(1) This document outlines the syllabus for CSC 450/550, an introductory computer networks course. It provides contact information for the instructor and discusses course objectives, topics, and evaluation methods.
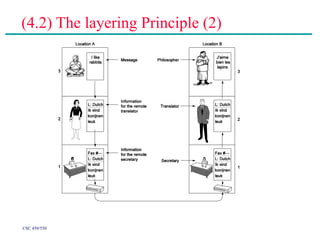
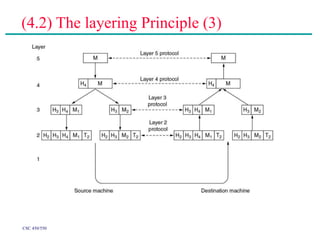
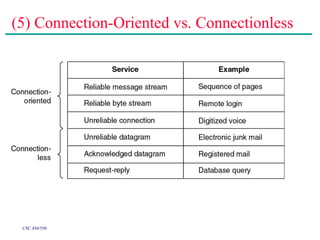
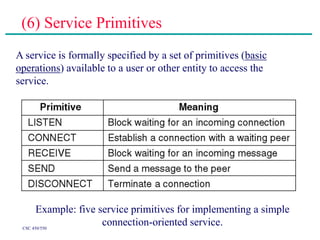
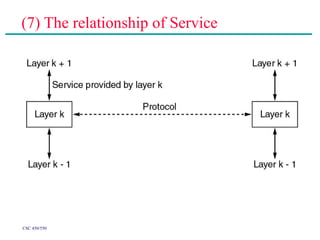
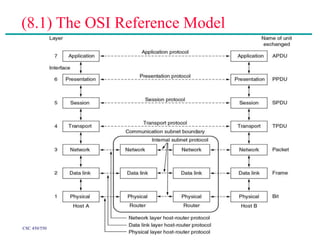
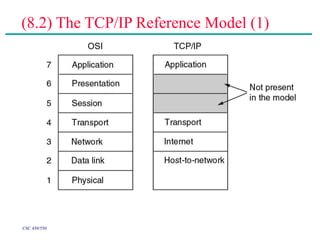
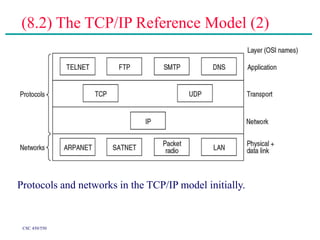
(2) Major topics that will be covered include an overview of network layers and protocols, such as the physical layer, data link layer, medium access control layer, network layer, and transport layer. Reference models like OSI and TCP/IP will also be examined.
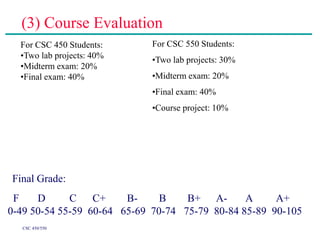
(3) Students will be evaluated based on lab projects, exams, and an optional course project. Course objectives are to understand network principles, learn protocol implementation, and grasp basic network research methods (for CSC 550 students).