Oxalic acid solution
Molecular wt. of Oxalic acid [H2C2O4.2H2O] = 126
As we know w =
w = = 6.3
6.3 gm Oxalic acid needed to prepare 250 ml of 0.2 M solution .
From the balanced ionic equation , it is clear that 2 mole of KMnO4 reacts with 5 mole of Oxalic acid.
=
M1 = Molarity of KMnO4
M2 = Molarity of Oxalic acid
V1 = Volume of KMnO4
V2 = Volume of Oxalic acid
=
S.No. Reading of pipette
(ml) (Oxalic acid)
Initial reading of
burette (ml) (KMnO4)
Final reading of
burette (ml) (KMnO4)
Volume of KMnO4
used (ml)
1 10 0.00 40 40
2 10 0.00 39.8 39.8
3 10 0.00 40 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempracticalpdf-220526153021-fe01c010/75/chemistry-Practical-Class-12th-CBSE-14-2048.jpg)

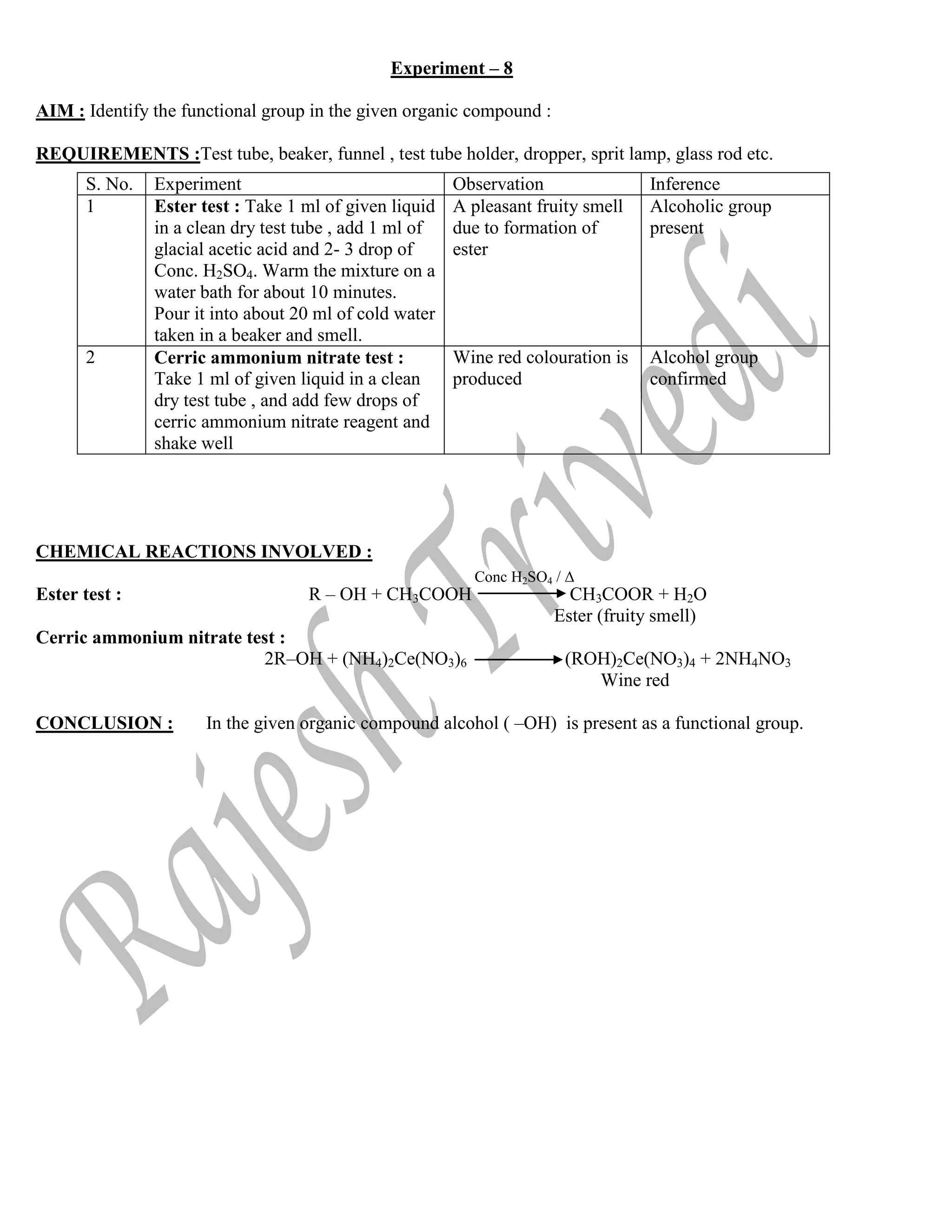
![Experiment – 9
AIM : Identify the functional group in the given organic compound :
REQUIREMENTS: Test tube, beaker, funnel , test tube holder, dropper, sprit lamp, glass rod etc.
CHEMICAL REACTIONS INVOLVED :
Ferric chloride test : FeCl3 + 6 C6H5OH [Fe(OC6H5)6
]–3
+ 3HCl
Violet complex
Libermann’stest :
2NaNO3 + H2SO4 2HNO2 + Na2SO4
OH ON OH
P -nitrophenol
ON OH + OH HO N O
Indo phenol (red)
HO N O Na+
O–
N O
Indo phenol anion (blue)
CONCLUSION : In the given organic compound Phenol ( OH) is present as a functional
group.
S. No. Experiment Observation Inference
1 Ferric chloride test : Take 1 ml of
neutral FeCl3 solution in a test tube
and add few drops of compound
A violet colouration
produced
Phenolic group is
present
2 Libermann’stest : Take 2- 3
crystals of NaNO2 in a test tube and
add about 1 ml of organic compound.
Heat gently for 30 seconds and allow
it to cool. Then add 1 ml of conc.
H2SO4 and shake the test tube .
Then add water carefully.
Finally add excess of NaOH solution.
A deep blue or deeo
green colouration
produced.
Colur turns red
The blue or green colur
appear
Phenolic group is
confirmed.
HNO2
NaOH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempracticalpdf-220526153021-fe01c010/75/chemistry-Practical-Class-12th-CBSE-17-2048.jpg)
![Experiment – 10
AIM : Identify the functional group in the given organic compound :
REQUIREMENTS : Test tube, beaker, funnel , test tube holder, dropper, sprit lamp, glass rod etc.
CHEMICAL REACTIONS INVOLVED :
2,4 – dinitrophenylhydrazine test:
RCHO + H2N NH NO2 R HC N NH NO2
NO2 NO2
Aldehyde 2,4 – dinitrophenylhydrazone (orange crystals)
Tollen’s test:
2[Ag(NH3)2]+
+ RCHO + 3OH–
RCOO–
+ 2Ag ↓ + 4NH3 +2H2O
Silver mirror
CONCLUSION : In the given organic compound Aldehyde (–COH) is present as a functional group.
S.No. Experiment Observation Inference
1 2,4- dinitrophenylhydarzine test
:Take 0.5 ml of given compound,
add rectified spirit. Now add 2,4DNP
solution . Cork the test tube , shake
the mixture and allow it to stand.
Yellow or orange
crystals formed
Aldehyde or Ketone is
present
2 Tollen’stest : Take 1 ml of AgNO3
solution in a test tube and add about
2-3 ml of dilNaOH.
Now add dil. Ammonia solution drop
wise.
To this add 3-4 drop of given organic
compound and warm the test tube on
water bath for 5 minutes.
A brown ppt produced.
Brown ppt dissolves.
A shining mirror
appear.
Aldehyde is
confirmed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempracticalpdf-220526153021-fe01c010/75/chemistry-Practical-Class-12th-CBSE-18-2048.jpg)
![Experiment - 11
AIM : Identify the functional group in the given organic compound :
REQUIREMENTS: Test tube, beaker, funnel , test tube holder, dropper, sprit lamp, glass rod etc.
CHEMICAL REACTIONS INVOLVED :
Tollen’s test:
2[Ag(NH3)2]+
+ RCOR + 3OH–
No formation of silver mirror
CONCLUSION : In the given organic compound Ketone (–CO– ) is present as a functional group.
S.No. Experiment Observation Inference
1 2,4- dinitrophenylhydarzine test :
Take 0.5 ml of given compound, add
rectified spirit. Now add 2,4DNP
solution . Cork the test tube , shake
the mixture and allow it to stand.
Yellow or orange
crystals formed
Aldehyde or Ketone is
present
2 Tollen’stest : Take 1 ml of AgNO3
solution in a test tube and add about
2-3 ml of dilNaOH.
Now add dil. Ammonia solution drop
wise.
To this add 3-4 drop of given organic
compound and warm the test tube on
water bath for 5 minutes.
No shining mirror
appear.
Ketone is confirmed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempracticalpdf-220526153021-fe01c010/75/chemistry-Practical-Class-12th-CBSE-19-2048.jpg)

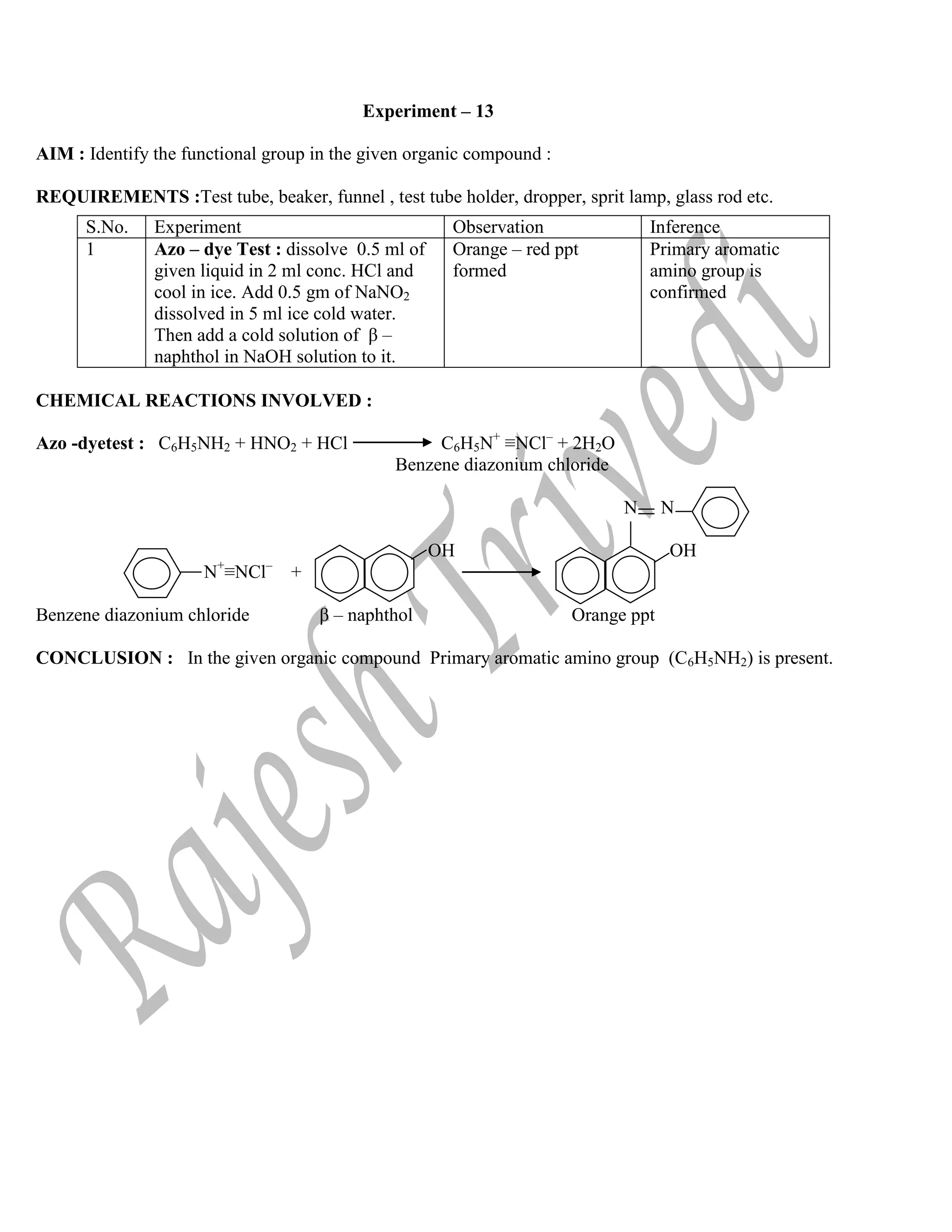
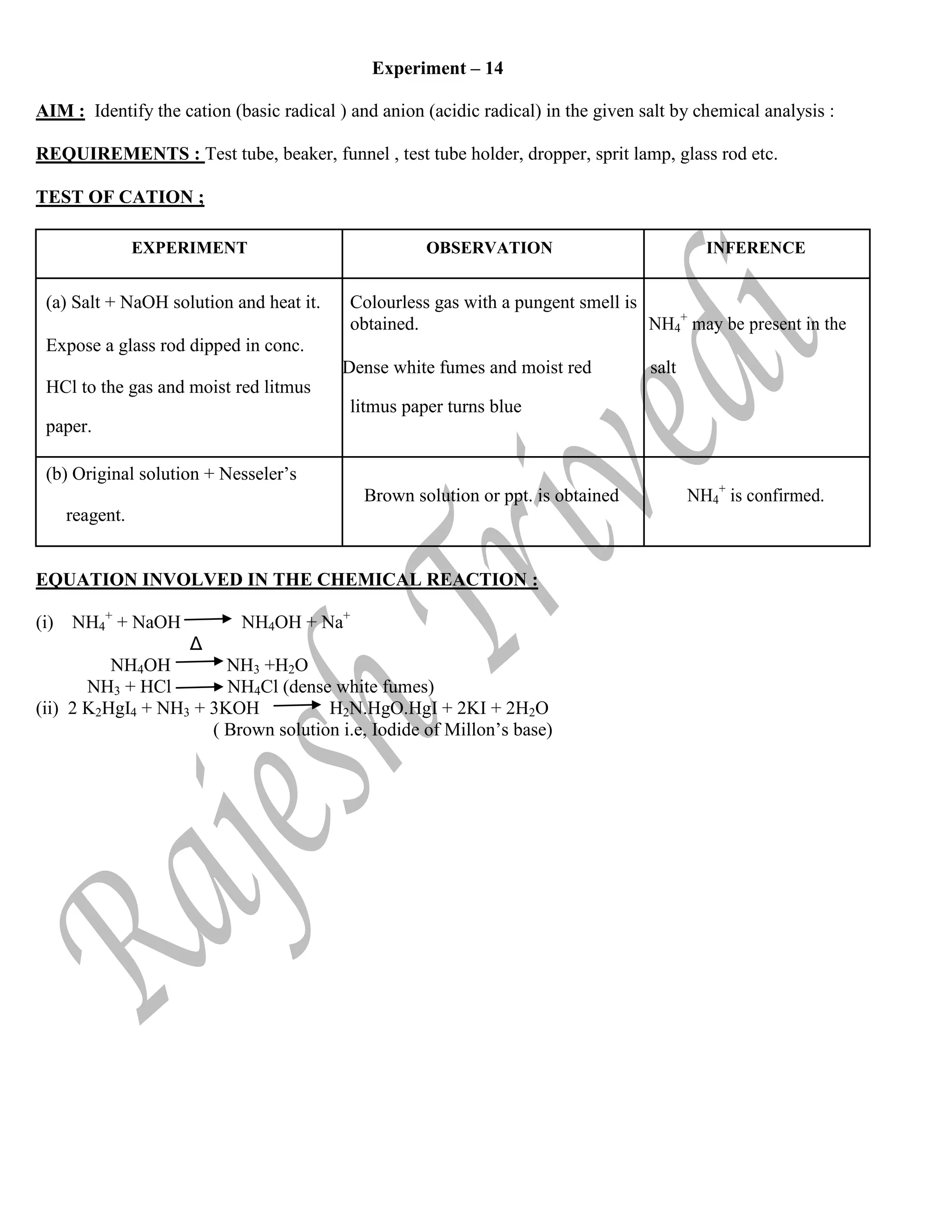
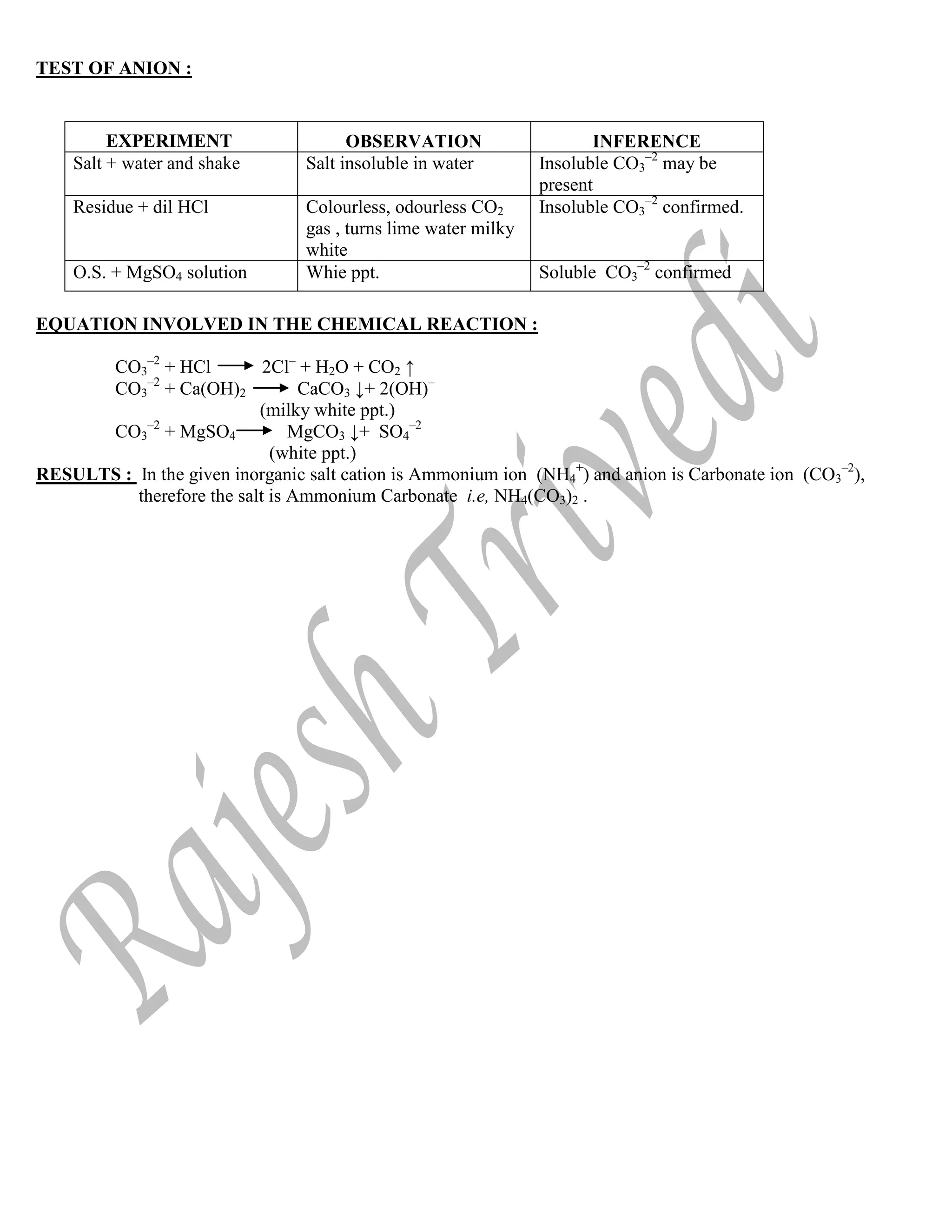
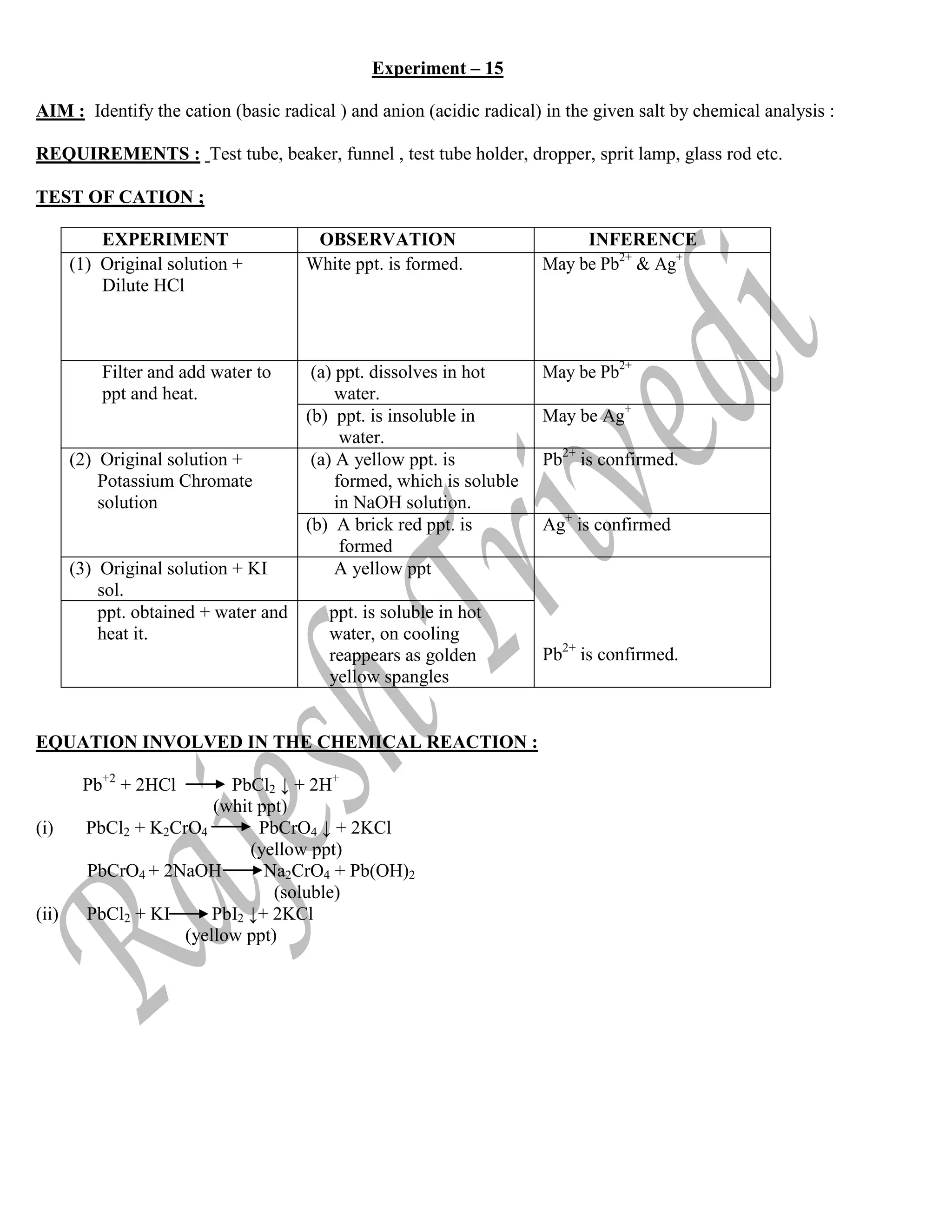
![TEST OF ANION :
EQUATION INVOLVED IN THE CHEMICAL REACTION :
(i) Ring Test :
NaNO3 + H2SO4 NaHSO4 + HNO3
2FeSO4 + 2HNO3 + H2SO4 Fe2(SO4)3 +2H2O + NO
FeSO4 + NO + 5H2O [Fe(H2O)5NO] SO4
(brown ring)
(ii) Copper turning Test :
KNO3 + H2SO4 KHSO4 + HNO3
Cu + 4HNO3 Cu(NO3)2 + H2O + 2NO2 ↑
RESULTS : In the given inorganic salt cation is Lead ion (Pb+2
) and anion is Nitrate ion (NO3
–
), therefore
the salt is Lead nitrate i.e, Pb(NO3)2 .
EXPERIMENT OBSERVATION INFERENCE
Salt + Conc. H2SO4 and heat if
necessary
Light brown gas and brown
gas with pieces of copper
turnings and the solution turns
blue in the test tube. The Acid radical may be NO3
-
Brown ring test: Strong solution
of the substance + 2 or3 drops of
conc. H2SO4, and cool. Add
freshly prepared FeSO4 solution
on the sides of the test tube.
A brown ring is formed at the
junction of two liquids.
Nitrate (NO3
-
) is confirmed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempracticalpdf-220526153021-fe01c010/75/chemistry-Practical-Class-12th-CBSE-25-2048.jpg)

![TEST OF ANION :
EQUATION INVOLVED IN THE CHEMICAL REACTION :
(i) Chromyl chloride test:
4NaCl + K2Cr2O7 + 6H2SO4 4NaHSO4 + 2KHSO4 + 2CrO2Cl2 + 3H2O
(yellow orange)
CrO2Cl2 + 4NaOH Na2CrO4 + 2NaCl + 2H2O
(yellow colour)
Pb(CH3COO)2 + Na2CrO4 PbCrO4↓ + 2CH3COONa
(yellow ppt)
(ii) Silver nitrate test :
NaCl + AgNO3 AgCl ↓+ NaNO3
(white ppt)
AgCl + 2NH4OH [Ag(NH3)2]Cl + 2H2O
(soluble)
RESULTS : In the given inorganic salt cation is Lead ( Pb+2
) and anion is Chloride (Cl–
), therefore
the salt is Lead Chloride i.e, PbCl2 .
EXPERIMENT OBSERVATION INFERENCE
Salt + Concentrated H2SO4
and heat
Effervescence with
colourless or coloured gases
2nd
group Acid radical is
present
(a) Colourless gas with a
pungent smell and gives
dense white fumes when a
glass rod dipped in
ammonium hydroxide
(NH4OH) is exposed
The Acid radical may be Cl-
(b) Brown gas and the
solution is not blue.
The acid radical may be Br-
(a) Chromyl – Chloride test:
(i) Salt + few K2Cr2O7
crystals + conc. H2SO4
and heat
(ii) Pass the vapours
through the test tube
which contains NaOH
solution
(iii) To this yellow
solution,add dilute
CH3COOH and lead
acetate solution.
Red vapours are obtained.
The solution turns yellow
Yellow ppt. is formed Chloride is confirmed.
(b) Silver Nitrate test:
Salt solution + AgNO3
solution + dilute HNO3
White ppt. is formed
which is soluble in NH4OH.
Chloride is confirmed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempracticalpdf-220526153021-fe01c010/75/chemistry-Practical-Class-12th-CBSE-27-2048.jpg)
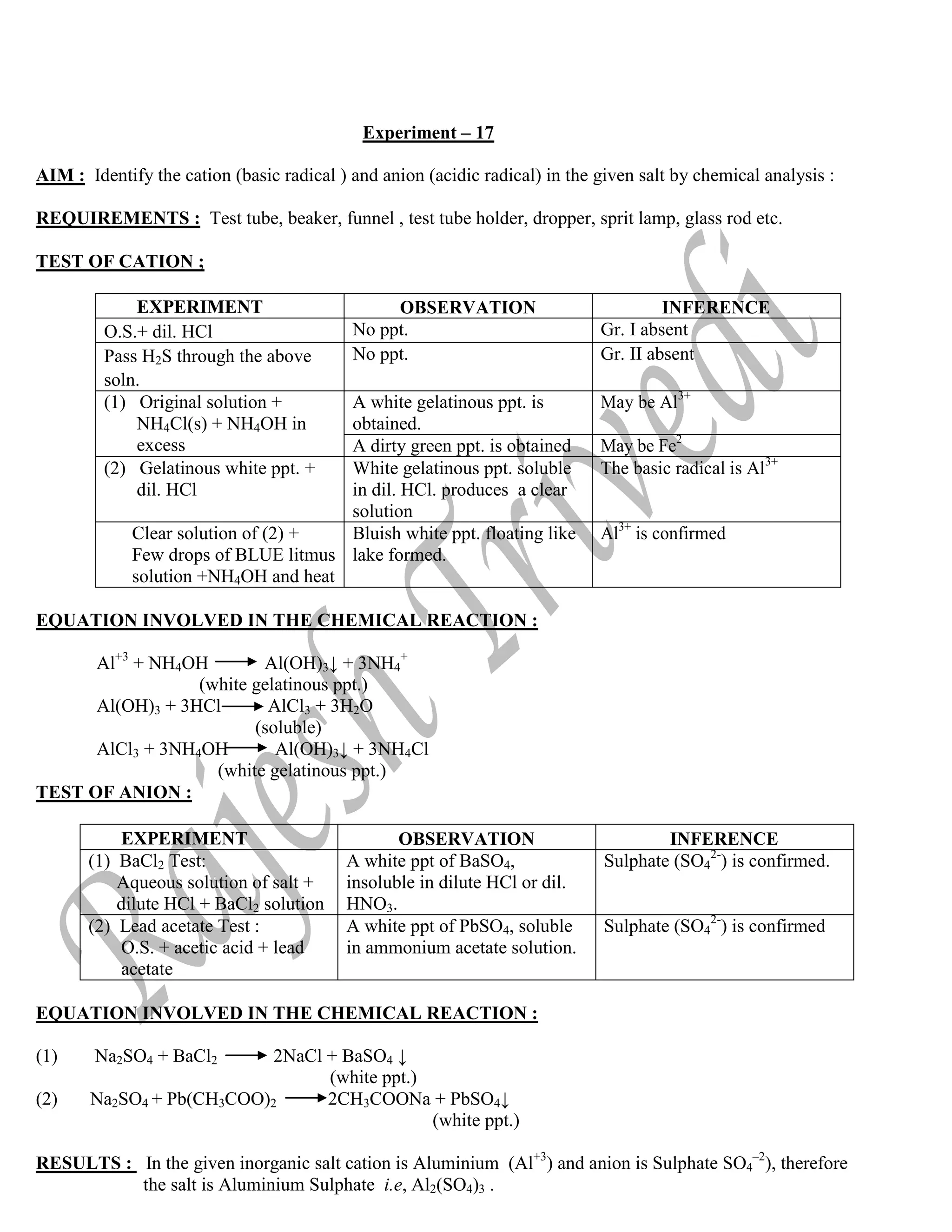
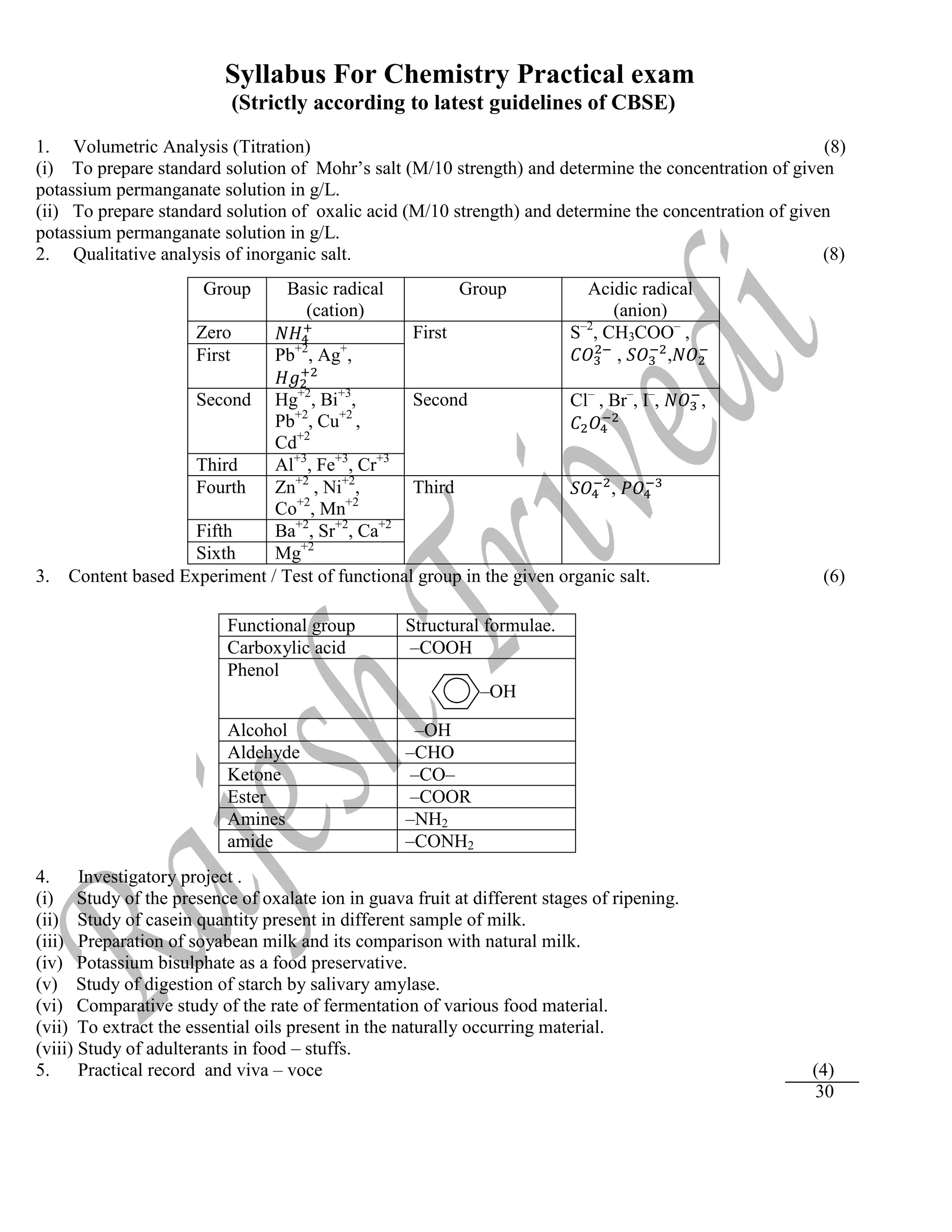
![Experiment – 18
AIM : Identify the cation (basic radical ) and anion (acidic radical) in the given salt by chemical analysis :
REQUIREMENTS : Test tube, beaker, funnel , test tube holder, dropper, sprit lamp, glass rod etc.
TEST OF CATION ;
EXPERIMENT OBSERVATION INFERENCE
O.S.+ dil. HCl No ppt. Gr. I absent
Pass H2S through the
above soln.
No ppt. Gr. II absent
Boil of H2S cool + 1 ml of
conc. HNO3. boil +
NH4Cl(s) + excess of
NH4OH
No ppt. Gr. III absent
(1) Original solution +
NH4Cl(s) + NH4OH in
excess + H2S(g)
a white ppt. is obtained May be Zn2+
, Mn2+
or Co2+
Buff or pale pink or flash
coloured ppt. soluble in
dilute HCl is obtained.
May be Mn2+
(2) Original solution +
NaOH drop wise in
excess.
The white ppt. is soluble in
excess of NaOH.
Zn2+
is confirmed
(3) Original solution +
NH4OH solution +
K4[Fe(CN)6] solution.
Blish white ppt. Zn2+
is confirmed
EQUATION INVOLVED IN THE CHEMICAL REACTION :
Zn+2
+ H2S ZnS↓ + 2H+
(white ppt.)
ZnS + 2HCl ZnCl2 + H2S
(soluble)
(1) ZnCl2 + NaOH Zn(OH)2↓ + 2 NaCl
(white ppt.)
Zn(OH)2 + 2 NaOH Na2ZnO2 + 2H2O
(soluble)
(2) ZnCl2 + K4[Fe(CN)6] Zn2[Fe(CN)6] + 4KCl
(bluish white ppt.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempracticalpdf-220526153021-fe01c010/75/chemistry-Practical-Class-12th-CBSE-29-2048.jpg)

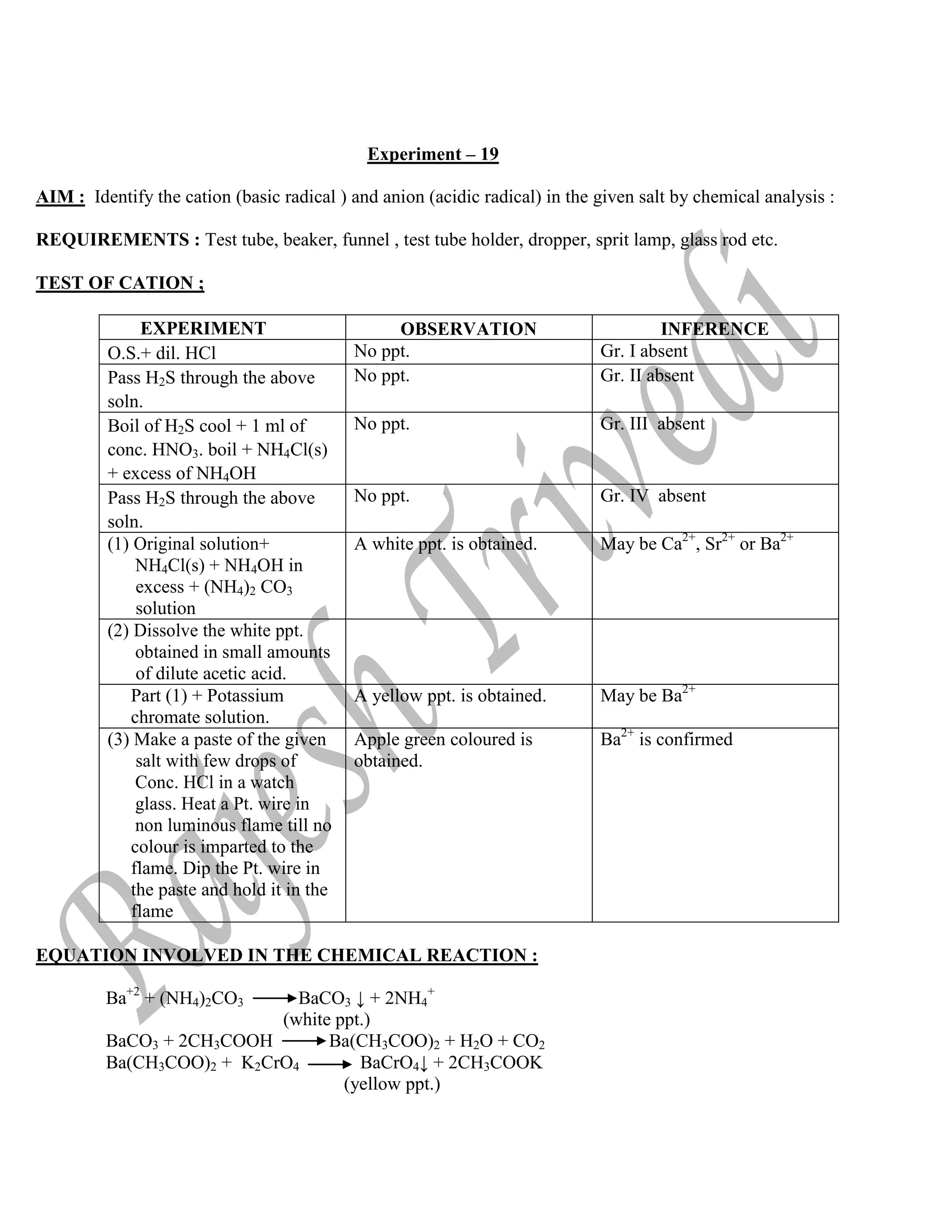
![TEST OF ANION :
EQUATION INVOLVED IN THE CHEMICAL REACTION :
(i) Chromyl chloride test:
4NaCl + K2Cr2O7 + 6H2SO4 4NaHSO4 + 2KHSO4 + 2CrO2Cl2 + 3H2O
(yellow orange)
CrO2Cl2 + 4NaOH Na2CrO4 + 2NaCl + 2H2O
(yellow colour)
Pb(CH3COO)2 + Na2CrO4 PbCrO4↓ + 2CH3COONa
(yellow ppt)
(ii) Silver nitrate test :
NaCl + AgNO3 AgCl ↓+ NaNO3
(white ppt)
AgCl + 2NH4OH [Ag(NH3)2]Cl + 2H2O
(soluble)
RESULTS : In the given inorganic salt cation is Barium (Ba+2
) and anion is Chloride (Cl–
), therefore
the salt is Barium Chloride i.e, BaCl2 .
EXPERIMENT OBSERVATION INFERENCE
Salt + Concentrated H2SO4
and heat
Effervescence with
colourless or coloured gases
2nd
group Acid radical is
present
(a) Colourless gas with a
pungent smell and gives
dense white fumes when a
glass rod dipped in
ammonium hydroxide
(NH4OH) is exposed
The Acid radical may be Cl-
(b) Brown gas and the
solution is not blue.
The acid radical may be Br-
(a) Chromyl – Chloride test:
(i) Salt + few K2Cr2O7
crystals + conc. H2SO4
and heat
(ii) Pass the vapours
through the test tube
which contains NaOH
solution
(iii) To this yellow
solution,add dilute
CH3COOH and lead
acetate solution.
Red vapours are obtained.
The solution turns yellow
Yellow ppt. is formed Chloride is confirmed.
(b) Silver Nitrate test:
Salt solution + AgNO3
solution + dilute HNO3
White ppt. is formed
which is soluble in NH4OH.
Chloride is confirmed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chempracticalpdf-220526153021-fe01c010/75/chemistry-Practical-Class-12th-CBSE-32-2048.jpg)