The document discusses several key topics in economics:
1. It outlines the major branches of economics - macroeconomics which focuses on a nation's overall economy, and microeconomics which focuses on behavior in specific markets.
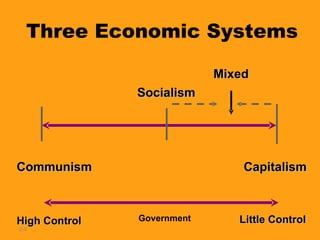
2. It describes different economic systems - capitalism with private ownership, socialism with some government ownership of utilities, and communism with government control of production.
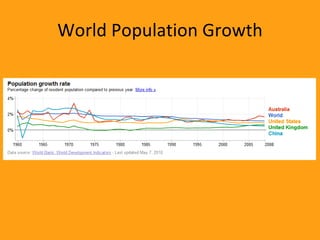
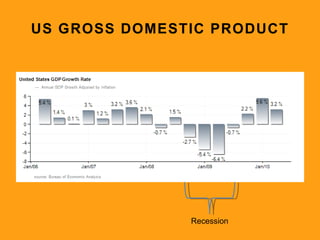
3. It explains that most countries now use mixed economic systems that combine aspects of free markets and government intervention. Gross domestic product and productivity are used to measure economic activity.