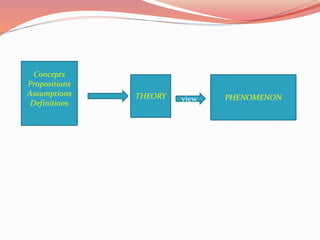
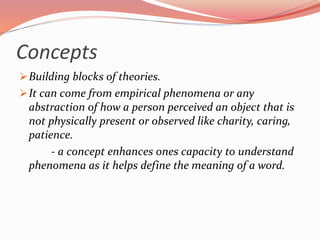
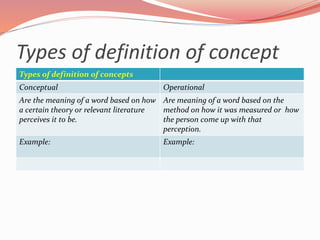
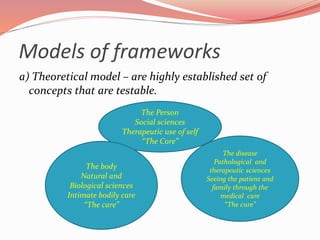
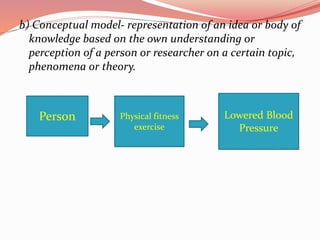
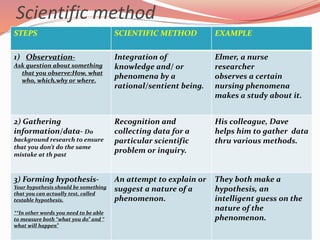
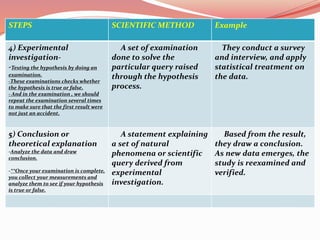
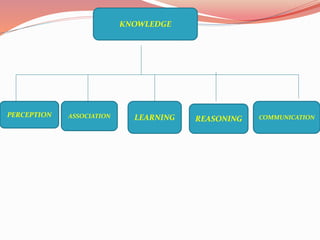
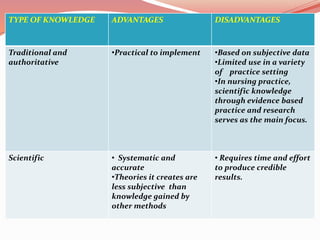
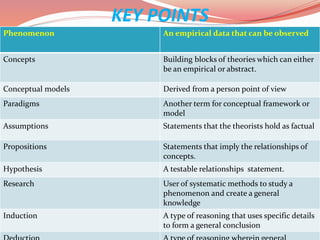
This document discusses concepts related to theory and the scientific method. It begins by defining key concepts in theory such as concepts, propositions, definitions, and assumptions. It then discusses characteristics of good theories and different types of nursing theories. The scientific method is introduced as a systematic process involving observation, hypothesis formation, experimentation, and conclusion. Different sources of knowledge are described including traditional, authoritative, and scientific knowledge. Finally, key terms related to theory development are explained such as phenomenon, concepts, models, and paradigms.