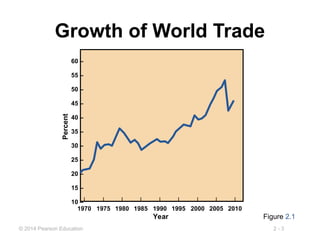
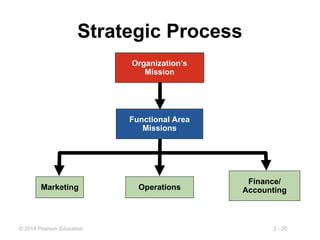
The document provides an overview of globalization in operations management, highlighting reasons for globalizing such as improving supply chains and reducing costs. It also discusses strategic development including mission statements and competitive advantages through differentiation, cost leadership, and response. Additionally, it outlines key issues in globalization and employs SWOT analysis for strategic planning.