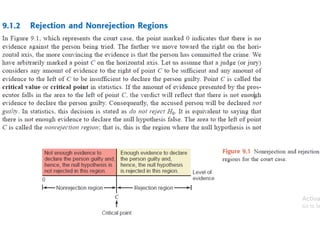
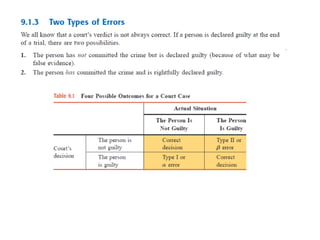
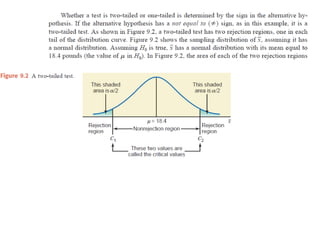
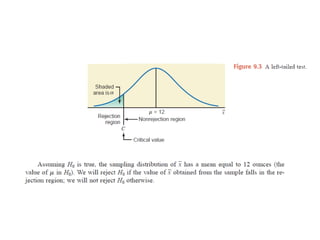
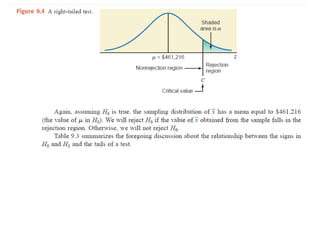
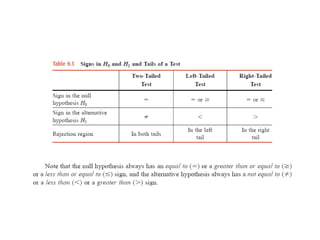
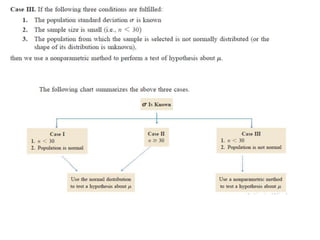
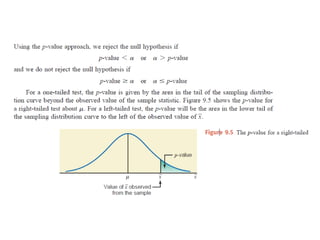
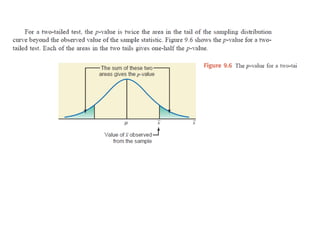
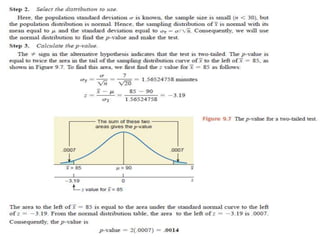
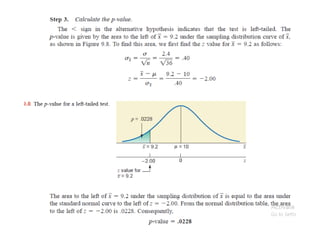
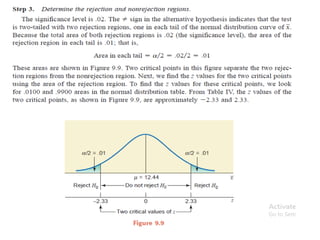
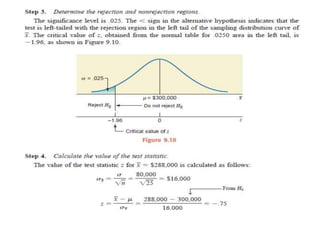
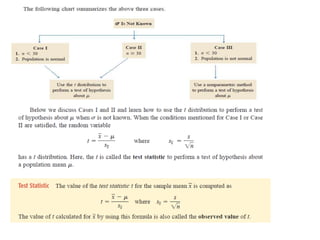
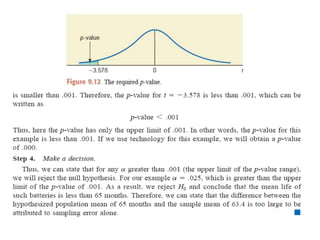
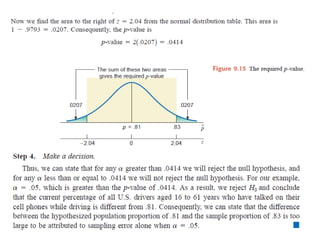
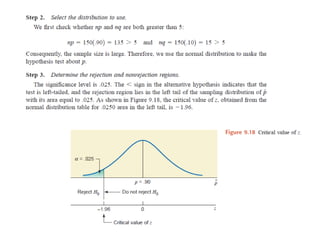
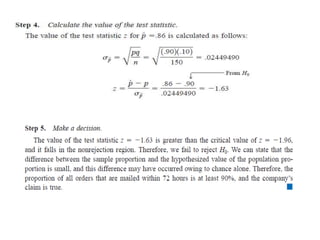
The document discusses the null hypothesis and how it is used to test claims about population parameters. Specifically, it gives an example of testing a soft drink company's claim that its cans contain 12 ounces on average. The null hypothesis would be that the company's claim is true. To test this, the procedure involves determining the critical value from the normal distribution table based on the significance level, finding the test statistic value, and comparing the two to make a decision about rejecting or failing to reject the null hypothesis.