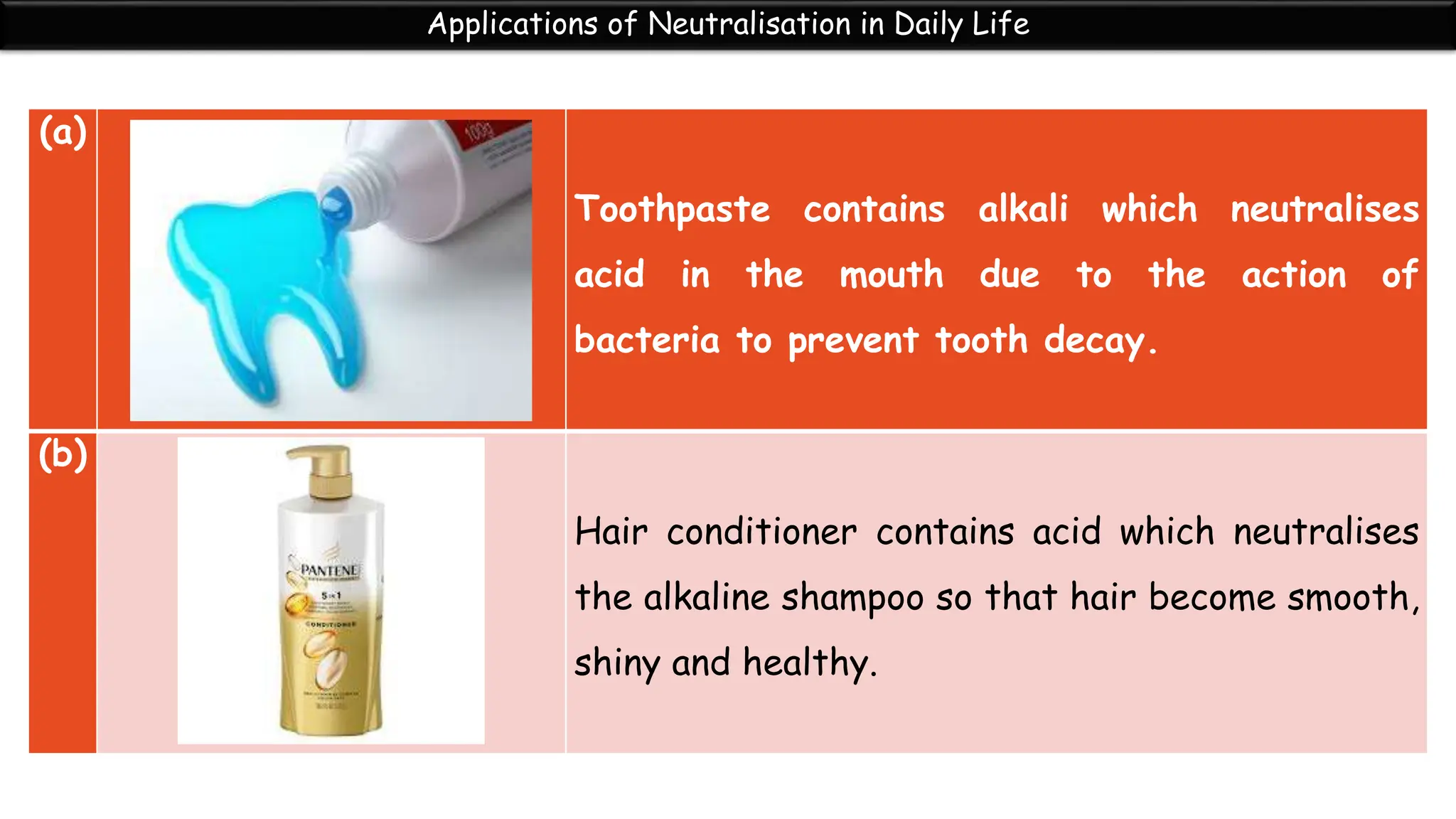
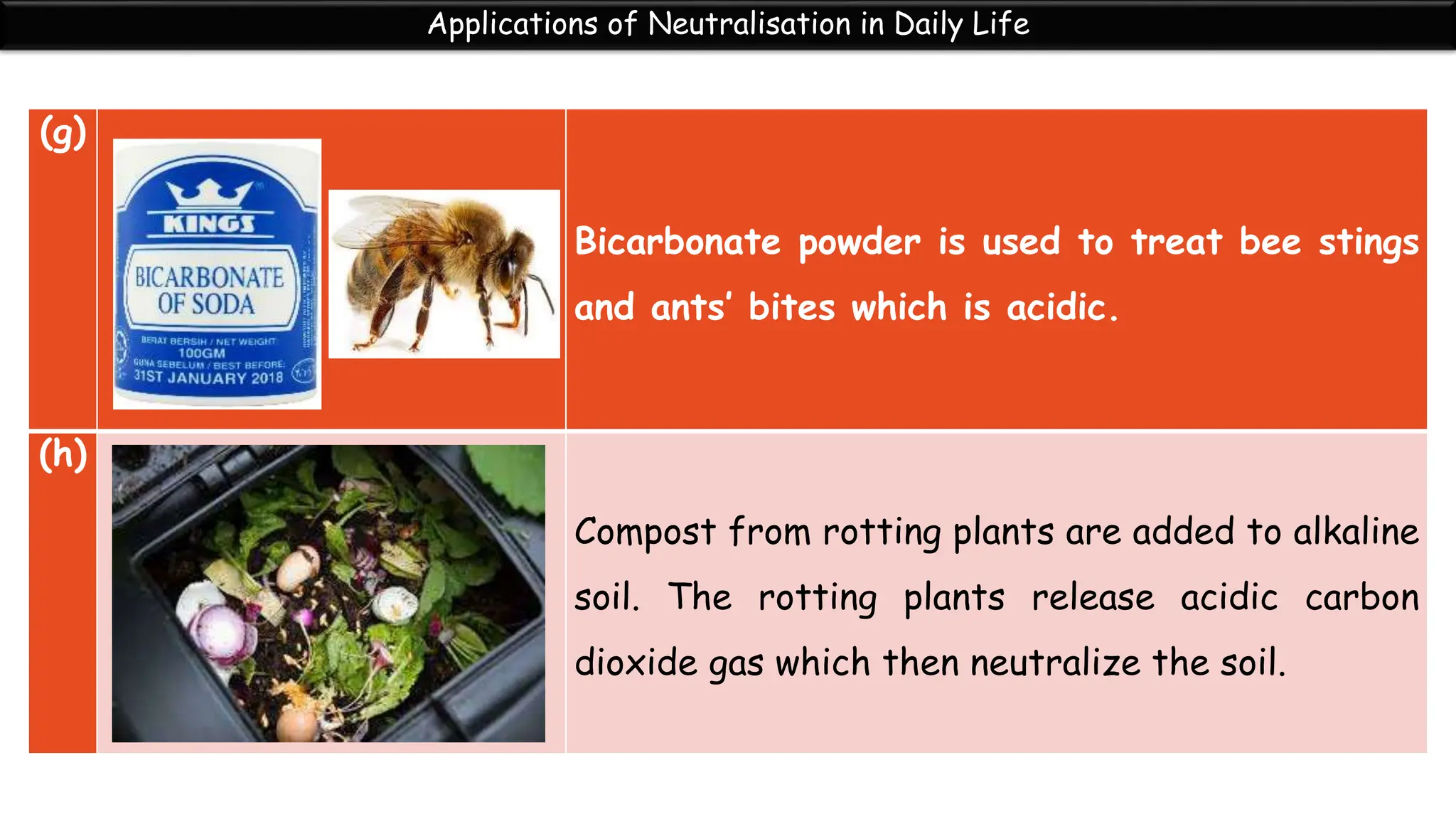
Neutralization is the reaction between an acid and a base that produces a salt and water. During neutralization, the hydrogen ions from the acid react with the hydroxide ions from the base. Titration is used to determine the endpoint of neutralization by adding small amounts of acid or base until the solution is neutral with a pH of 7. Neutralization has many applications in daily life, such as using toothpaste to neutralize acid in the mouth, hair conditioner to neutralize alkaline shampoo, and vinegar or baking soda to treat bee stings and insect bites.