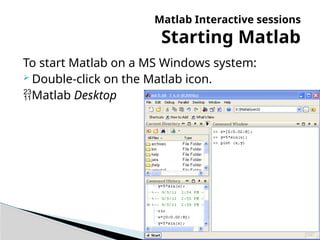
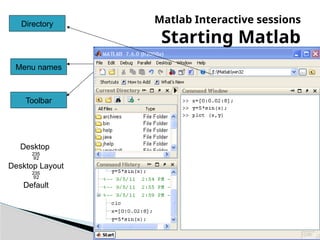
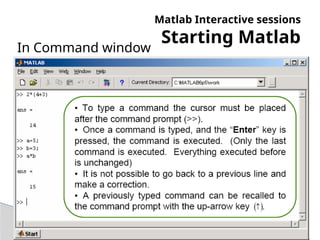
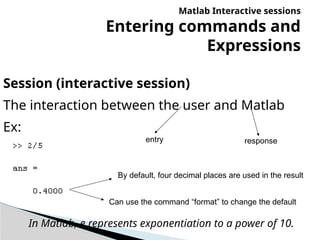
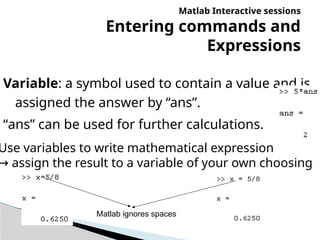
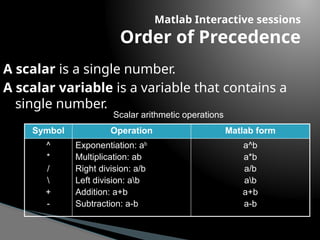
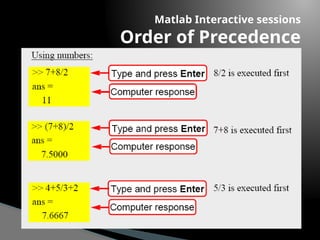
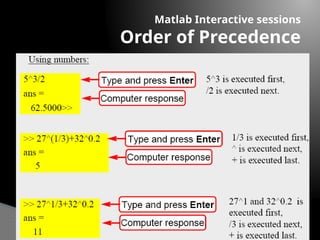
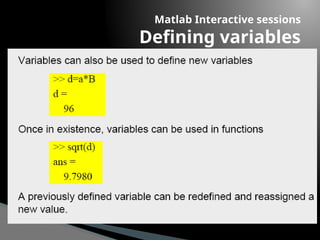
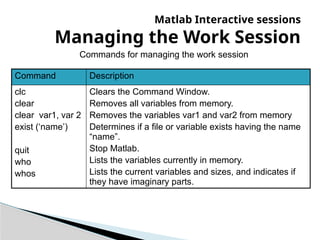
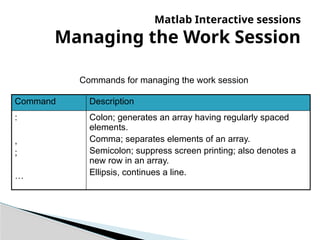
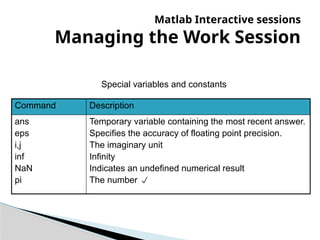
The document provides an introduction to MATLAB, detailing how to start the software, the purpose of its interactive sessions, and basic commands for managing variables and performing arithmetic operations. It covers the structure of commands, the order of precedence in calculations, and how to manipulate arrays, including defining variables and utilizing built-in functions. Additionally, it includes practice problems to apply the learned concepts.

















![Practice
Problem 2
Use Matlab to determine how many elements
are in the array [sin(-pi/2):0.05:Cos(0)]. Use
Matlab to:
1. Determine the 10th
element.
2. Create a new array taking the values from the
4th
to 8th
element.
3. Calculate sum of the first three elements of the
new array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter1matlab-240924112151-512436f4/85/Chapter-1-_-Introduction-to-Matlab-pptx-41-320.jpg)

