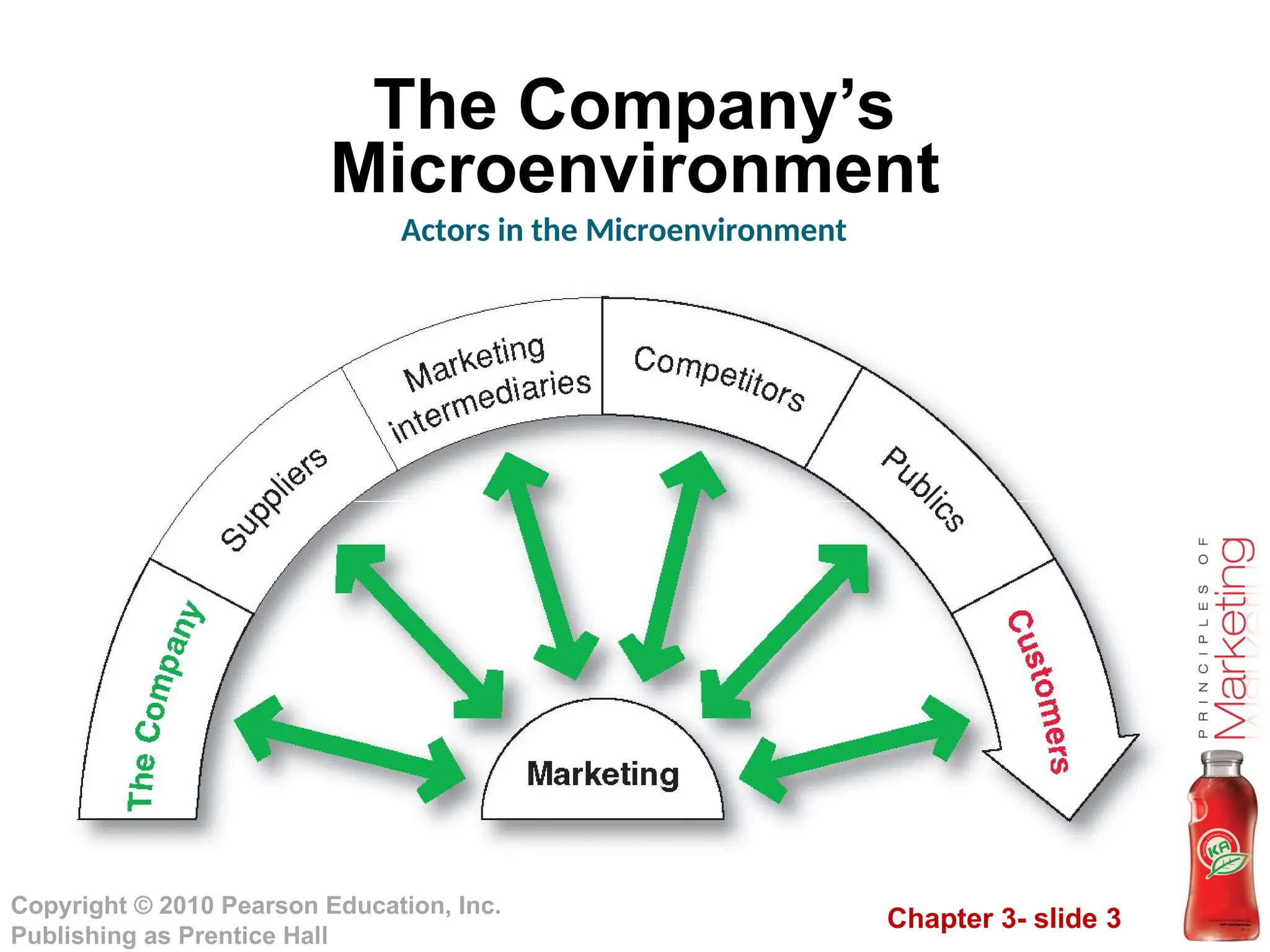
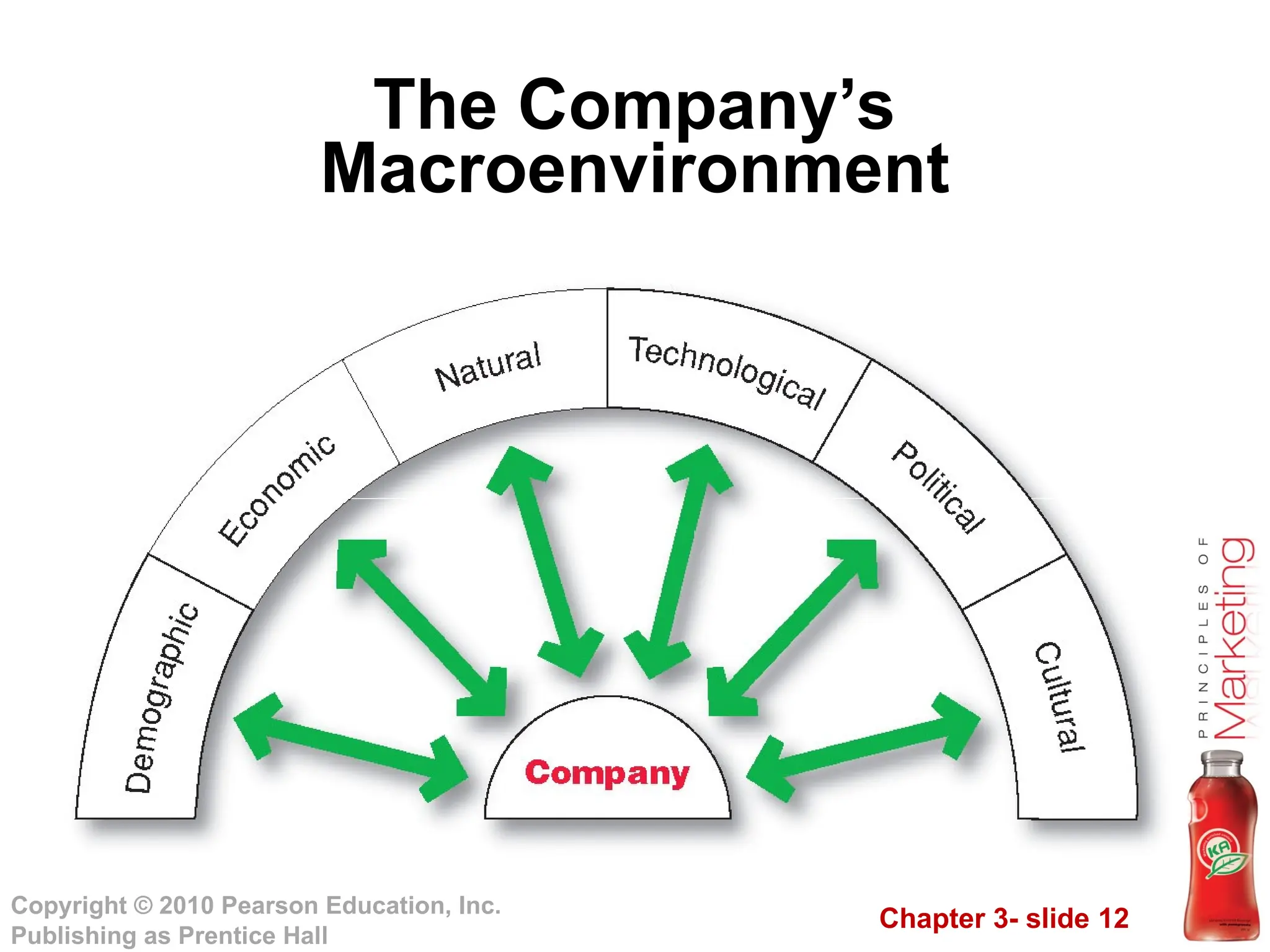
The document discusses the marketing environment, which comprises both microenvironment and macroenvironment factors that influence marketing management's ability to develop relationships with customers. The microenvironment includes close actors like the company, suppliers, intermediaries, competitors, customers, and various publics, while the macroenvironment encompasses broader forces such as demographic, economic, natural, technological, political, and cultural factors. Understanding these elements is essential for effective marketing strategy and decision-making.