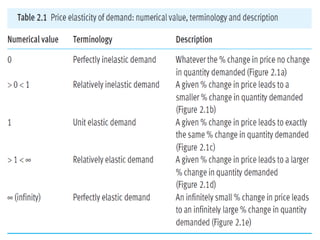
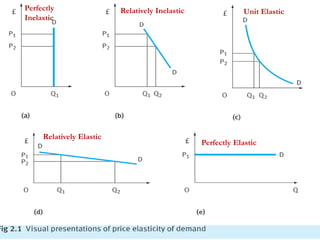
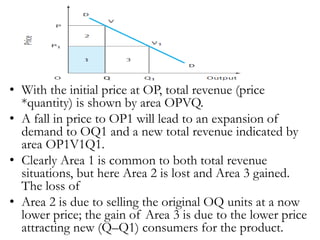
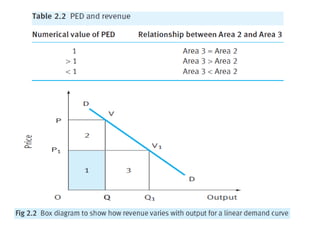
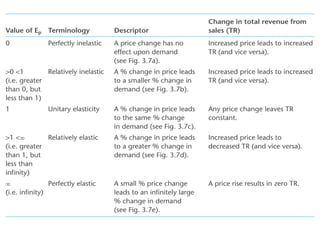
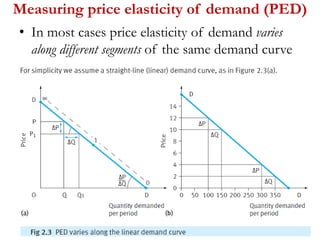
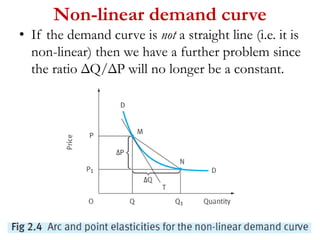
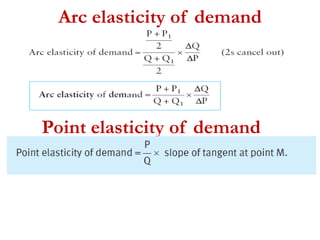
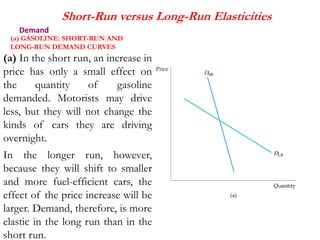
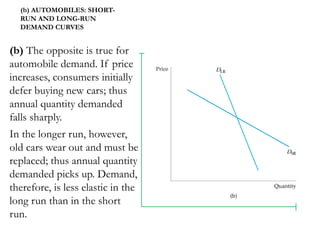
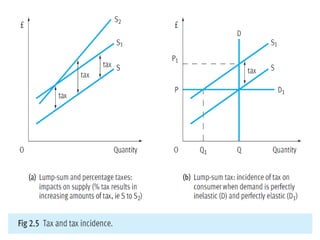
1) Price elasticity of demand (PED) measures the responsiveness of demand to a change in price. It is calculated as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price. PED can be perfectly inelastic, unit elastic, or perfectly elastic depending on available substitutes and importance of the product.
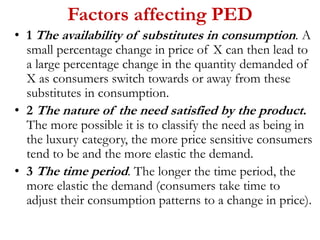
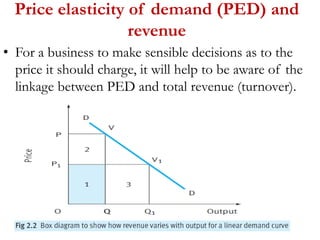
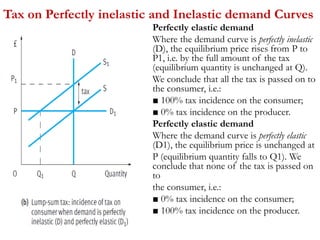
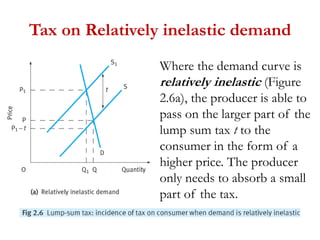
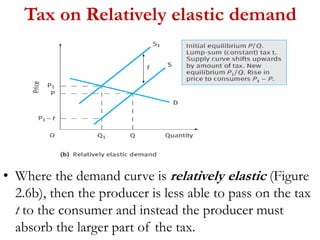
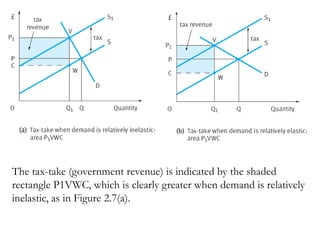
2) Factors like substitutes, luxury status of the product, time period, and income spent affect PED. Changes in price impact total revenue differently depending on whether demand is elastic or inelastic. Governments consider PED when implementing taxes as it determines tax incidence on consumers and producers.
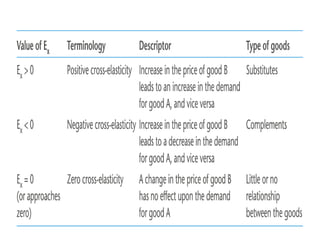
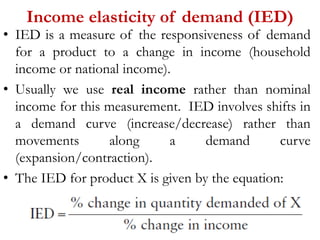
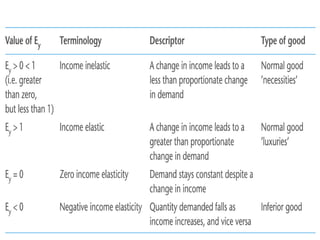
3) Other elasticities include cross elasticity of demand and income elasticity of demand which