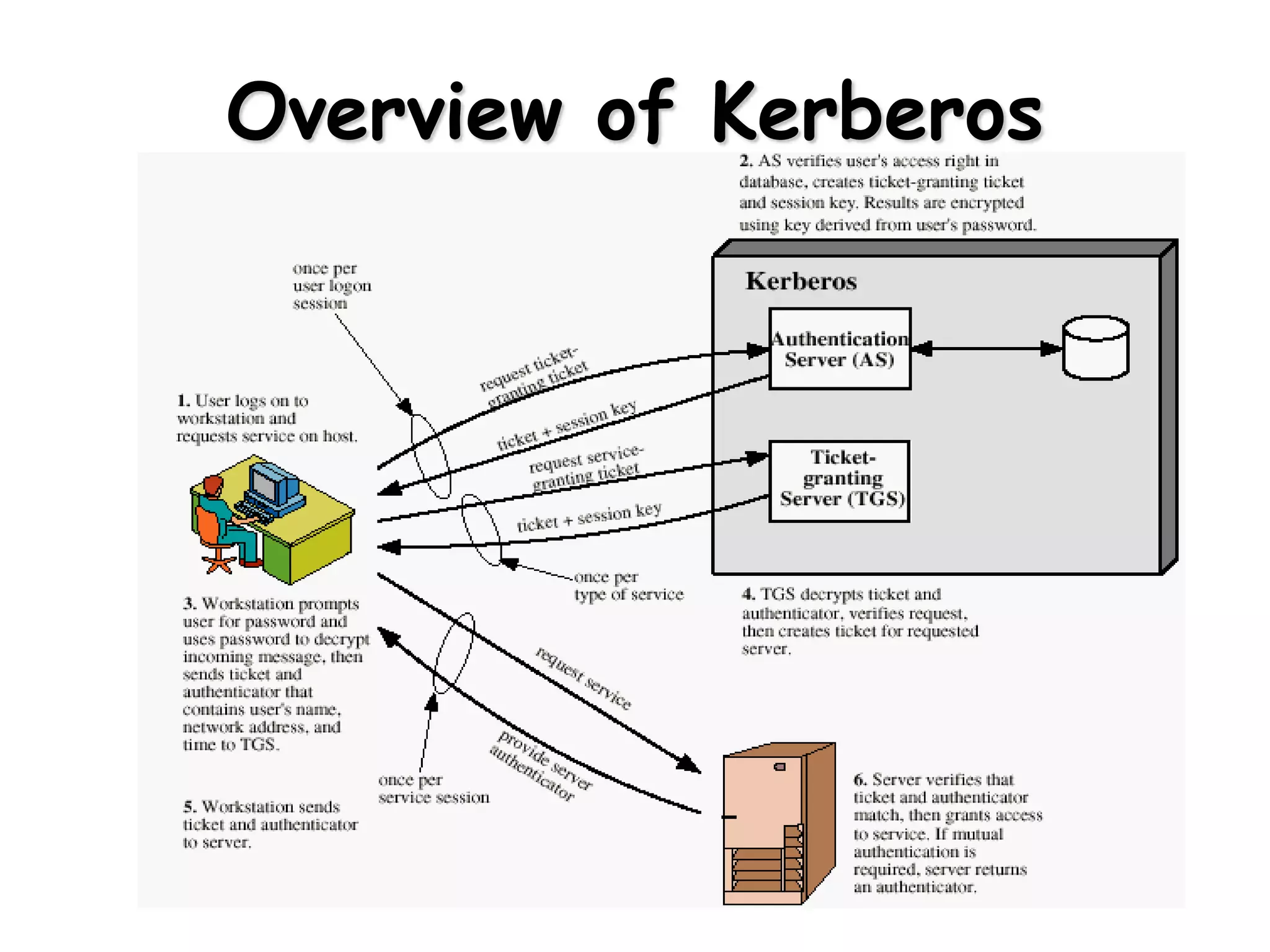
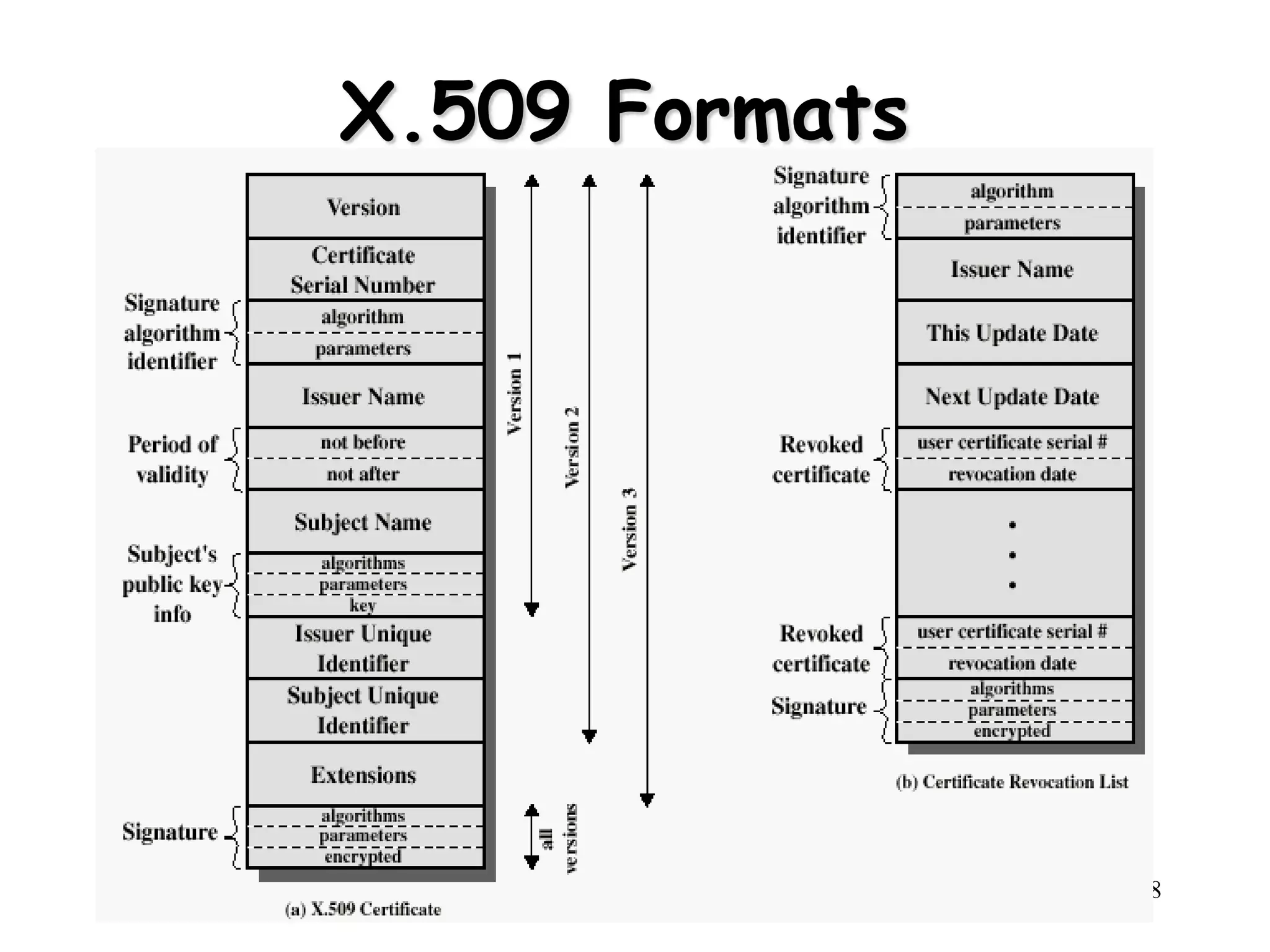
1) The document discusses authentication methods including Kerberos and X.509. Kerberos provides centralized authentication using encryption keys without public key encryption. X.509 uses public key encryption and digital signatures to authenticate users through certificates signed by certificate authorities.
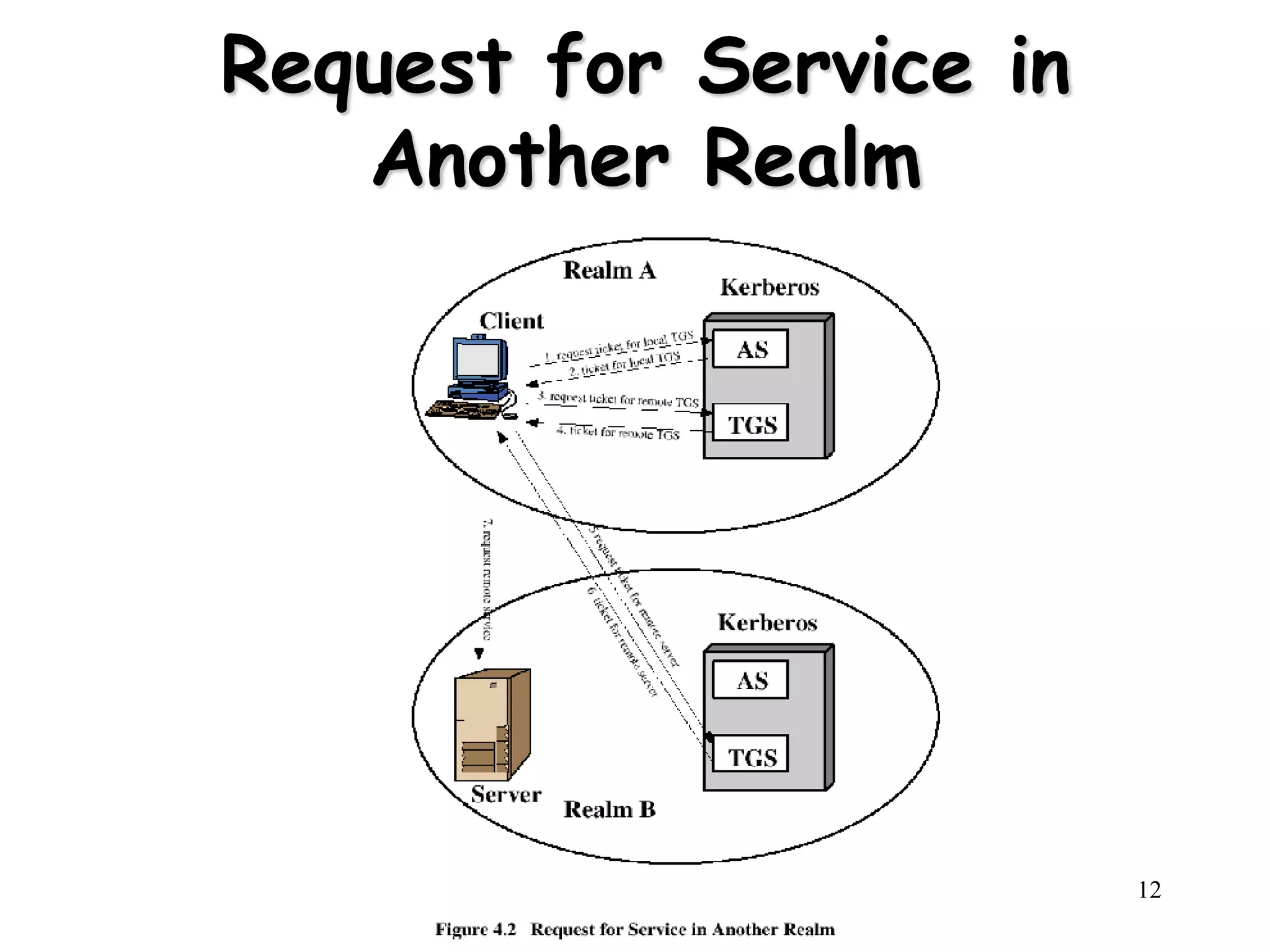
2) Kerberos versions 4 and 5 are described, with version 5 allowing inter-realm authentication. Kerberos uses tickets and authenticators to allow clients access to services. X.509 certificates contain a user's public key and are signed by a certificate authority.
3) Recommended reading on Kerberos and authentication includes websites on the Kerberos protocol and papers describing its evolution.







![Henric Johnson 8
A Simple Authentication
Dialogue
(1) C AS: IDc || Pc || IDv
(2) AS C: Ticket
(3) C V: IDc || Ticket
Ticket = EKv[IDc || Pc || IDv]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter4-200601100655/75/Chapter-4-8-2048.jpg)

![Henric Johnson 10
Version 4 Authentication Dialogue
Authentication Service Exhange: To obtain Ticket-Granting Ticket
(1) C AS: IDc || IDtgs ||TS1
(2) AS C: EKc [Kc,tgs|| IDtgs || TS2 || Lifetime2 || Tickettgs]
Ticket-Granting Service Echange: To obtain Service-Granting Ticket
(3) C TGS: IDv ||Tickettgs ||Authenticatorc
(4) TGS C: EKc [Kc,¨v|| IDv || TS4 || Ticketv]
Client/Server Authentication Exhange: To Obtain Service
(5) C V: Ticketv || Authenticatorc
(6) V C: EKc,v[TS5 +1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter4-200601100655/75/Chapter-4-10-2048.jpg)