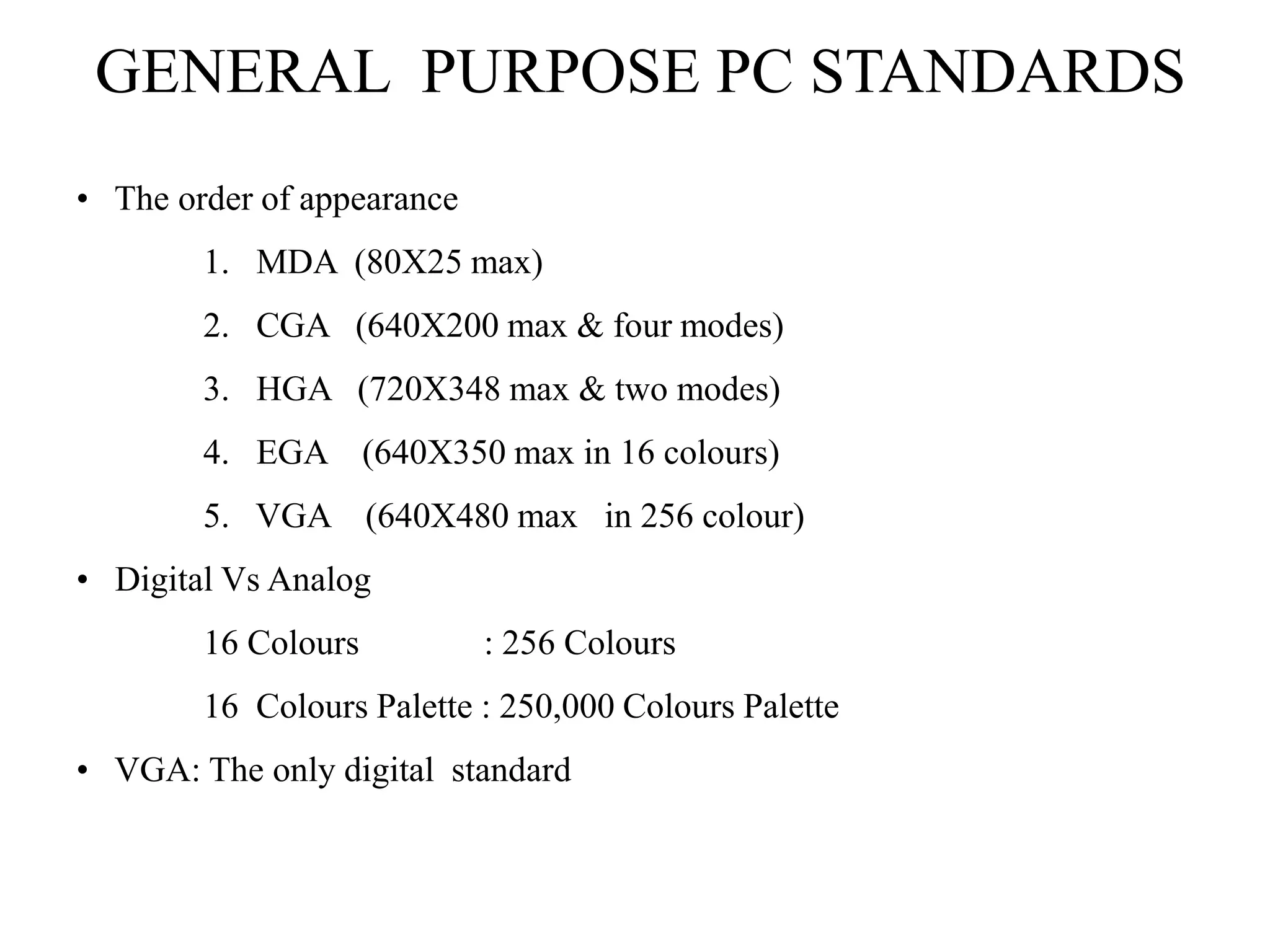
This document discusses different types of video standards and graphics systems, including general purpose PC standards like MDA, CGA, EGA, and VGA; super PC standards with additional display modes; advanced/intelligent systems like IBM PGA and 8514/A; and specialized displays. It covers topics like pixels and resolutions, parts of video systems, the evolution of standards over time, differences between digital and analog displays, factors that affect monitor selection and performance, and video drivers.