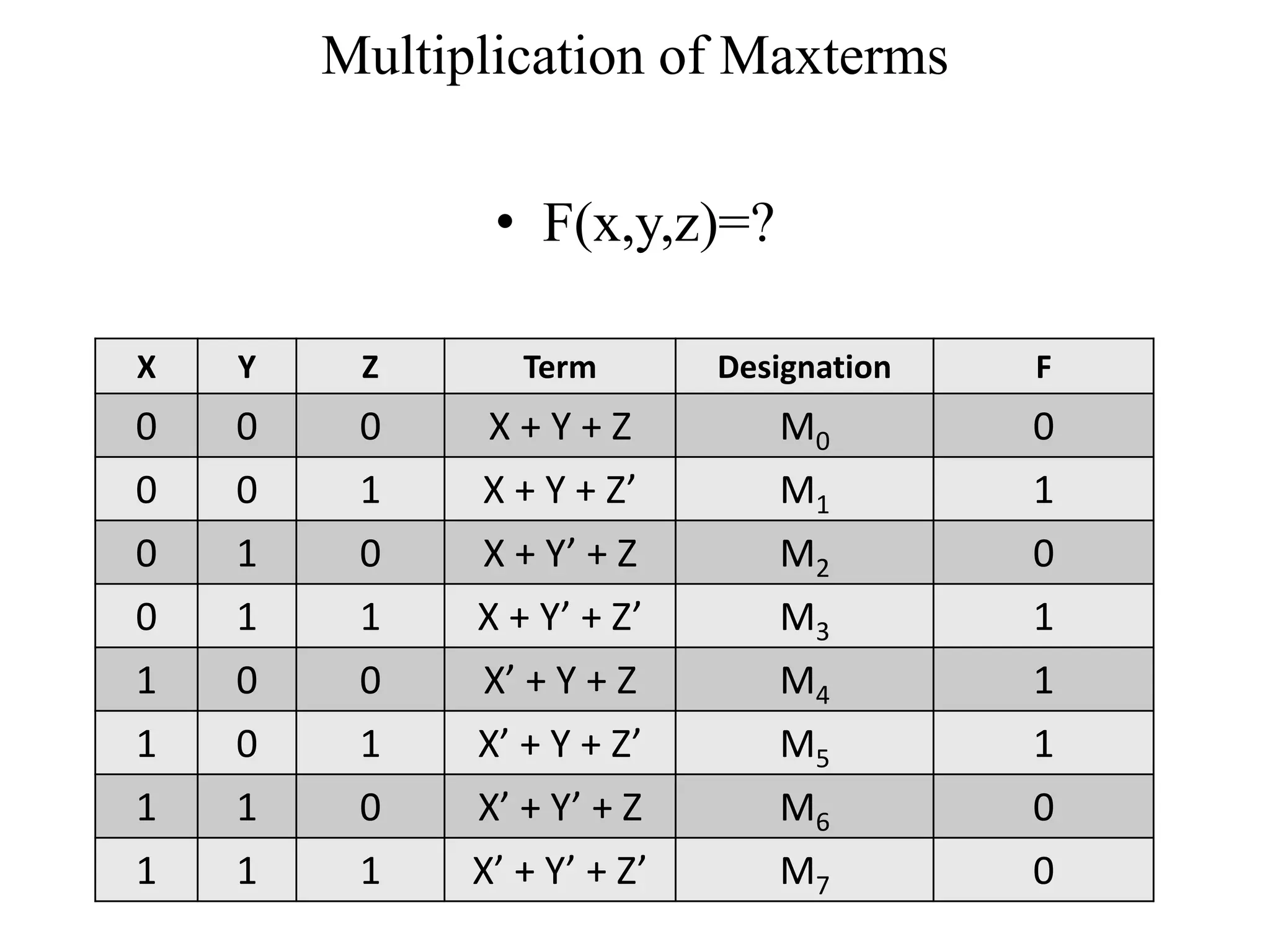
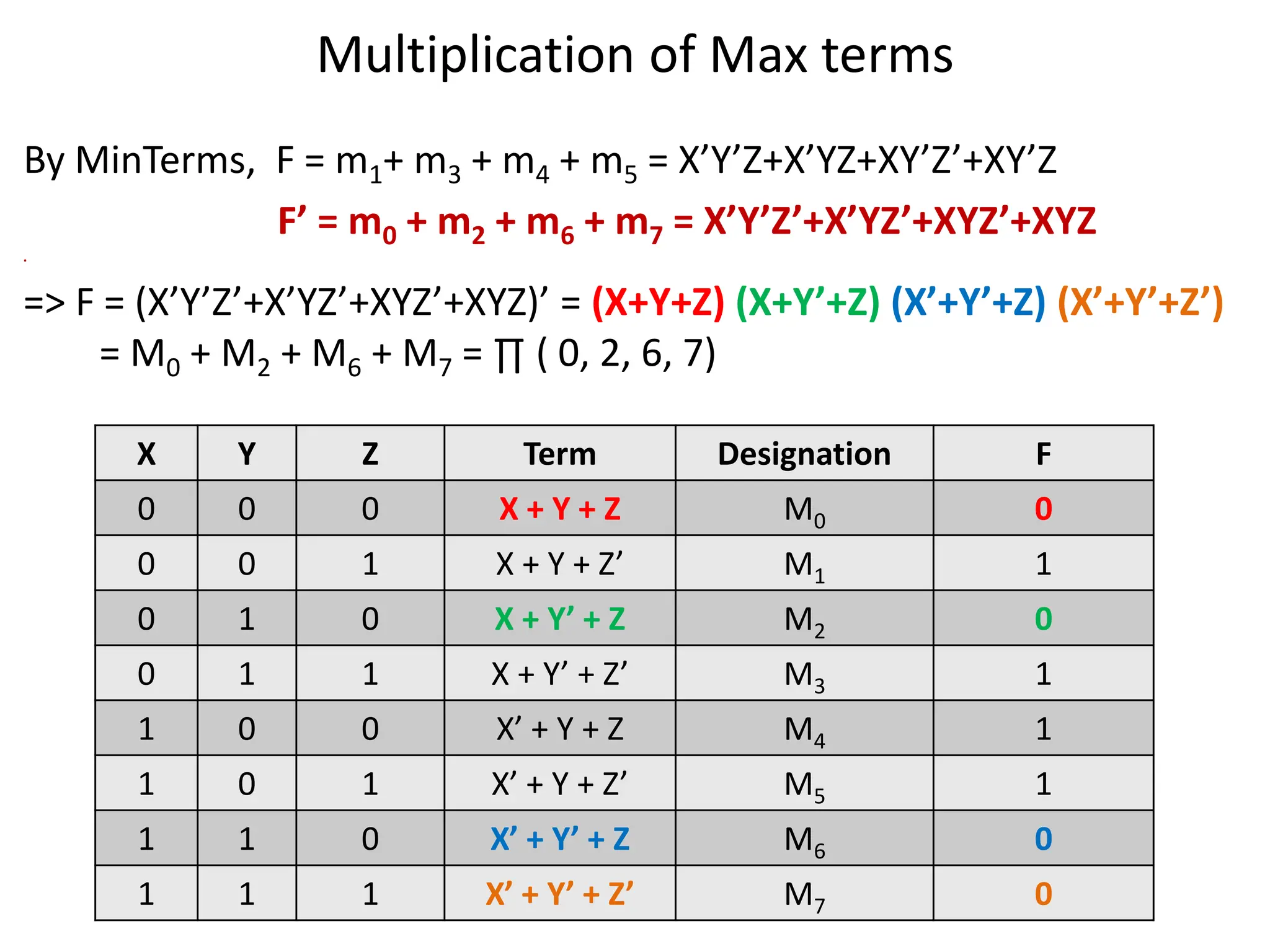
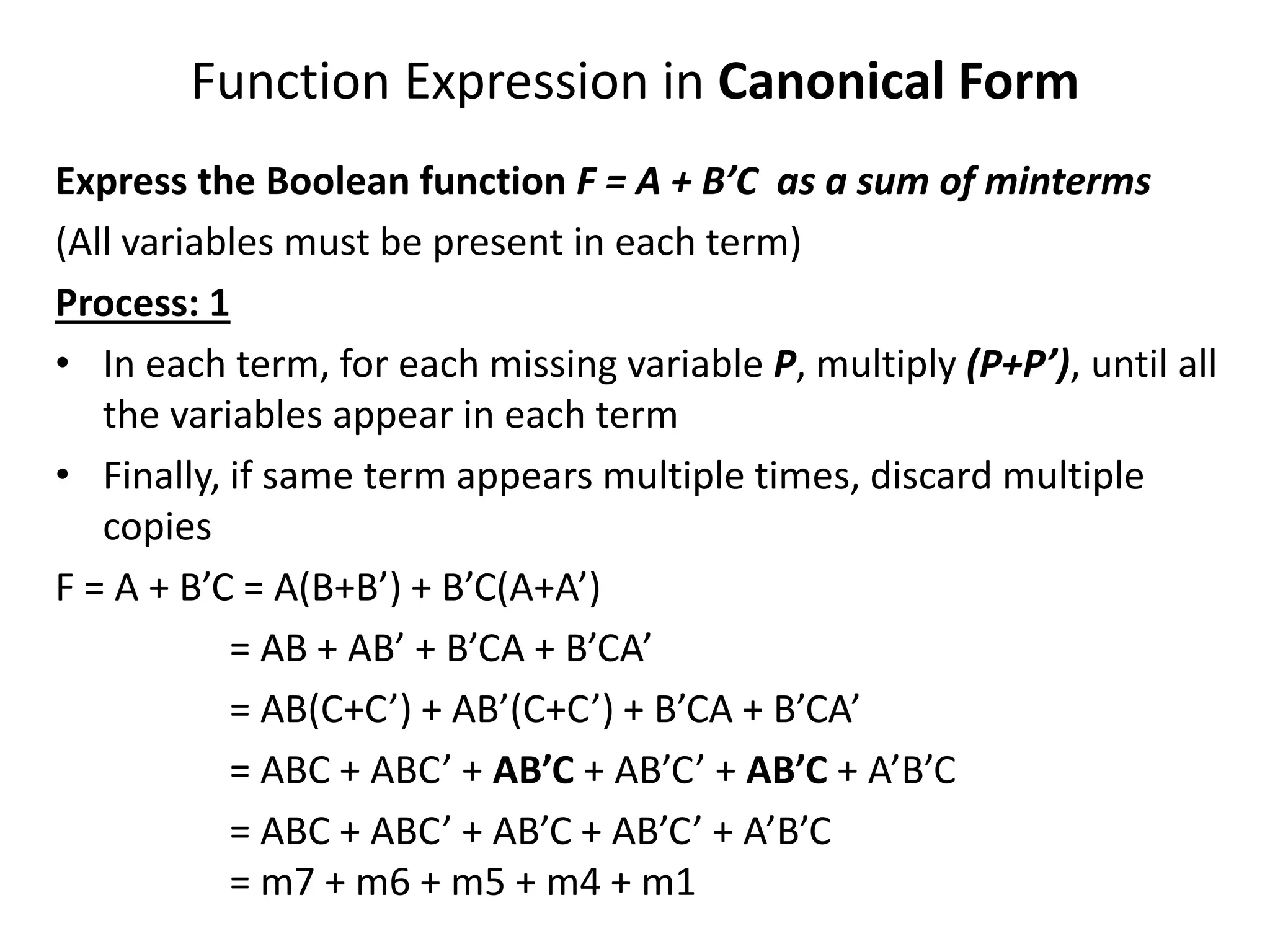
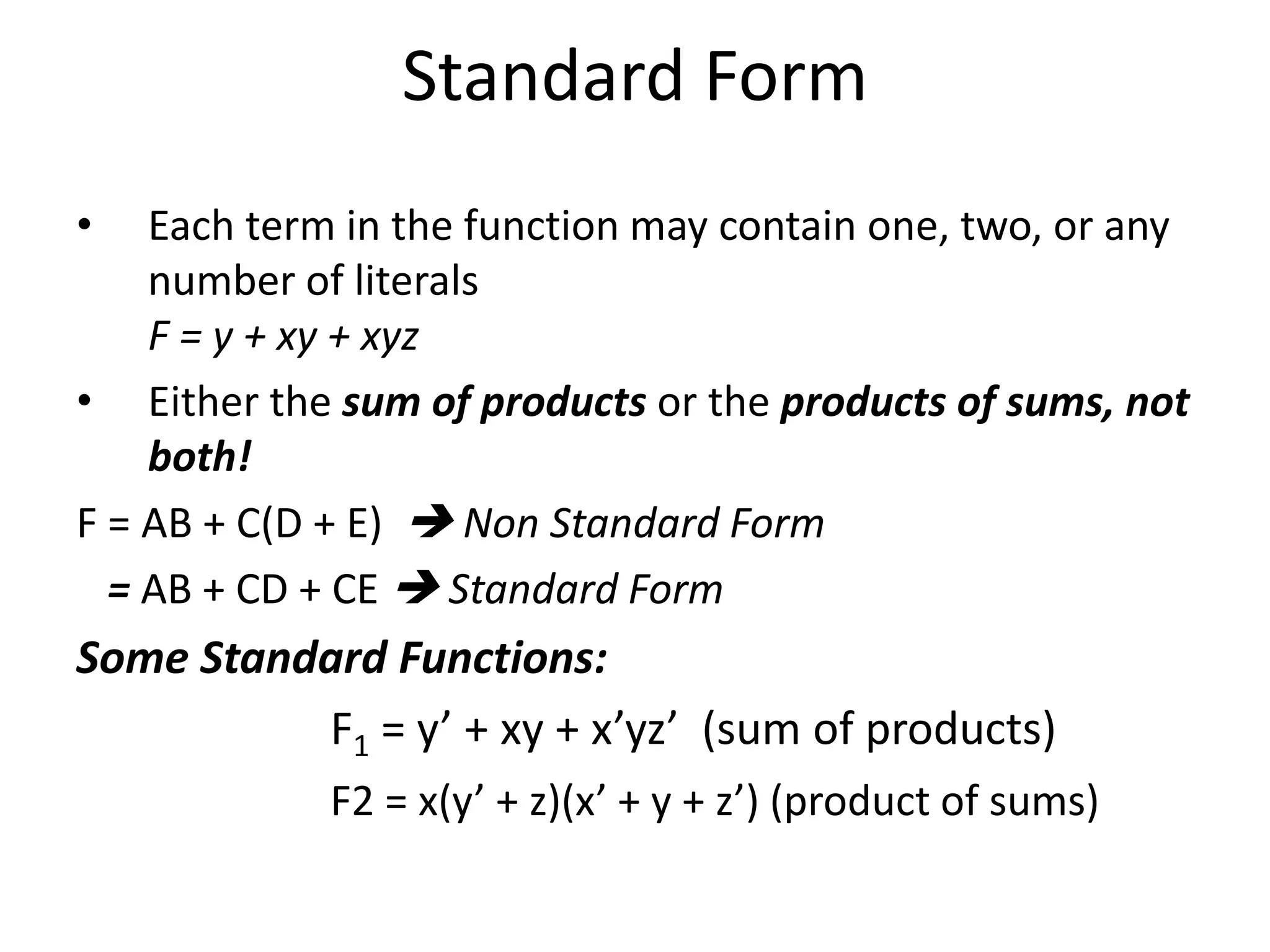
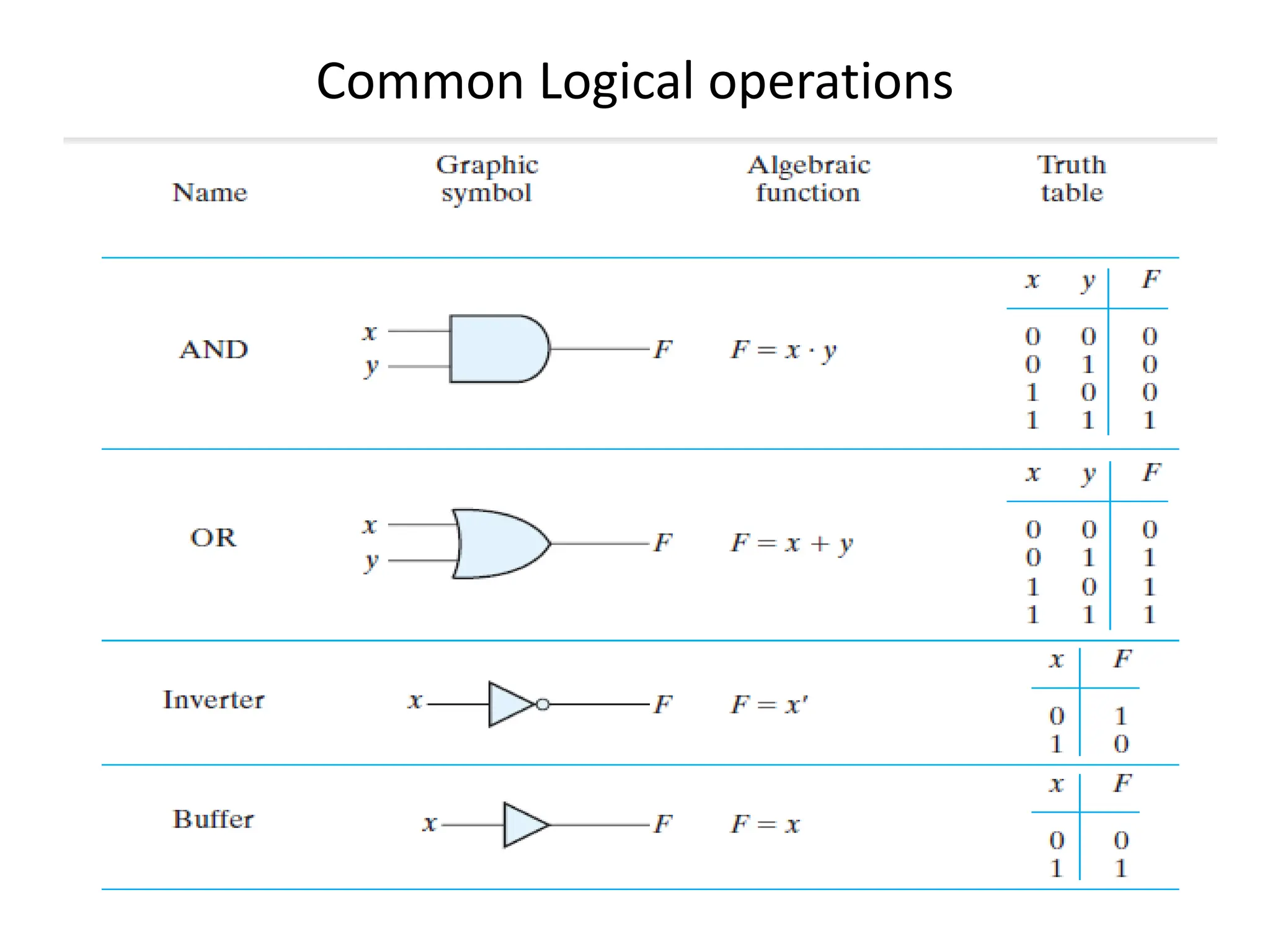
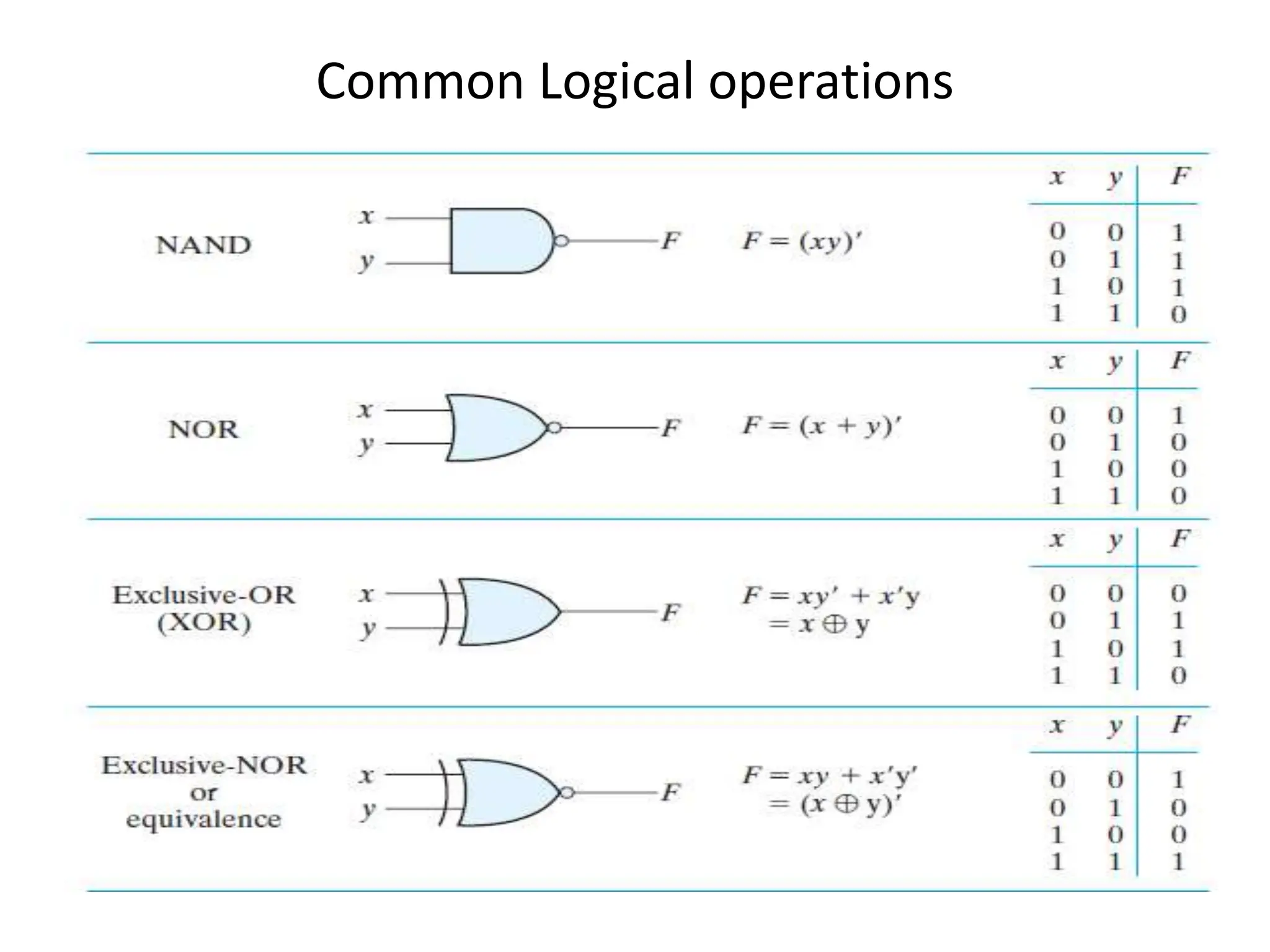
Chapter 2 discusses Boolean algebra and logic gates, focusing on expressing Boolean functions algebraically from truth tables using minterms and maxterms. It outlines the processes for converting functions into canonical forms, including summation and multiplication of minterms and maxterms, along with various Boolean function expressions. The chapter includes examples and standard forms to illustrate the concepts of Boolean functions.