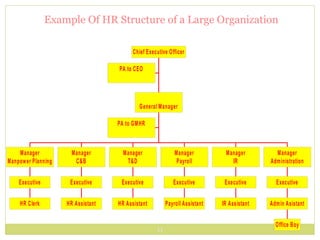
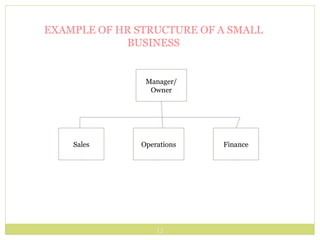
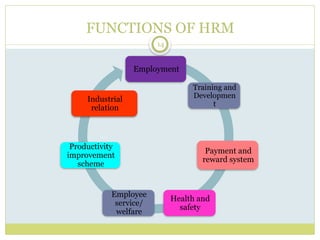
Human Resource Management (HRM) involves the development and implementation of systems for attracting, developing, and retaining a high-performing workforce. It addresses the importance of managing employee needs, the complexity of recruitment, legalities, technological advancements, globalization, workforce diversity, and the distinct structures required for HRM in large versus small organizations. Effective HRM is essential for organizational performance and productivity, focusing on functions such as employment, training, safety, and employee welfare.