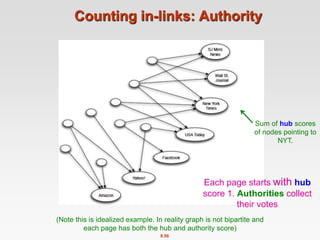
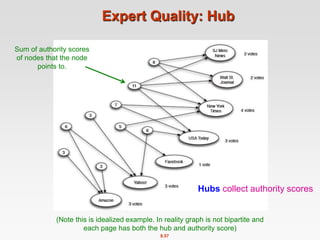
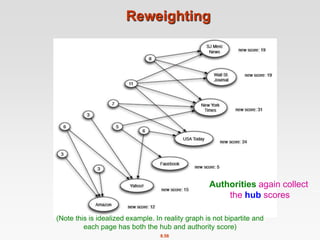
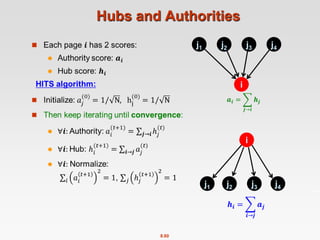
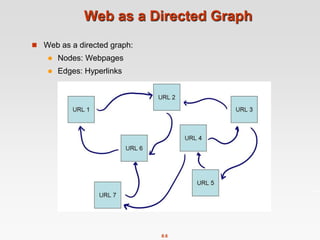
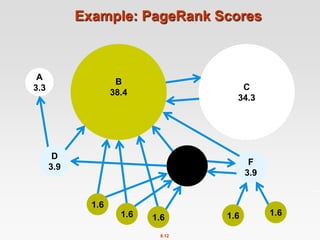
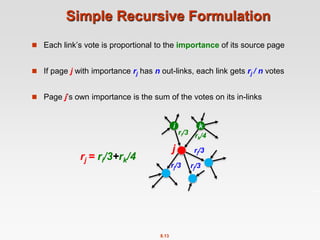
This document discusses the PageRank algorithm for ranking nodes in a graph based on their importance. It begins by introducing graph data examples like social networks and the web graph. It then describes how PageRank works by modeling a random walk over the graph and defining the stationary distribution of this random walk as the rank of each node. Key aspects covered include: using the eigenvector formulation to solve the system of equations efficiently via power iteration; adding random teleports to address problems of dead ends and spider traps; and formulating the full PageRank algorithm using a sparse matrix to handle large graphs. The document provides detailed explanations of the mathematical foundations and implementation of PageRank.

![8.3
Graph Data: Social Networks
Facebook social graph
4-degrees of separation [Backstrom-Boldi-Rosa-Ugander-Vigna, 2011]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-linkanalysis-230507141855-a63941bd/85/Chapter8-Link_Analysis-pptx-3-320.jpg)
![8.4
Graph Data: Information Nets
Citation networks and Maps of science
[Börner et al., 2012]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-linkanalysis-230507141855-a63941bd/85/Chapter8-Link_Analysis-pptx-4-320.jpg)




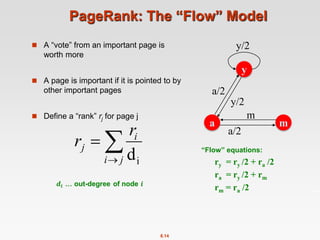

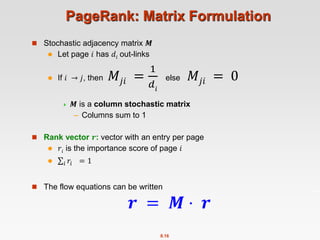
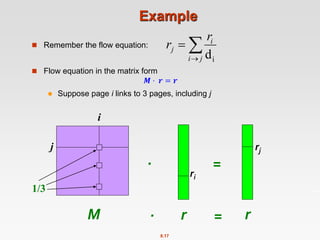

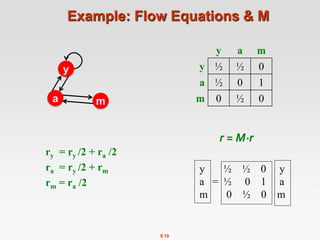
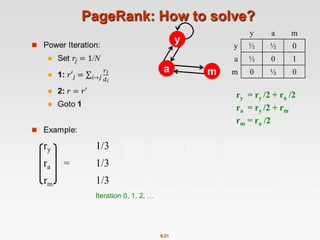
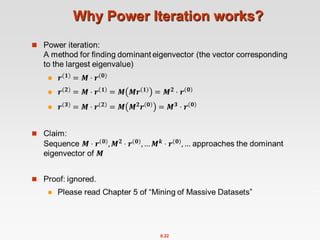
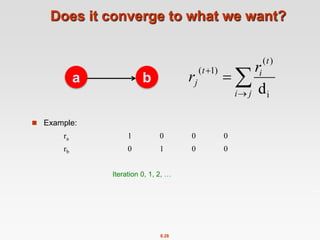
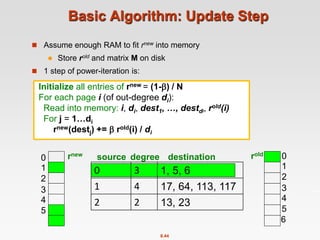
![8.20
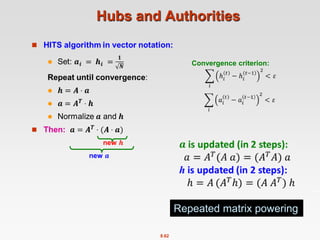
Power Iteration Method
Given a web graph with n nodes, where the nodes are pages and
edges are hyperlinks
Power iteration: a simple iterative scheme
Suppose there are N web pages
Initialize: r(0) = [1/N,….,1/N]T
Iterate: r(t+1) = M ∙ r(t)
Stop when |r(t+1) – r(t)|1 <
j
i
t
i
t
j
r
r
i
)
(
)
1
(
d
di …. out-degree of node i
|x|1 = 1≤i≤N|xi| is the L1 norm
Can use any other vector norm, e.g., Euclidean](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-linkanalysis-230507141855-a63941bd/85/Chapter8-Link_Analysis-pptx-20-320.jpg)




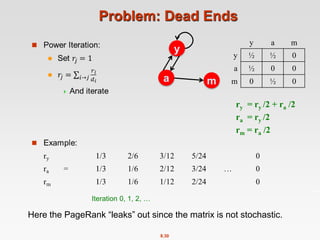
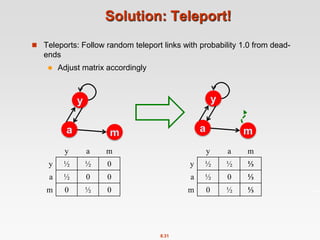
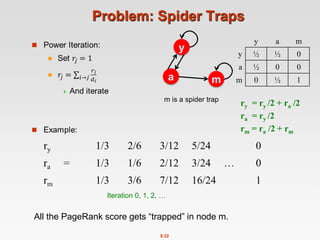




![8.37
Random Teleports ( = 0.8)
y
a =
m
1/3
1/3
1/3
0.33
0.20
0.46
0.24
0.20
0.52
0.26
0.18
0.56
7/33
5/33
21/33
. . .
y
a
m
13/15
7/15
1/2 1/2 0
1/2 0 0
0 1/2 1
1/3 1/3 1/3
1/3 1/3 1/3
1/3 1/3 1/3
y 7/15 7/15 1/15
a 7/15 1/15 1/15
m 1/15 7/15 13/15
0.8 + 0.2
M [1/N]NxN
A](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-linkanalysis-230507141855-a63941bd/85/Chapter8-Link_Analysis-pptx-37-320.jpg)
![8.38
Computing Page Rank
Key step is matrix-vector multiplication
rnew = A ∙ rold
Easy if we have enough main memory to hold A, rold, rnew
Say N = 1 billion pages
We need 4 bytes for
each entry (say)
2 billion entries for
vectors, approx 8GB
Matrix A has N2 entries
1018 is a large number!
½ ½ 0
½ 0 0
0 ½ 1
1/3 1/3 1/3
1/3 1/3 1/3
1/3 1/3 1/3
7/15 7/15 1/15
7/15 1/15 1/15
1/15 7/15 13/15
0.8 +0.2
A = ∙M + (1-) [1/N]NxN
=
A =](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-linkanalysis-230507141855-a63941bd/85/Chapter8-Link_Analysis-pptx-38-320.jpg)

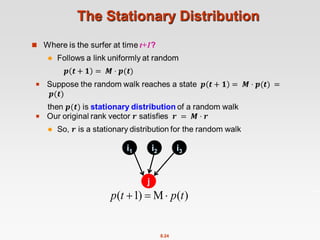
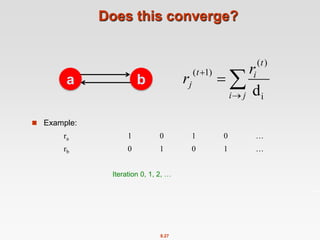
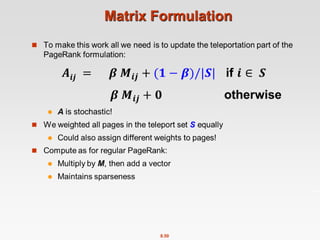
![8.40
Rearranging the Equation
[x]N … a vector of length N with all entries x
Note: Here we assumed M
has no dead-ends](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-linkanalysis-230507141855-a63941bd/85/Chapter8-Link_Analysis-pptx-40-320.jpg)








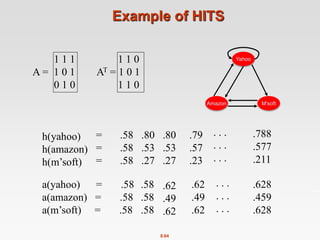
![8.51
Example: Topic-Specific PageRank
1
2 3
4
Suppose S = {1}, = 0.8
Node Iteration
0 1 2 … stable
1 0.25 0.4 0.28 0.294
2 0.25 0.1 0.16 0.118
3 0.25 0.3 0.32 0.327
4 0.25 0.2 0.24 0.261
0.2
0.5
0.5
1
1 1
0.4 0.4
0.8
0.8 0.8
S={1,2,3,4}, β=0.8:
r=[0.13, 0.10, 0.39, 0.36]
S={1,2,3} , β=0.8:
r=[0.17, 0.13, 0.38, 0.30]
S={1,2} , β=0.8:
r=[0.26, 0.20, 0.29, 0.23]
S={1} , β=0.8:
r=[0.29, 0.11, 0.32, 0.26]
S={1}, β=0.90:
r=[0.17, 0.07, 0.40, 0.36]
S={1} , β=0.8:
r=[0.29, 0.11, 0.32, 0.26]
S={1}, β=0.70:
r=[0.39, 0.14, 0.27, 0.19]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-linkanalysis-230507141855-a63941bd/85/Chapter8-Link_Analysis-pptx-51-320.jpg)