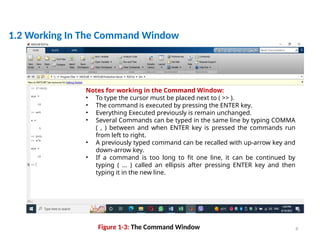
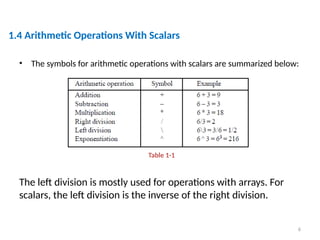
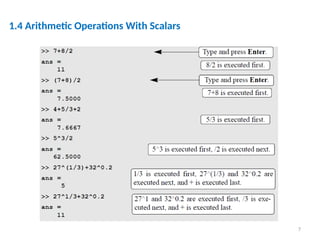
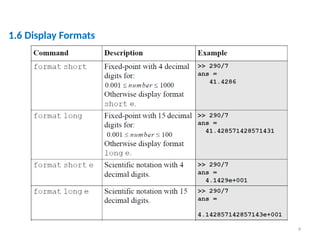
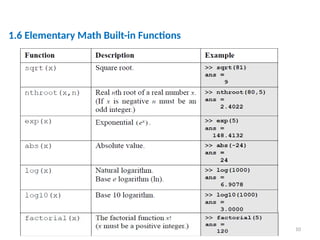
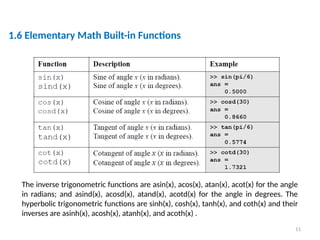
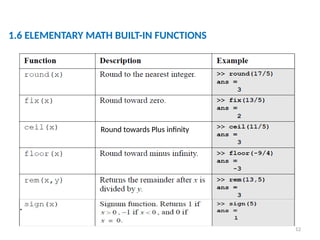
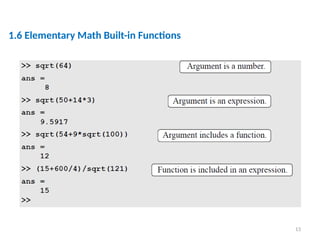
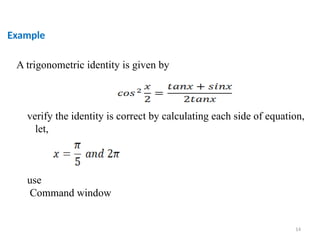
The document is a tutorial on using MATLAB, covering the command window, variable definitions, and arithmetic operations. It includes details on executing commands, recalling previous commands, and a list of reserved keywords. Additionally, it describes useful commands and elementary math built-in functions within MATLAB.