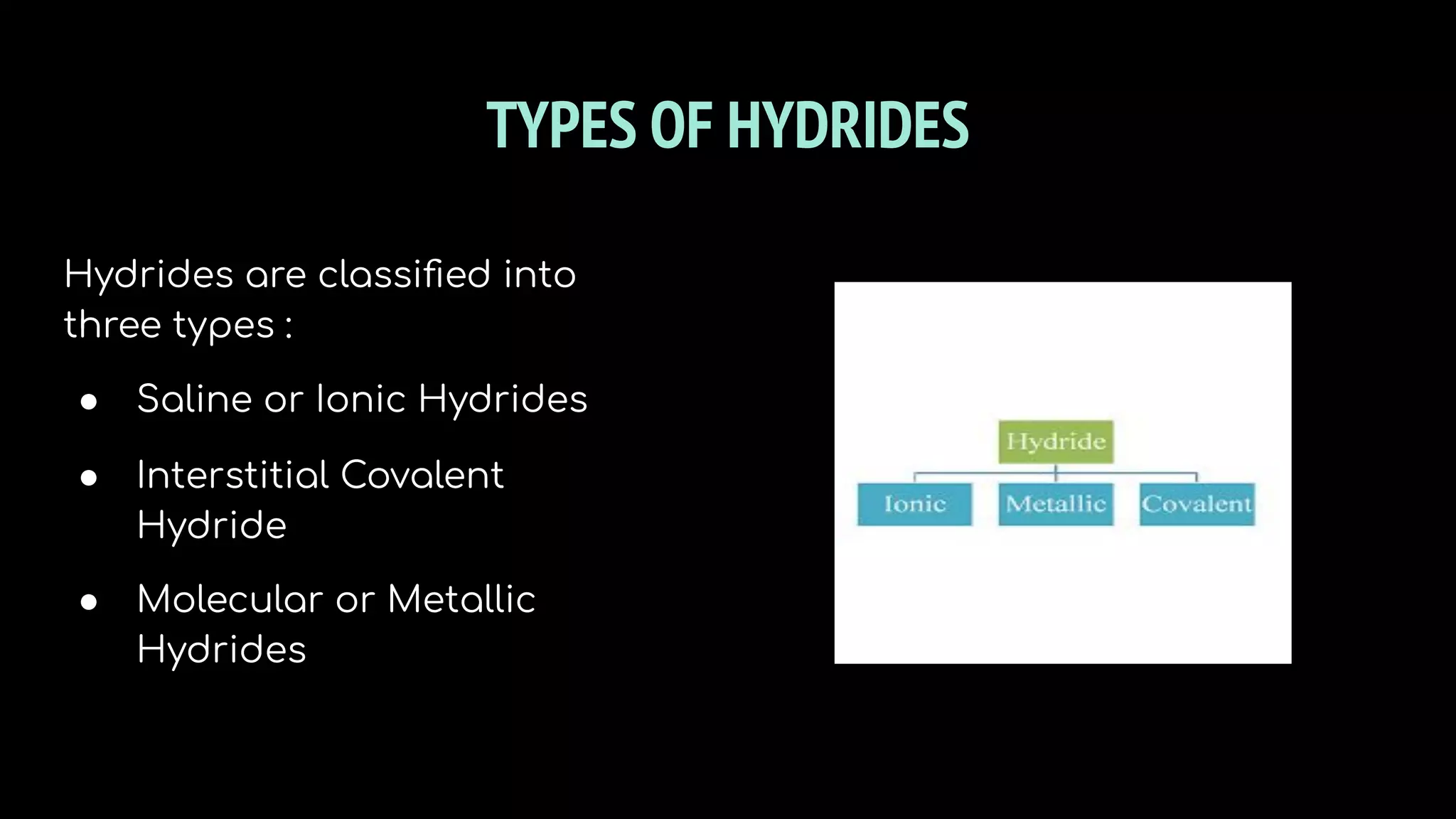
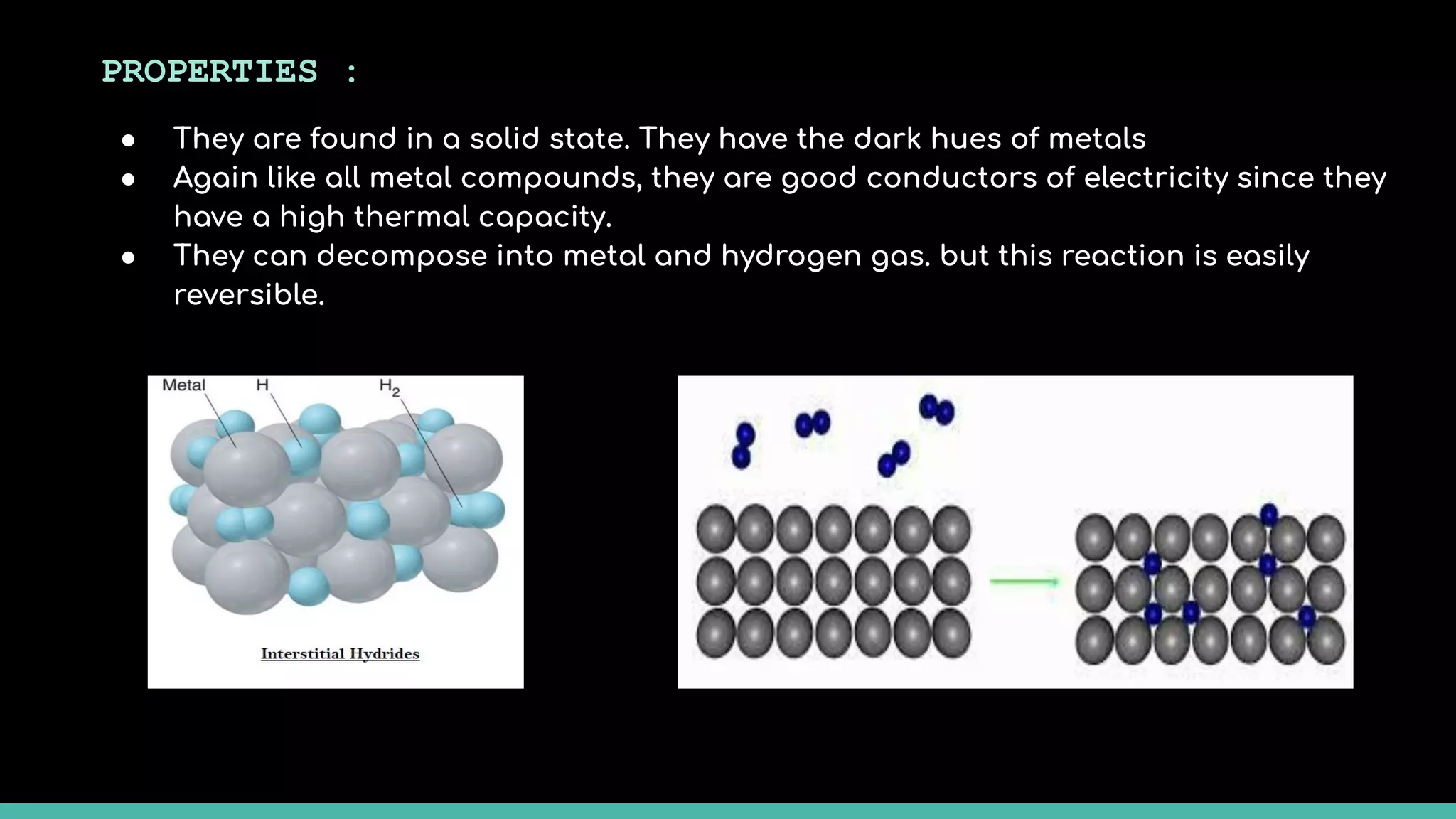
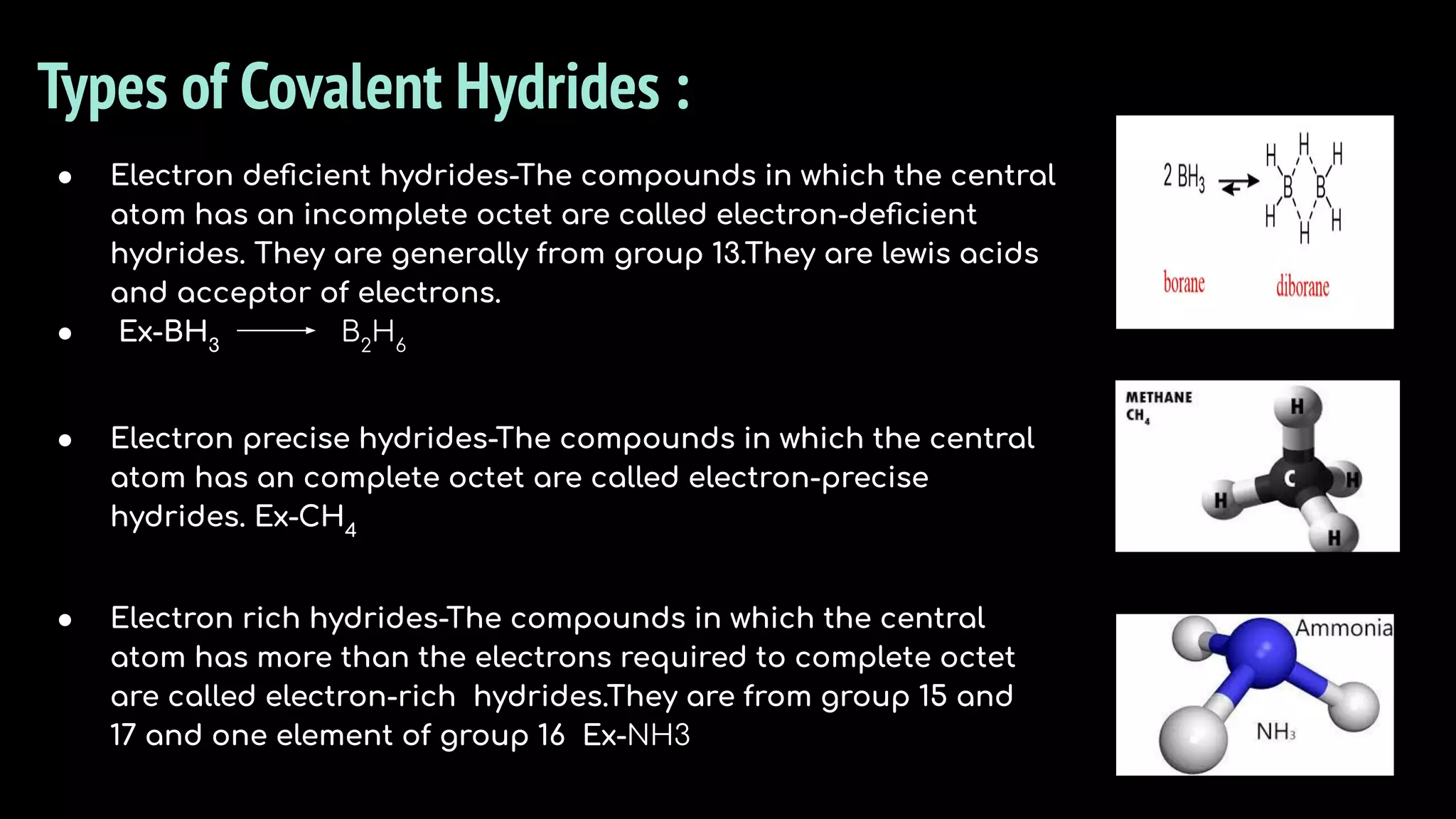
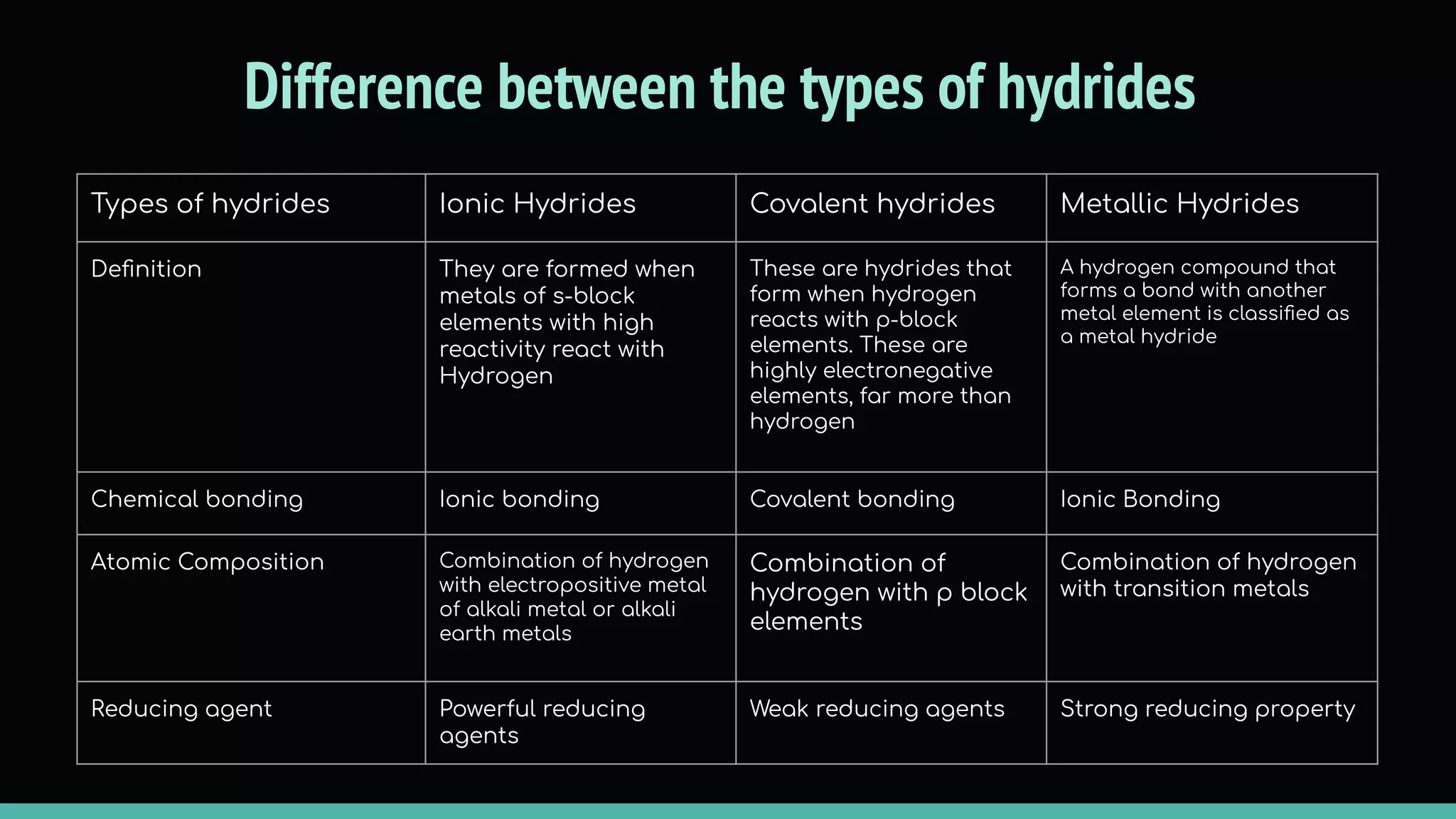
The document discusses different types of hydrides including ionic, covalent, and metallic hydrides. Ionic hydrides form between hydrogen and highly electropositive metals, with hydrogen acting as the hydride ion. Covalent hydrides form between hydrogen and nonmetals like carbon and silicon, sharing a covalent bond. Metallic hydrides form between hydrogen and transition metals, usually with a covalent or ionic bond. Hydrides find uses as reducing agents, in battery technologies, and as drying agents.
![TYPES OF HYDRIDES
By : Ishita , Pradhna , Raeshmikhaa ,
Santwana , Swaranya [ 11 A ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemproject-220911163612-db12996b/75/Chem-Project-pdf-class-11-1-2048.jpg)