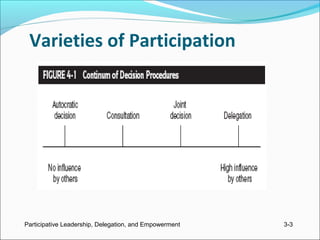
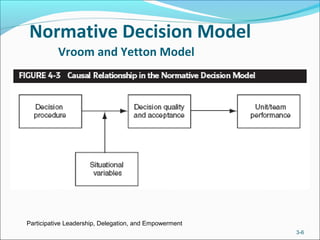
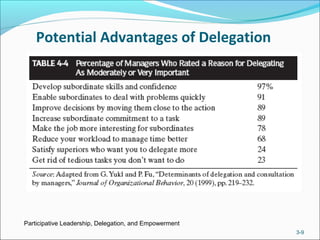
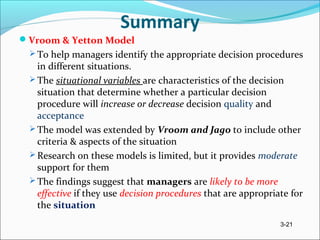
The document discusses participative leadership, delegation, and empowerment. It describes different forms of participation including revising decisions jointly, asking for suggestions, and delegating decisions. Participative leadership can improve decision quality and increase acceptance. Research on its effects is inconclusive due to inconsistent results. Delegation assigns new responsibilities and authority to subordinates, benefiting decisions and motivation but requiring manager confidence. Empowerment involves meaningful work, self-efficacy, and influence, and leaders can affect it through participation and delegation.