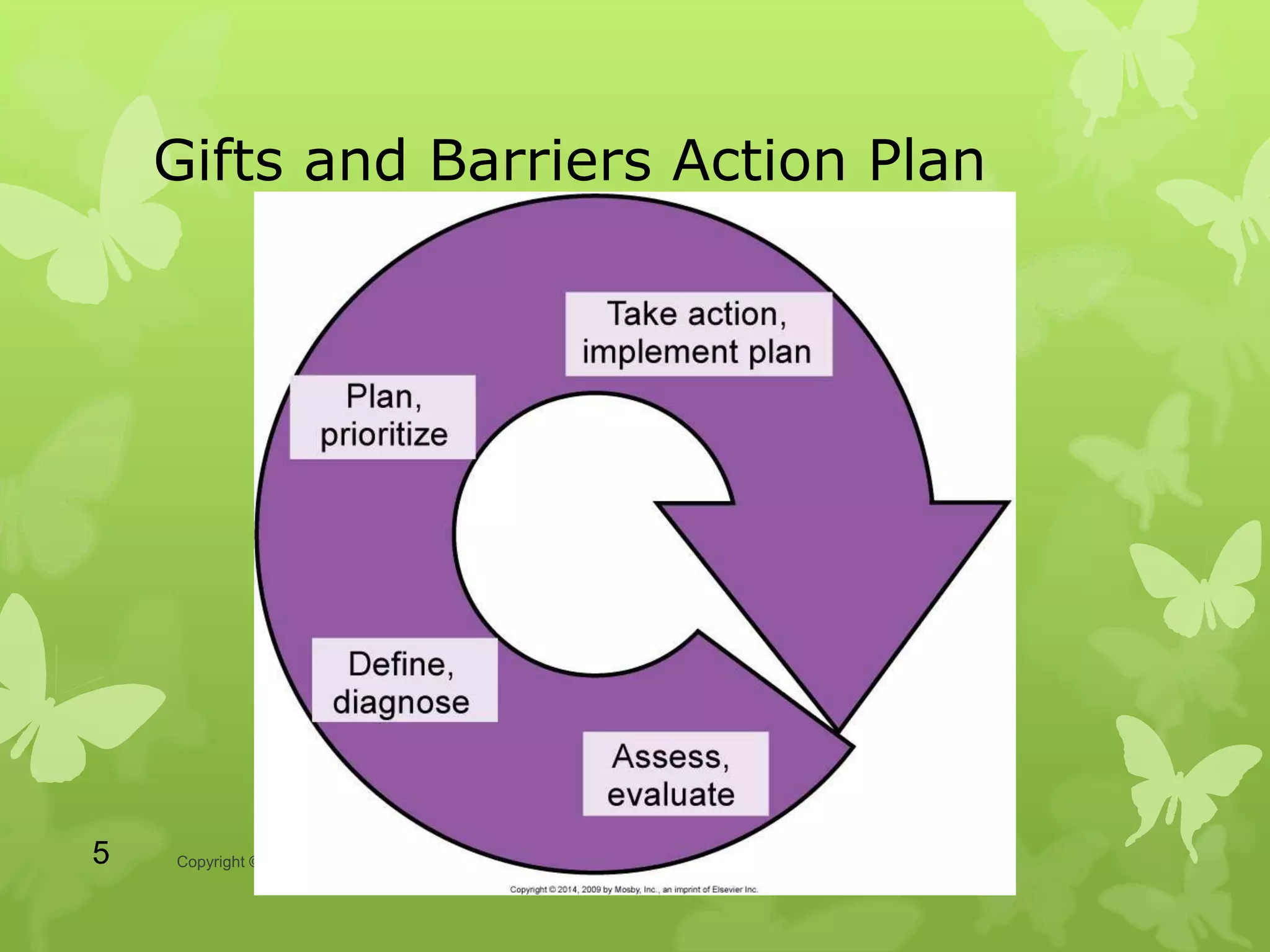
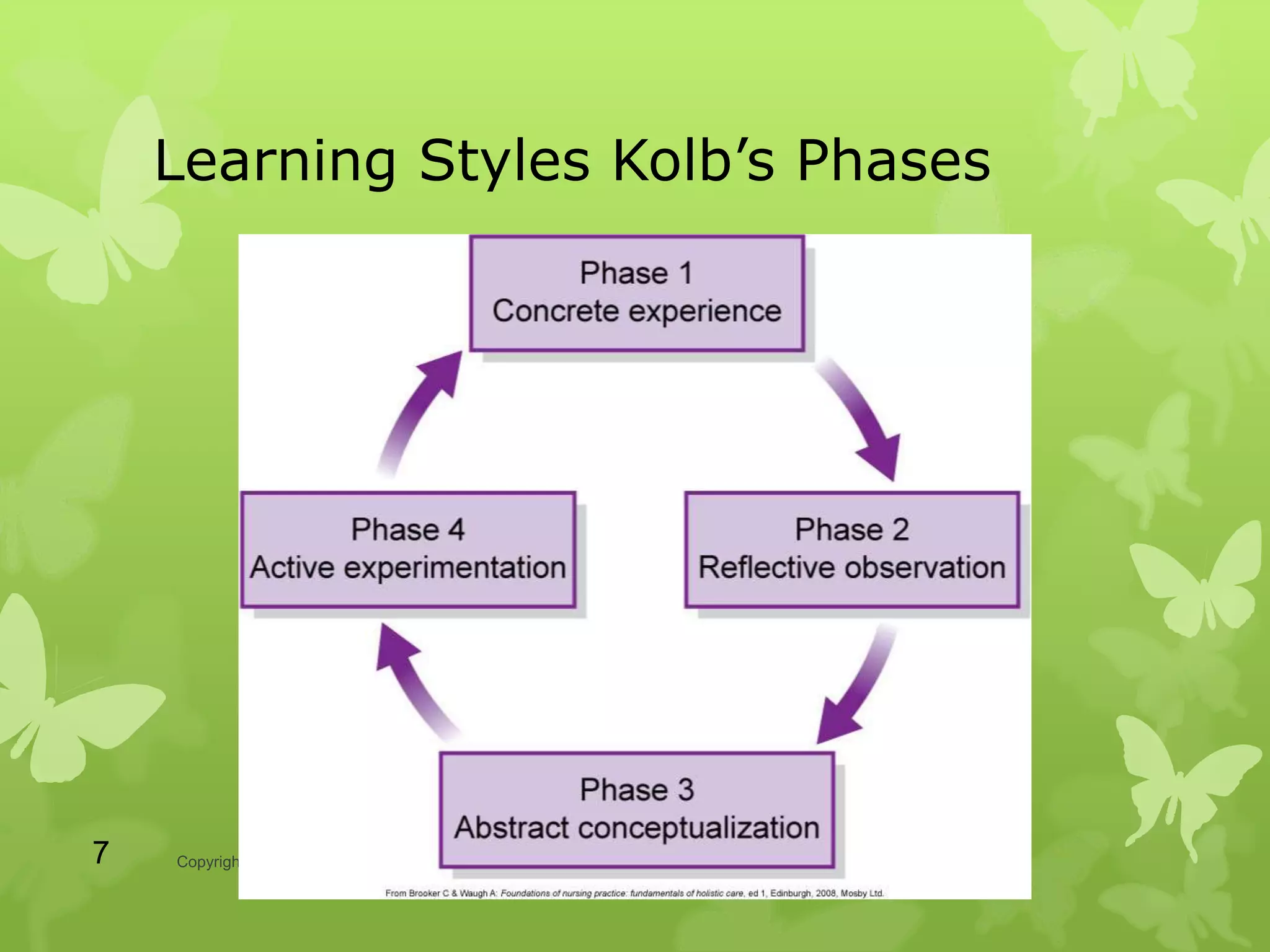
The document discusses various tools and strategies for managing time and designing success, including identifying positive and negative behaviors, learning styles, personality traits, self-directed learning, locus of control, self-talk, stress management, and time management. Specific models and techniques are presented, such as Kolb's learning styles, Myers-Briggs personality types, managing stress through identifying cognitive distortions, and choosing effective coping mechanisms.