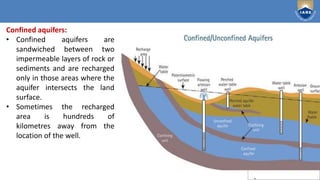
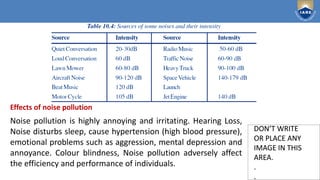
This document provides an overview of natural resources and environmental pollution from a module taught by Dr. P. Reddy Prasad. It discusses various types of energy resources like solar, wind, tidal, geothermal, and biomass. For each energy resource, it describes how the energy is harnessed or generated, advantages and disadvantages, and examples. It also discusses energy consumption patterns in different sectors like domestic, industrial, and agricultural in India.