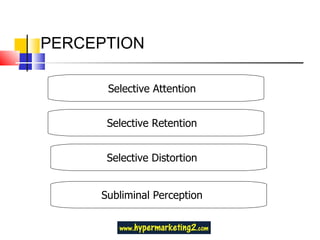
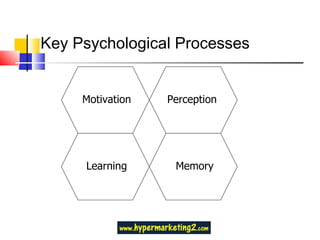
This document contains questions and answers about consumer behavior concepts. It discusses key topics like consumer behaviourism being the study of how people select, buy, use and dispose of products. It also addresses influences on consumer behavior like cultural, social and personal factors. Other concepts covered include perception, motivation theories, subcultures, memory processes, and stages of the consumer buying process.