Recommended
DOCX
Case Analysis of Molycorp: Financing the Production of Rare Earth Minerals”
PDF
Analysis of Marketing environment
PPTX
PPT
strategic management - krispy kreme, is turnaround possible?
PPTX
PPT
Strategic Management: Concepts & Cases Chapter 03
PPTX
Corporate Social Responsibility
PPT
PPT
Analyzing the marketing environment in the markets
PPT
Principles of Marketing Chapter #3
PDF
Chapter-3-Analyzing-the-Marketing-Environment.pdf
PPT
chapter-3 Analyzing the Marketing Environment .ppt
PDF
Marketing Chapteasasasadasdasadadar #3.pdf
PPTX
chapter. analyzing the marketing environmentv
PPT
marketing environment including macro and micro
PPT
Principles of Marketing Analyzing the Marketing Environment.ppt
PPTX
ch-3marketing-150227111908-conversion-gate01(1).pptx
PPT
Ch3 analyzing-the-marketing
PPT
Chapter #3 Principles of Marketing kotler
PPT
PPT
Chapter-3 Marketing: Analyzing the Marketing Environment
PPT
Chapt03ppt.pptfffdffdffdfdfsffdffdfdffdf
PDF
DOCX
Analyzing the Marketing Environment Chapter .docx
PPT
Chapter 3.ppt Marketing environment analyzing
PPTX
PPTX
Principles of Marketing 2011 03
PPTX
PPTX
Increase Google LSA Impression Share: 5 Fixes to Spend More of Your Budget
PDF
Digital Marketing Agency Lahore Driving Real Business Growth Online
More Related Content
DOCX
Case Analysis of Molycorp: Financing the Production of Rare Earth Minerals”
PDF
Analysis of Marketing environment
PPTX
PPT
strategic management - krispy kreme, is turnaround possible?
PPTX
PPT
Strategic Management: Concepts & Cases Chapter 03
PPTX
Corporate Social Responsibility
PPT
Similar to Kotler_POM13e_Instructor_CRS_03-Marketing
PPT
Analyzing the marketing environment in the markets
PPT
Principles of Marketing Chapter #3
PDF
Chapter-3-Analyzing-the-Marketing-Environment.pdf
PPT
chapter-3 Analyzing the Marketing Environment .ppt
PDF
Marketing Chapteasasasadasdasadadar #3.pdf
PPTX
chapter. analyzing the marketing environmentv
PPT
marketing environment including macro and micro
PPT
Principles of Marketing Analyzing the Marketing Environment.ppt
PPTX
ch-3marketing-150227111908-conversion-gate01(1).pptx
PPT
Ch3 analyzing-the-marketing
PPT
Chapter #3 Principles of Marketing kotler
PPT
PPT
Chapter-3 Marketing: Analyzing the Marketing Environment
PPT
Chapt03ppt.pptfffdffdffdfdfsffdffdfdffdf
PDF
DOCX
Analyzing the Marketing Environment Chapter .docx
PPT
Chapter 3.ppt Marketing environment analyzing
PPTX
PPTX
Principles of Marketing 2011 03
PPTX
Recently uploaded
PPTX
Increase Google LSA Impression Share: 5 Fixes to Spend More of Your Budget
PDF
Digital Marketing Agency Lahore Driving Real Business Growth Online
PPTX
Life Science Digital Marketing and AI Search for 2026
PDF
Facebook Event Marketing Tips for High-ROI Campaigns
PDF
Unlock 3 Best Websites to Buy Verified Cash App Accounts
PPTX
Google Business Video Verification in 2026: The 3-Minute Walkthrough That Get...
PDF
Tommynguyne in vietnam ecosystem report modern marketing
PDF
Why Voice of Customer Is the Missing Layer in Positioning and Competitive Str...
PDF
Black Hat SEO Techniques That Still Work in 2026
PDF
🥳 BUKTI KEMENANGAN HARI INI MINGGU 01 FEBRUARI 2026 🥰
PDF
Sell on Nykaa Fashion: A Visual Guide for New Brands & Sellers
PPTX
The New Game Changer: How Interactive Advertising Is Transforming Sports Brands
PPTX
Google LSA Ranking Factors: 4 Levers That Move Your Local Services Ads Position
PDF
Romanian Fashion Google Searches 2025 vs 2024
PPTX
Google Local Services Ads Not Showing? 5 Fixes for Zero Impressions (LSA)
PDF
SFMC User Group CPH - January 2026 - From Campaigns to Conversations
PPTX
Advanced SEO: Ranking in a Competitive Digital World
PDF
McDonald’s expansion into India hrough the lens of consumer behavior and cult...
PPTX
Top_Undergraduate_Courses_India_2026.pptx
PDF
Webinar - Measuring & Winning AI Search Visibility | VertoDigital x Rankscale
Kotler_POM13e_Instructor_CRS_03-Marketing 1. Chapter 3- slide 1
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
Chapter Three
Analyzing the Marketing Environment
2. Chapter 3- slide 2
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
Analyzing the Marketing
Environment
• The Company’s Microenvironment
• The Company’s Macroenvironemnt
• Responding to the Marketing Environment
Topic Outline
3. Chapter 3- slide 3
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Marketing Environment
The marketing environment includes the
actors and forces outside marketing that
affect marketing management’s ability to
build and maintain successful relationships
with customers
4. Chapter 3- slide 4
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Marketing Environment
Microenvironment consists of the actors
close to the company that affect its ability
to serve its customers, the company,
suppliers, marketing intermediaries,
customer markets, competitors, and
publics
5. Chapter 3- slide 5
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Microenvironment
Actors in the Microenvironment
6. Chapter 3- slide 6
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Microenvironment
• Top management
• Finance
• R&D
• Purchasing
• Operations
• Accounting
The Company
7. Chapter 3- slide 7
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Microenvironment
• Provide the resources to produce goods
and services
• Treated as partners to provide customer
value
Suppliers
8. Chapter 3- slide 8
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Microenvironment
Help the company to
promote, sell and
distribute its
products to final
buyers
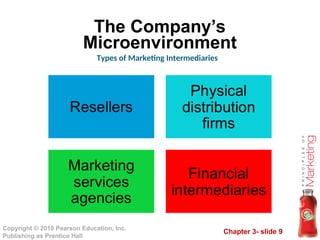
Marketing Intermediaries
9. Chapter 3- slide 9
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Microenvironment
Types of Marketing Intermediaries
10. Chapter 3- slide 10
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
________ include resellers, marketing service
agencies, and financial firms that help a
company to promote and sell its offerings to its
final customers.
1. Advertising agencies
2. Suppliers
3. Intelligence firms
4. Marketing intermediaries
11. Chapter 3- slide 11
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
________ include resellers, marketing service
agencies, and financial firms that help a
company to promote and sell its offerings to its
final customers.
1. Advertising agencies
2. Suppliers
3. Intelligence firms
4. Marketing intermediaries
12. Chapter 3- slide 12
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
Banks, insurance companies, and credit
companies that aid in financial transactions
are called ________.
1. financial intermediaries
2. marketing services agencies
3. physical distribution firms
4. positioning
13. Chapter 3- slide 13
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
Banks, insurance companies, and credit
companies that aid in financial transactions
are called _________.
1. financial intermediaries
2. marketing services agencies
3. physical distribution firms
4. positioning
14. Chapter 3- slide 14
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Microenvironment
• Firms must gain strategic advantage by
positioning their offerings against
competitors’ offerings
Competitors
15. Chapter 3- slide 15
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Microenvironment
Publics
• Any group that has an actual or
potential interest in or impact on
an organization’s ability to
achieve its objectives
– Financial publics
– Media publics
– Government publics
– Citizen-action publics
– Local publics
– General public
– Internal publics
16. Chapter 3- slide 16
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
Financial, media, government, and citizen-action
are several types of ________.
1. taxing authorities
2. legal departments
3. publics
4. marketing mix elements
17. Chapter 3- slide 17
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
Financial, media, government, and citizen-action
are several types of ________.
1. taxing authorities
2. legal departments
3. publics
4. marketing mix elements
18. Chapter 3- slide 18
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
A company’s ________ consists of its suppliers,
marketing intermediaries, customers,
competitors, and publics.
1. macroenvironment
2. microenvironment
3. business environment
4. marketing environment
19. Chapter 3- slide 19
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
A company’s ________ consists of its suppliers,
marketing intermediaries, customers,
competitors, and publics.
1. macroenvironment
2. microenvironment
3. business environment
4. marketing environment
20. Chapter 3- slide 20
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
21. Chapter 3- slide 21
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
Demography is the study of human populations
in terms of size, density, location, age, gender,
race, occupation, and other statistics
• Demographic environment is important
because it involves people, and people make
up markets
• Demographic trends include age, family
structure, geographic population shifts,
educational characteristics, and population
diversity
Demographic Environment
22. Chapter 3- slide 22
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
• Changing age structure of the population
– Baby boomers include people born between
1946 and 1964
– Most affluent Americans
Demographic Environment
23. Chapter 3- slide 23
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
• Generation X includes people born
between 1965 and 1976
– High parental divorce rates
– Cautious economic outlook
– Less materialistic
– Family comes first
– Lag behind on retirement savings
Demographic Environment
24. Chapter 3- slide 24
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
• Millennials (gen Y or echo boomers) include
those born between 1977 and 2000
– Comfortable with technology
– Includes
• Tweens (ages 8–12)
• Teens (13–19)
• Young adults (20’s)
Demographic Environment
25. Chapter 3- slide 25
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
Generational marketing is important in
segmenting people by lifestyle of life
state instead of age
Demographic Environment
26. Chapter 3- slide 26
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
More people are:
• Divorcing or separating
• Choosing not to marry
• Choosing to marry later
• Marrying without intending to have
children
• Increased number of working women
• Stay-at-home dads
Demographic Environment
27. Chapter 3- slide 27
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
• Growth in U.S. West and
South and decline in Midwest
and Northeast
• Moving from rural to
metropolitan areas
• Changes in where people work
– Telecommuting
– Home office
– Divorcing or separating
Demographic Environment
28. Chapter 3- slide 28
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
• Changes in the Workforce
– More educated
– More white collar
Demographic Environment
29. Chapter 3- slide 29
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
Demographic Environment
Increased Diversity
Markets are becoming more diverse
– International
– National
• Includes:
– Ethnicity
– Gay and lesbian
– Disabled
30. Chapter 3- slide 30
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The baby boomer generation is made up of the
period ________.
1. 1960–1971
2. 1946–1964
3. 1980s
4. 1920–1929
31. Chapter 3- slide 31
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The baby boomer generation is made up of the
period ________.
1. 1960–1971
2. 1946–1964
3. 1980s
4. 1920–1929
32. Chapter 3- slide 32
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
Economic environment consists of factors
that affect consumer purchasing power and
spending patterns
• Industrial economies are richer markets
• Subsistence economies consume most of
their own agriculture and industrial output
Economic Environment
33. Chapter 3- slide 33
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
• Changes in income
• Value marketing involves
ways to offer financially
cautious buyers greater
value—the right
combination of quality and
service at a fair price
Economic Environment
34. Chapter 3- slide 34
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The “shop until you drop” mentality of the 1990s
has been replaced with a more ________
approach.
1. “save all you can”
2. “value is key”
3. “don’t shop at all”
4. “splurge regularly”
35. Chapter 3- slide 35
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The “shop until you drop” mentality of the 1990s
has been replaced with a more ________
approach.
1. “save all you can”
2. “value is key”
3. “don’t shop at all”
4. “splurge regularly”
36. Chapter 3- slide 36
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
• Ernst Engel—Engel’s Law
• As income rises:
– The percentage spent on food declines
– The percentage spent on housing remains
constant
– The percentage spent on savings increases
Economic Environment
Changes in Consumer Spending Patterns
37. Chapter 3- slide 37
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
Natural environment involves the natural
resources that are needed as inputs by
marketers or that are affected by marketing
activities
• Trends
– Shortages of raw materials
– Increased pollution
– Increase government intervention
– Environmentally sustainable strategies
Natural Environment
38. Chapter 3- slide 38
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
There are three trends in the natural environment that marketers
are monitoring. These are ________, ________, and ________.
1. shortages of raw materials; increased legislation; increased
consumerism
2. the green movement; shortages of raw materials;
increased pollution
3. increased pollution; increased government intervention;
shortages of raw materials
4. increased consumerism; increased population; increased
ethical expectations
39. Chapter 3- slide 39
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
There are three trends in the natural environment that marketers
are monitoring. These are ________, ________, and ________.
1. shortages of raw materials; increased legislation; increased
consumerism
2. the green movement; shortages of raw materials;
increased pollution
3. increased pollution; increased government intervention;
shortages of raw materials
4. increased consumerism; increased population; increased
ethical expectations
40. Chapter 3- slide 40
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
Technological Environment
• Most dramatic force
in changing the
marketplace
• Creates new
products and
opportunities
• Safety of new
product always a
concern
41. Chapter 3- slide 41
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
Political environment consists of laws,
government agencies, and pressure groups
that influence or limit various organizations
and individuals in a given society
Political Environment
42. Chapter 3- slide 42
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
• Legislation regulating business
– Increased legislation
– Changing government agency
enforcement
• Increased emphasis on ethics
– Socially responsible behavior
– Cause-related marketing
Political Environment
43. Chapter 3- slide 43
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
Which of the following is not one of the reasons
business legislation is enacted?
1. To protect companies from each other
2. To protect companies from consumers
3. To protect consumers from unfair business
practices
4. To protect the interests of society
44. Chapter 3- slide 44
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
Which of the following is not one of the reasons
business legislation is enacted?
1. To protect companies from each other
2. To protect companies from consumers
3. To protect consumers from unfair business
practices
4. To protect the interests of society
45. Chapter 3- slide 45
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
In exercising their corporate social responsibility
and building a more positive image, companies
are now linking themselves to worthwhile
causes. This is referred to as ________.
1. marketing mix
2. marketing concept
3. cause-related marketing
4. Engel’s Law
46. Chapter 3- slide 46
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
In exercising their corporate social responsibility
and building a more positive image, companies
are now linking themselves to worthwhile
causes. This is referred to as
__________________.
1. marketing mix
2. marketing concept
3. cause-related marketing
4. Engel’s Law
47. Chapter 3- slide 47
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
Cultural environment consists of institutions
and other forces that affect a society’s
basic values, perceptions, and behaviors
Cultural Environment
48. Chapter 3- slide 48
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
Core beliefs and values are persistent and are
passed on from parents to children and are
reinforced by schools, churches, businesses,
and government
Secondary beliefs and values are more open to
change and include people’s views of
themselves, others, organization, society,
nature, and the universe
Cultural Environment
Persistence of Cultural Values
49. Chapter 3- slide 49
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
• People’s view of themselves
– Yankelovich Monitor’s consumer
segments:
• Do-it-yourselfers—recent movers
• Adventurers
• People’s view of others
– More “cocooning”
Cultural Environment
Shifts in Secondary Cultural Values
50. Chapter 3- slide 50
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
Yankelovich identifies consumer segments whose
purchases are motivated by self-views. Two
examples are _________ and __________.
1. Generation M; generation N
2. Refilled nests; do-it-yourselfers
3. Do-it-yourselfers; adventurers
4. marketing mix; positioning
51. Chapter 3- slide 51
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
Yankelovich identifies consumer segments whose
purchases are motivated by self-views. Two
examples are _________ and __________.
1. Generation M; generation N
2. Refilled nests; do-it-yourselfers
3. Do-it-yourselfers; adventurers
4. marketing mix; positioning
52. Chapter 3- slide 52
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
• People’s view of organizations
• People’s view of society
– Patriots defend it
– Reformers want to change it
– Malcontents want to leave it
Cultural Environment
Shifts in Secondary Cultural Values
53. Chapter 3- slide 53
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Company’s
Macroenvironment
Cultural Environment
Shifts in Secondary Cultural Values
• People’s view of nature
– Some feel ruled by it
– Some feel in harmony with it
– Some seek to master it
• People’s view of the universe
– Renewed interest in spirituality
54. Chapter 3- slide 54
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
A woman who drives a hybrid car, consistently
recycles, and buys “earth-friendly” products is
acting out her view of ________.
1. cost
2. non-profit organizations
3. others
4. nature
55. Chapter 3- slide 55
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
A woman who drives a hybrid car, consistently
recycles, and buys “earth-friendly” products is
acting out her view of ________.
1. cost
2. non-profit organizations
3. others
4. nature
56. Chapter 3- slide 56
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
Which of the following are included in the major
forces affecting a company’s
macroenvironment?
1. Marketing mix, positioning, price
2. cultural, political/legal, economic
3. Marketing concept, goal setting, cultural
4. Baby boomers, minimum wage rates,
product/service
57. Chapter 3- slide 57
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
Which of the following are included in the major
forces affecting a company’s
macroenvironment?
1. Marketing mix, positioning, price
2. Cultural, political/legal, economic
3. Marketing concept, goal setting, cultural
4. Baby boomers, minimum wage rates,
product/service
58. Chapter 3- slide 58
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
Responding to the Marketing
Environment
Views on Responding
59. Chapter 3- slide 59
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
A company has several options with regard to its
marketing environment. A strong company
takes a(n) ________ approach.
1. proactive
2. reactive
3. ingenuous
4. peaceful
60. Chapter 3- slide 60
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
A company has several options with regard to its
marketing environment. A strong company
takes a(n) ________ approach.
1. proactive
2. reactive
3. ingenuous
4. peaceful
61. Chapter 3- slide 61
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
A company’s macroenvironment consists of all of
the following except ________.
1. demographic forces
2. economic forces
3. competitive forces
4. technological forces
62. Chapter 3- slide 62
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
A company’s macroenvironment consists of all of
the following except ________.
1. demographic forces
2. economic forces
3. competitive forces
4. technological forces
63. Chapter 3- slide 63
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a
retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic,
mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written
permission of the publisher. Printed in the United States of America.
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
Publishing as Prentice Hall
Editor's Notes #6 Note to Instructor
Discussion Questions
What types of collaboration does there need to be between the departments?
How might projects be integrated between marketing and finance?
How might projects be integrated between marketing and information systems?
This question on finance could lead to a discussion about budgeting for marketing. The collaboration between marketing and IS could lead to discussions of market research, ordering systems, and customer relationship management systems. #8 Note to Instructor
The text explains how Coke delivers value for their marketing intermediaries:
They understand each retailer partner’s business
The conduct consumer research and share with partners
They develop marketing programs and merchandising for partners
#14 Note to Instructor
Students should note that the competition is just a click away with online purchasing. This link goes to Bizrate—one of many comparison shopping sites online. Enter a product like coffee makers to see the competing products and retailers for this category. #15 Note to Instructor
In slideshow view, click on movie icon to launch Tom’s Shoes video snippet. See accompanying DVD for full video segment #22 Note to Instructor
There are many Web sites targeted to boomers including this link to Boomers International. Before following the link it might be interesting to ask the following:
Discussion Questions
What type of information boomers might be seeking? #28 Note to Instructor
Students are probably very familiar with job search sites such as this link to monster.com. It might be interesting to compare the listings for white collar versus blue collar job opportunities including the associated pay and benefits. #33 Note to Instructor
This graphic highlights a car targeted to India’s growing middle class.
Discussion Questions
What changes might there be in U.S. income over the next year? What are positioned as “value cars.”
The students might quote current economic declines or rises. The “value cars” will probably include some of the smaller cars by Kia, Ford, Honda, and Toyota. #37 Note to Instructor
This Web link connects to greenbiz.com. There are several Web sites like this that provide information on business as to how to practice green strategies including green marketing. #40 Note to Instructor
Discussion Question
Ask students what changes they have seen in technology in the past four years including medical products, communications, and media.
They will most likely talk about the use of artificial organs and stem cell research, the growth of PDA’s like the iPod, and the use of new media products including DVR or TiVo. #49 Note to Instructor
Do-It-Yourselfers—Recent Movers:
Active consumers also view the experience as a form of self-expression.
They view their homes as their havens
View their projects as personal victories over the high-priced marketplace.
Adventurers:
Rarely follow a single path or do the same thing twice.
View the experience as far more exciting than the entertainment value.
They are more likely to engage in activities most think are too dangerous.