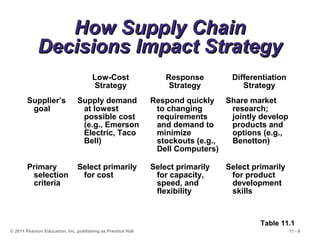
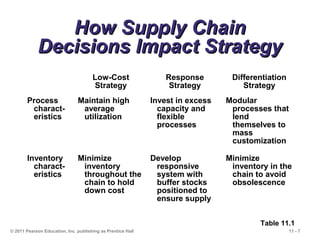
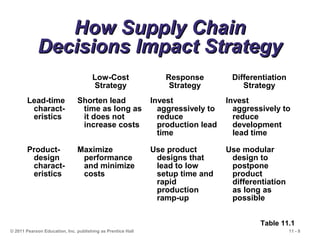
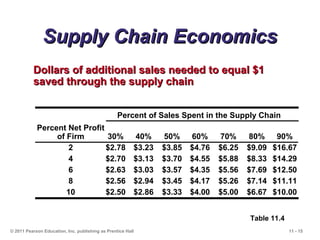
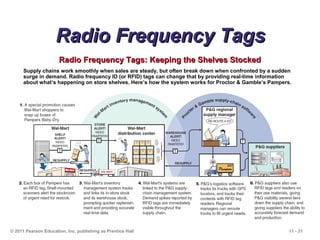
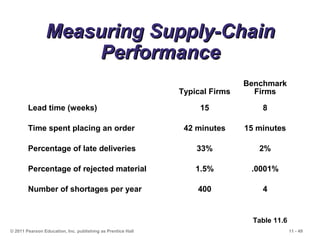
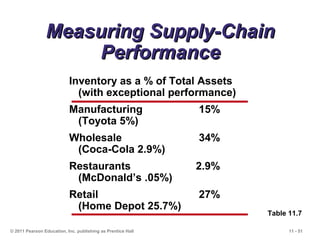
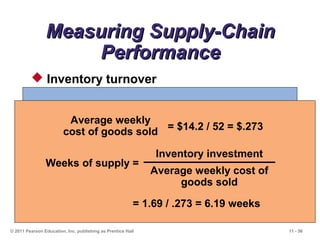
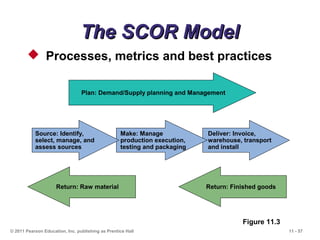
The document discusses the principles and strategies of supply chain management, emphasizing the integration of activities that transform materials into products and deliver them to customers. It covers various supply chain strategies, risks, outsourcing, and vendor selection processes, highlighting the importance of collaboration and maintaining efficiency. Lastly, it examines logistics management and the methods to reduce costs and improve service in supply chains.