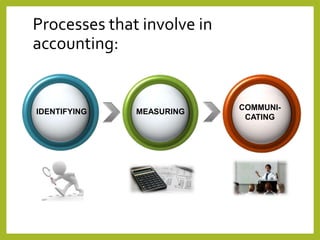
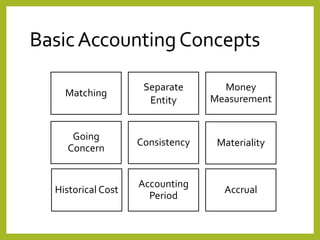
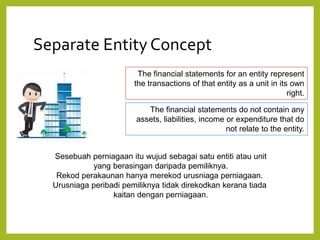
The document provides an overview of accounting concepts, including definitions of accounting and bookkeeping, the purpose and users of financial accounting, and the importance of accounting standards. It outlines basic accounting concepts such as the matching, separate entity, money measurement, going concern, accruals, consistency, materiality, historical cost, and accounting period concepts. The information aims to educate on how financial data is classified, recorded, and communicated for decision-making purposes.