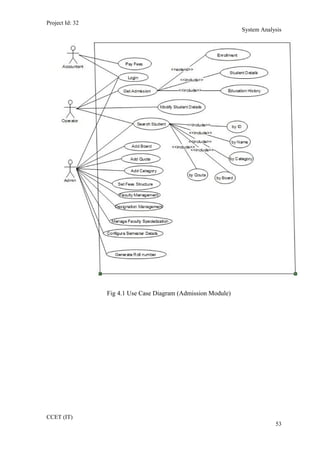
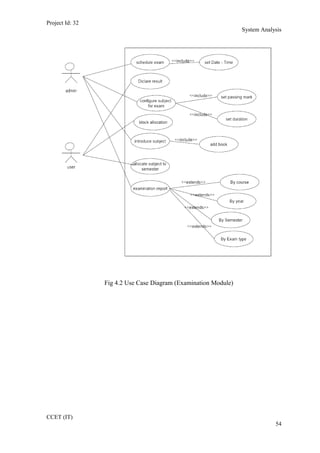
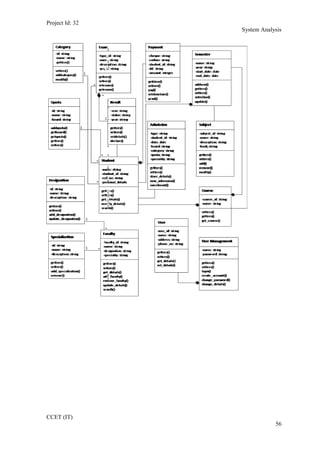
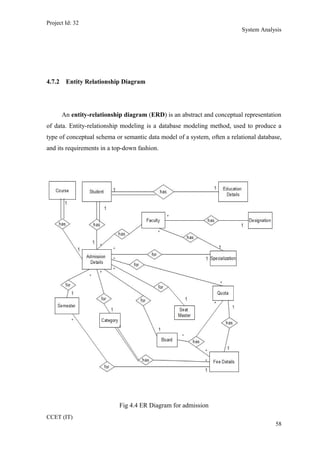
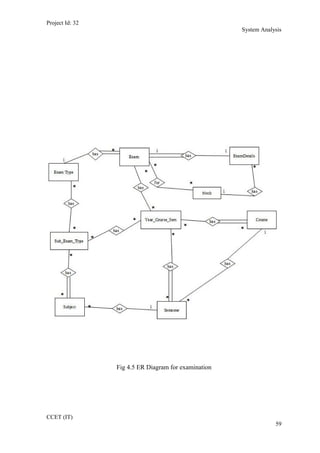
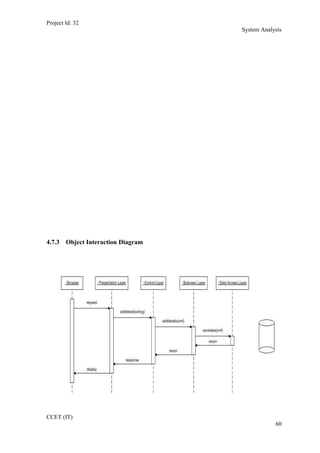
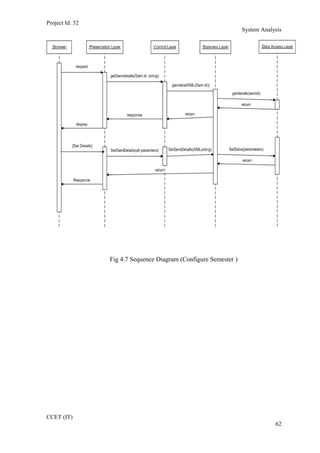
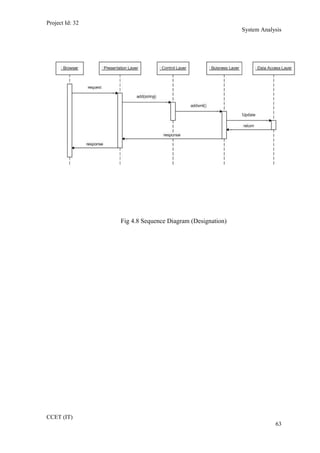
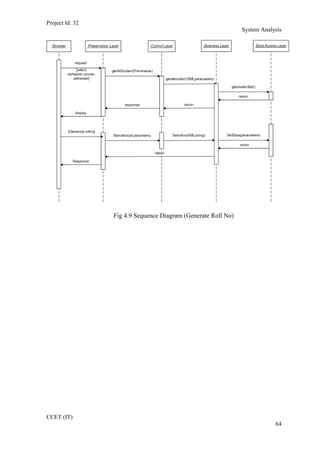
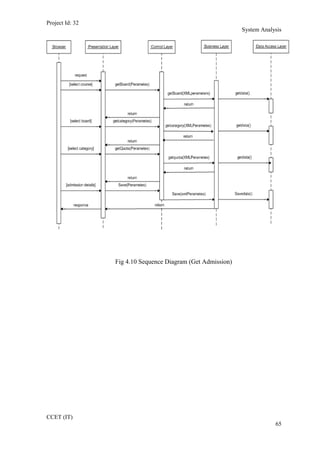
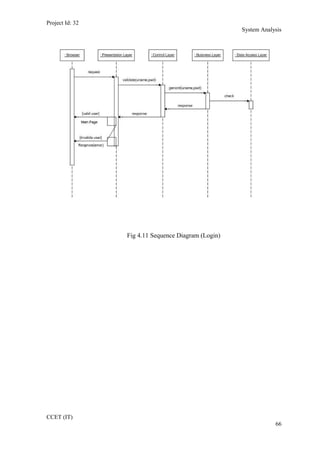
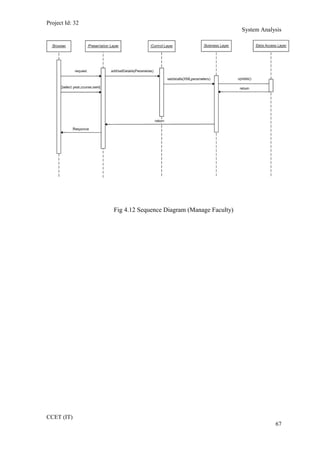
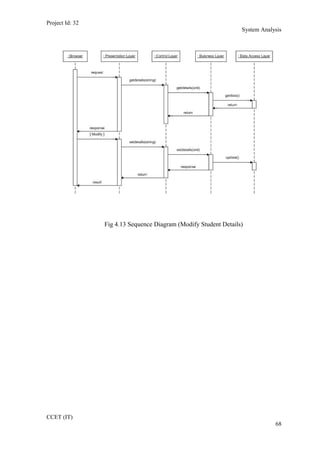
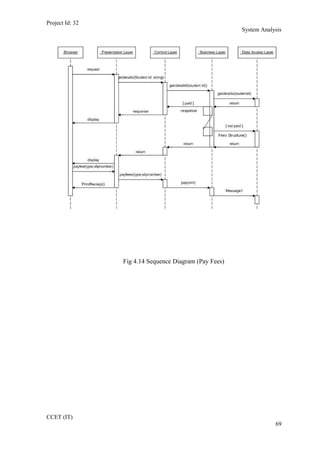
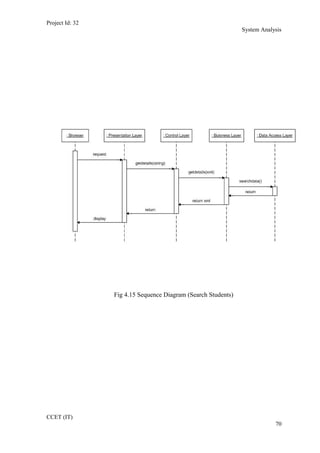
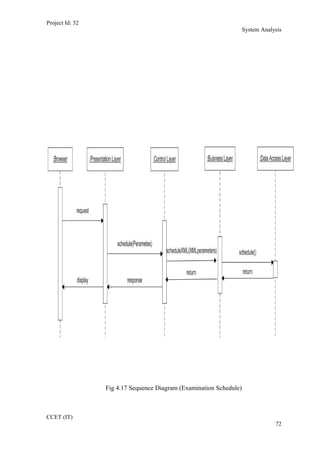
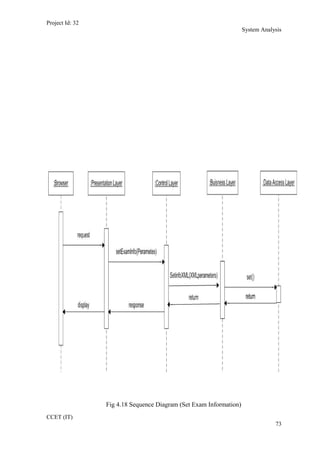
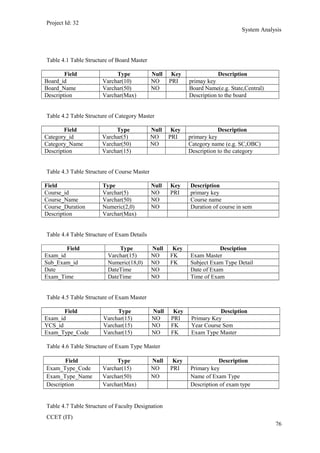
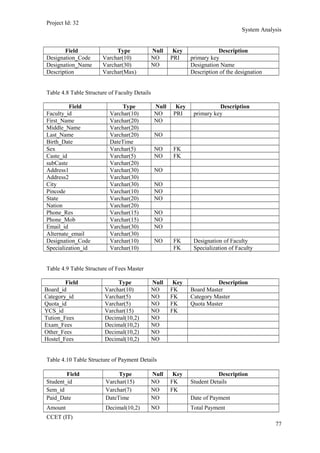
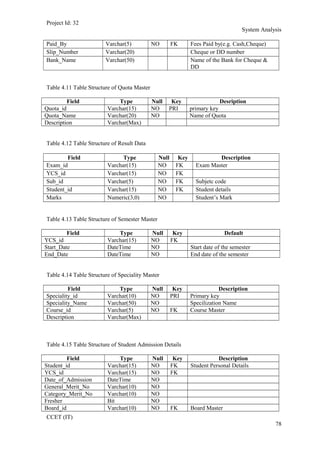
The current student management system requires physical paperwork submission and interaction between students and the academy management department. The new proposed system aims to automate this process and make it online. It will allow students and administrators to access and manage student records, enrollments, fees payments, exams and more through a centralized online portal. The document outlines 20 user requirements for the key functions of the new proposed student management system, including requirements for login, fees payment, admission, student record modification and more. It describes the inputs, outputs, main and alternate flows for each requirement.