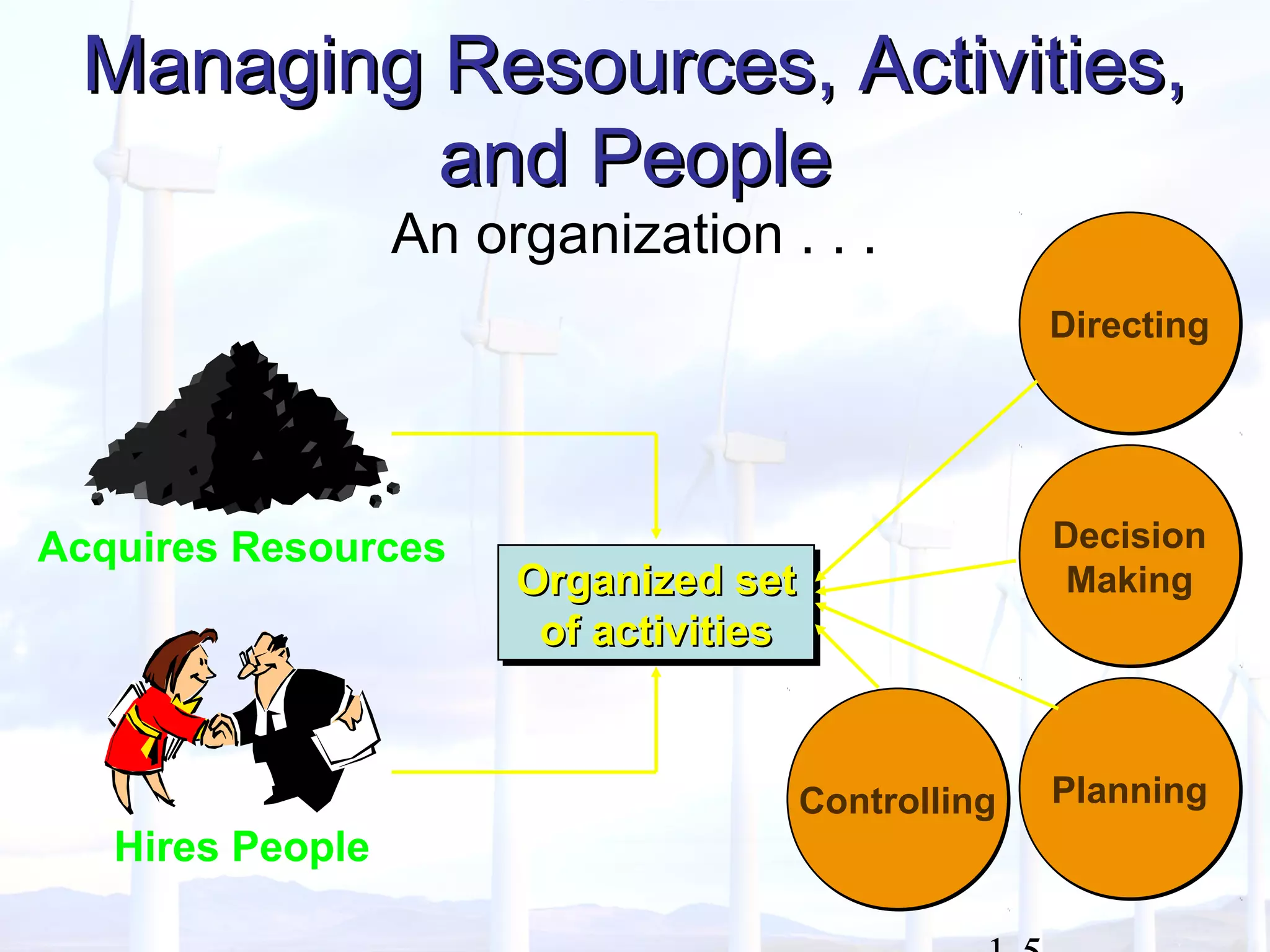
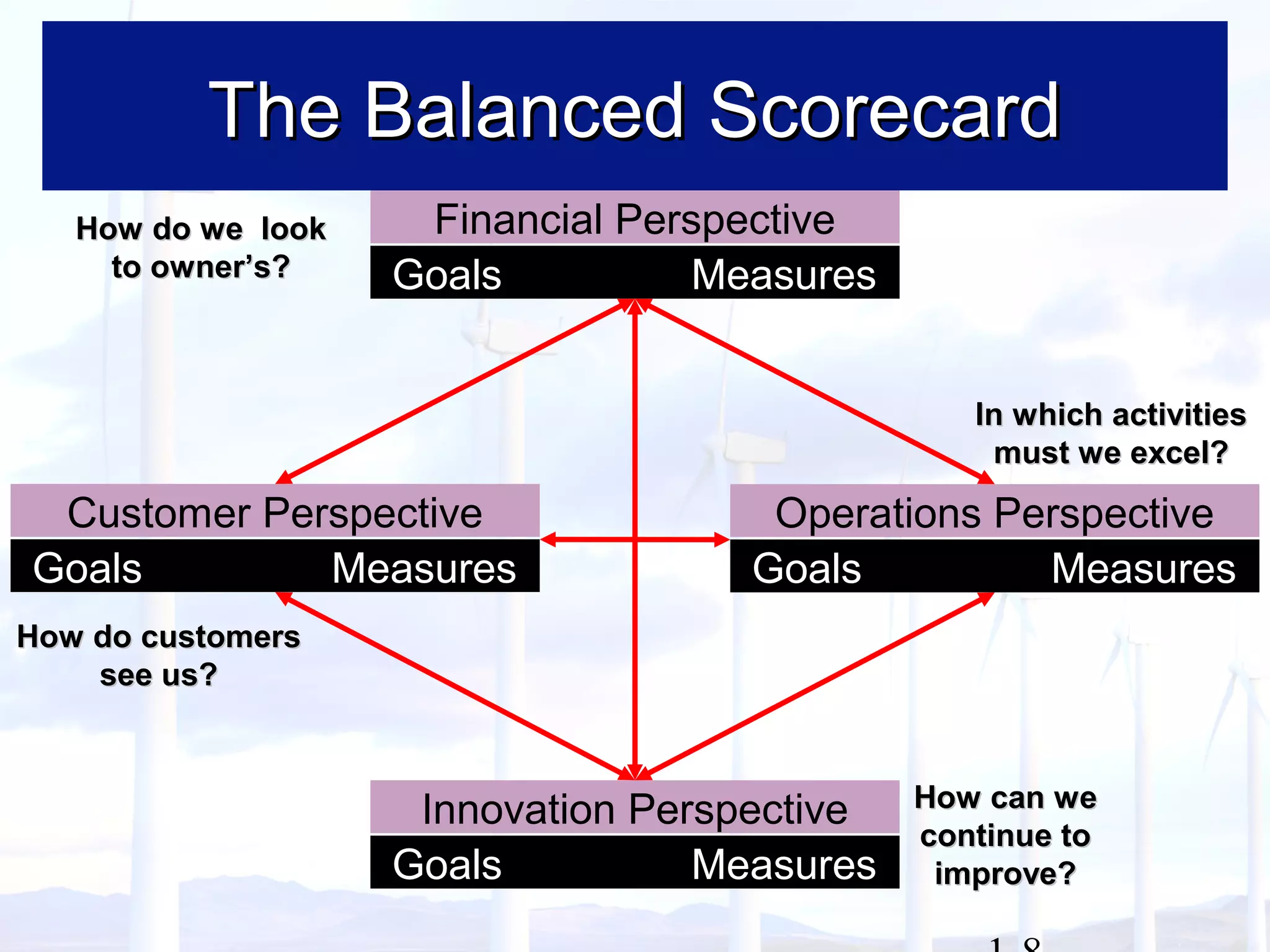
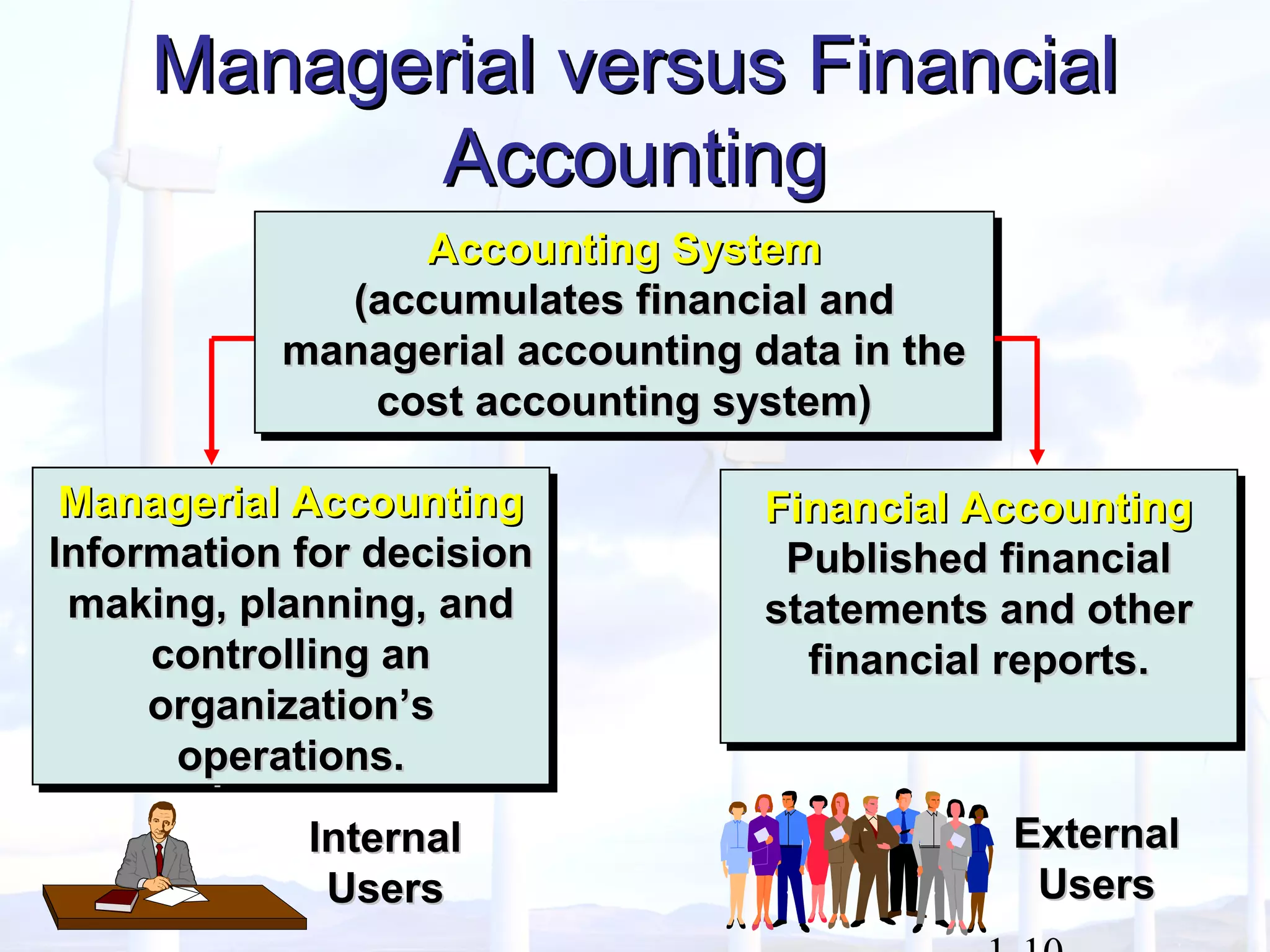
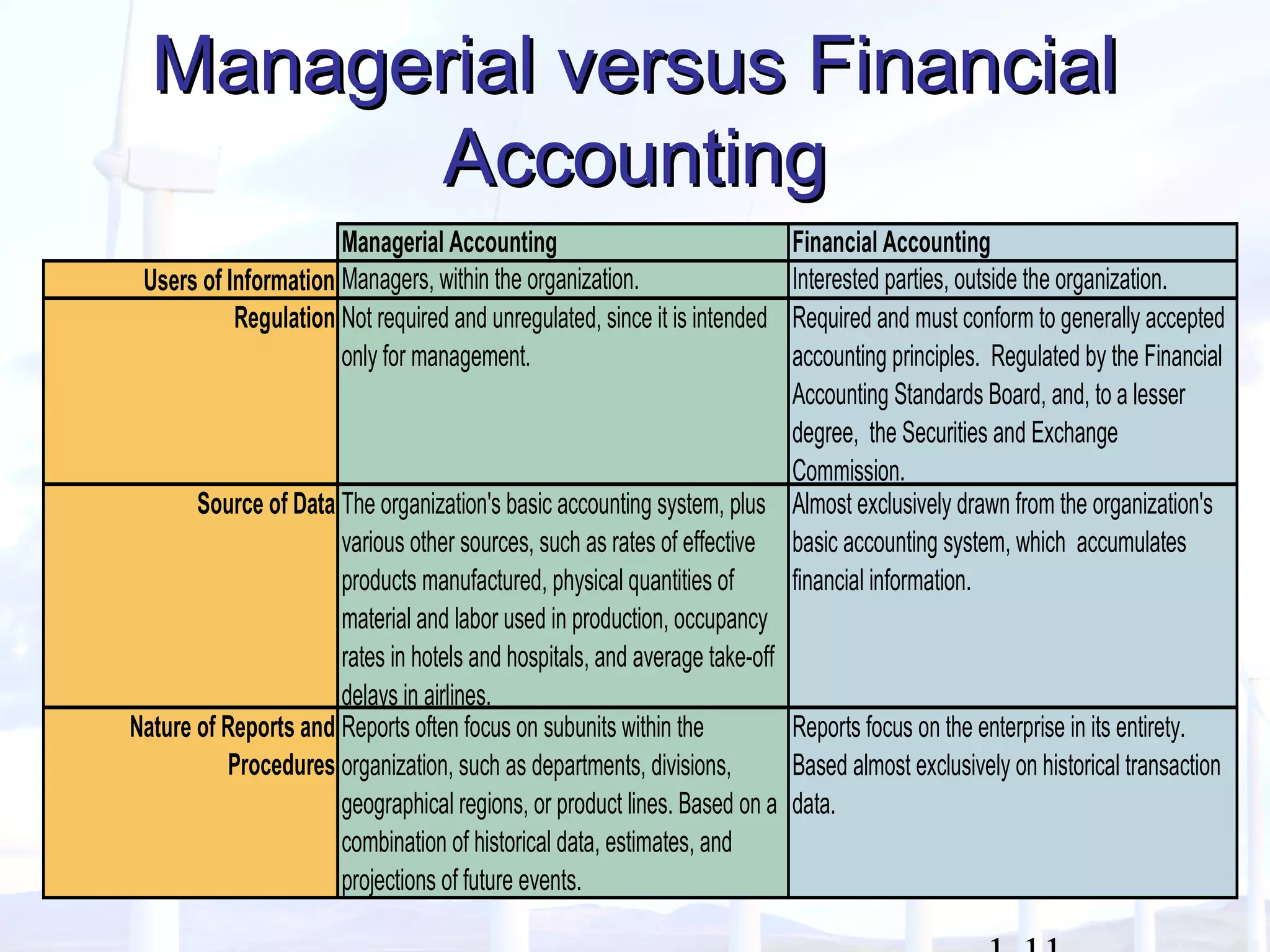
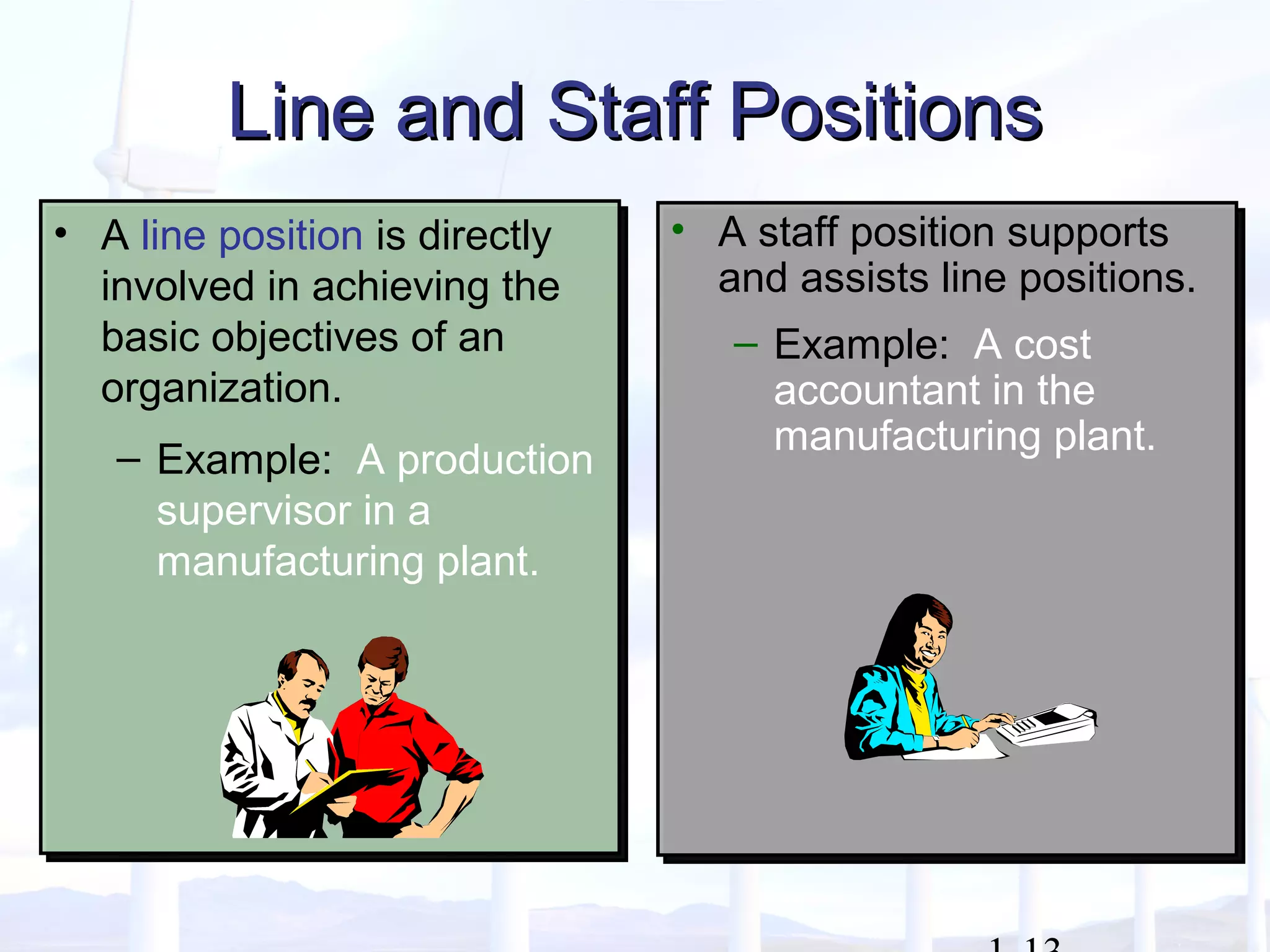
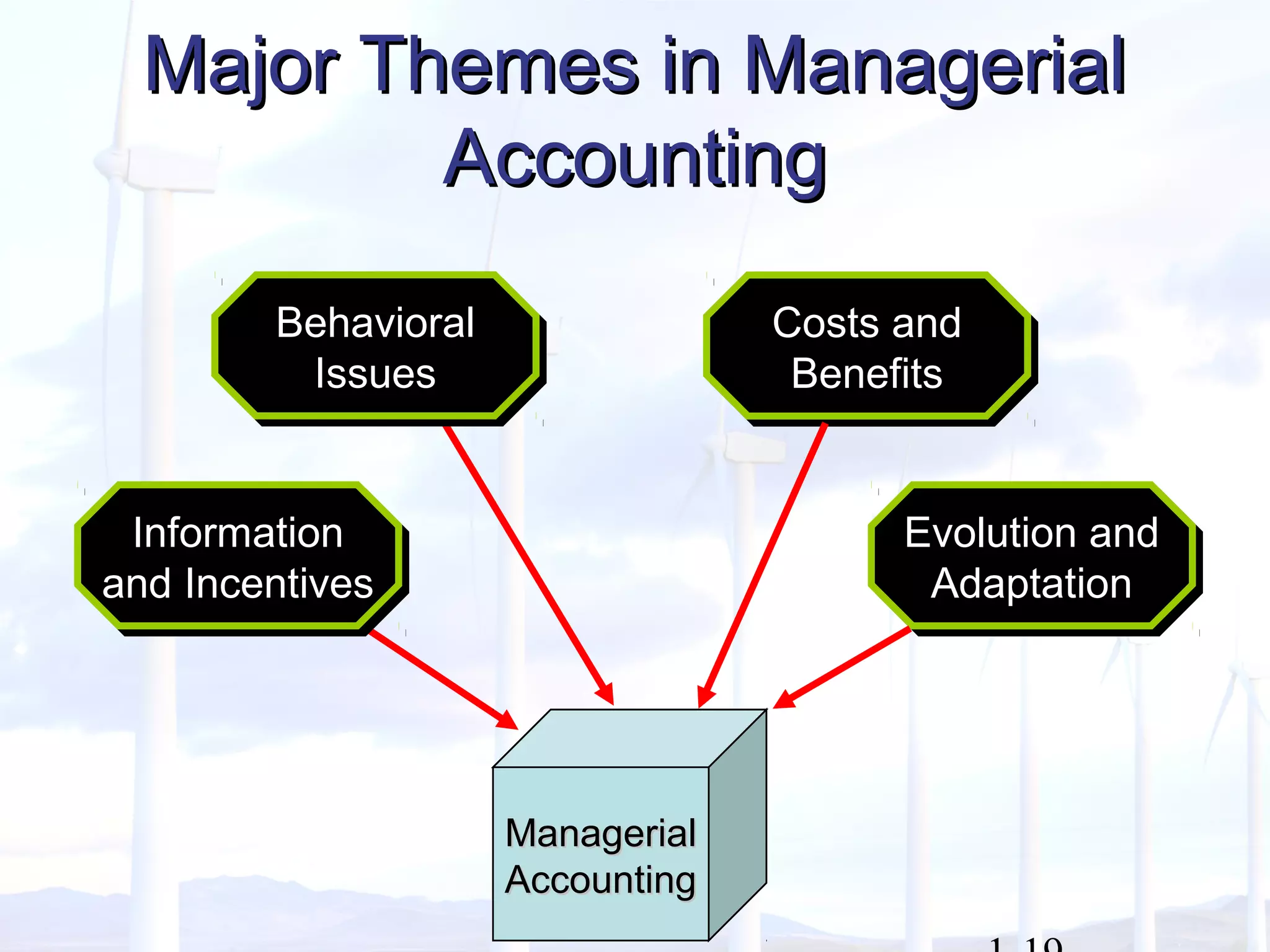
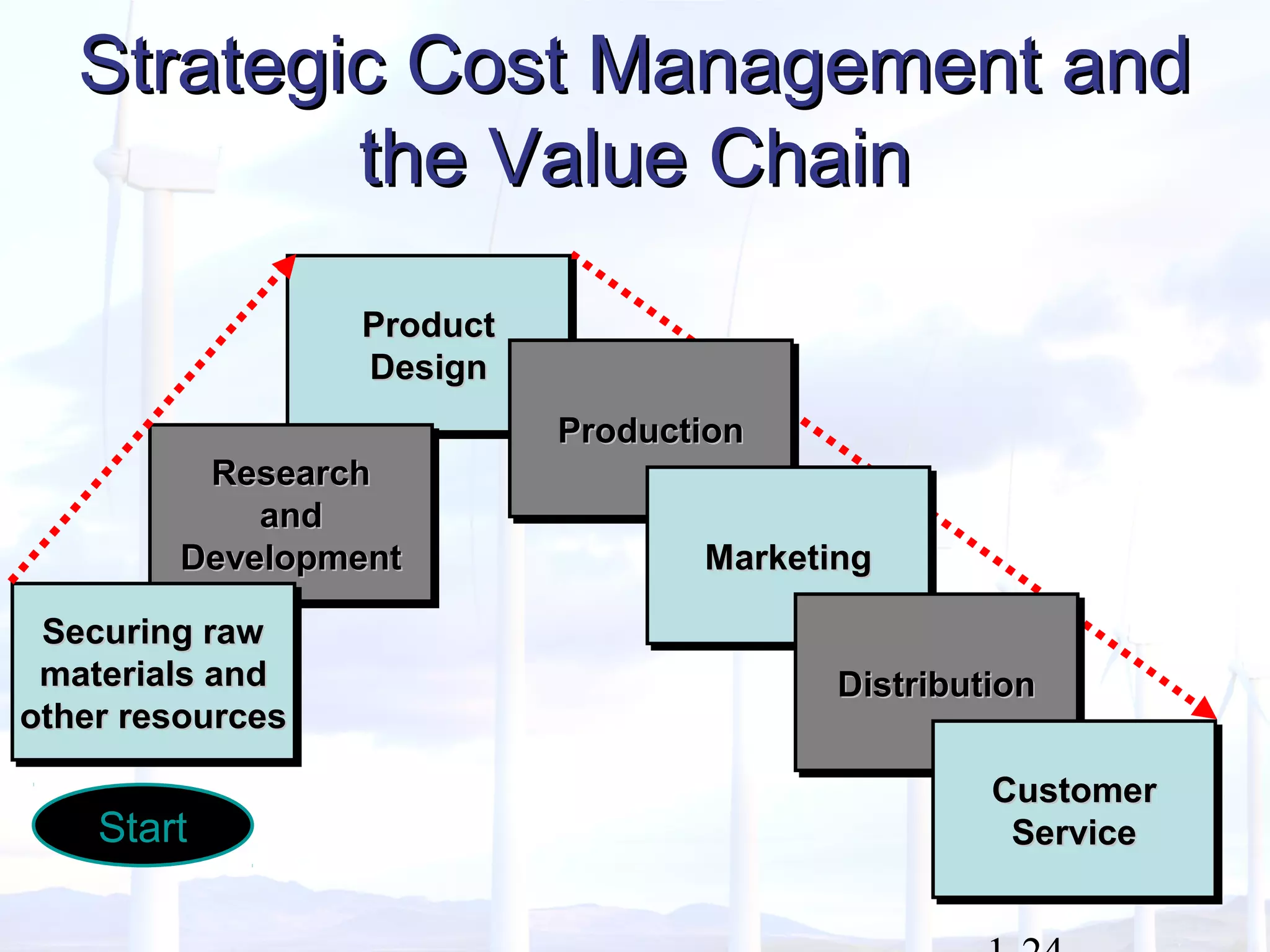
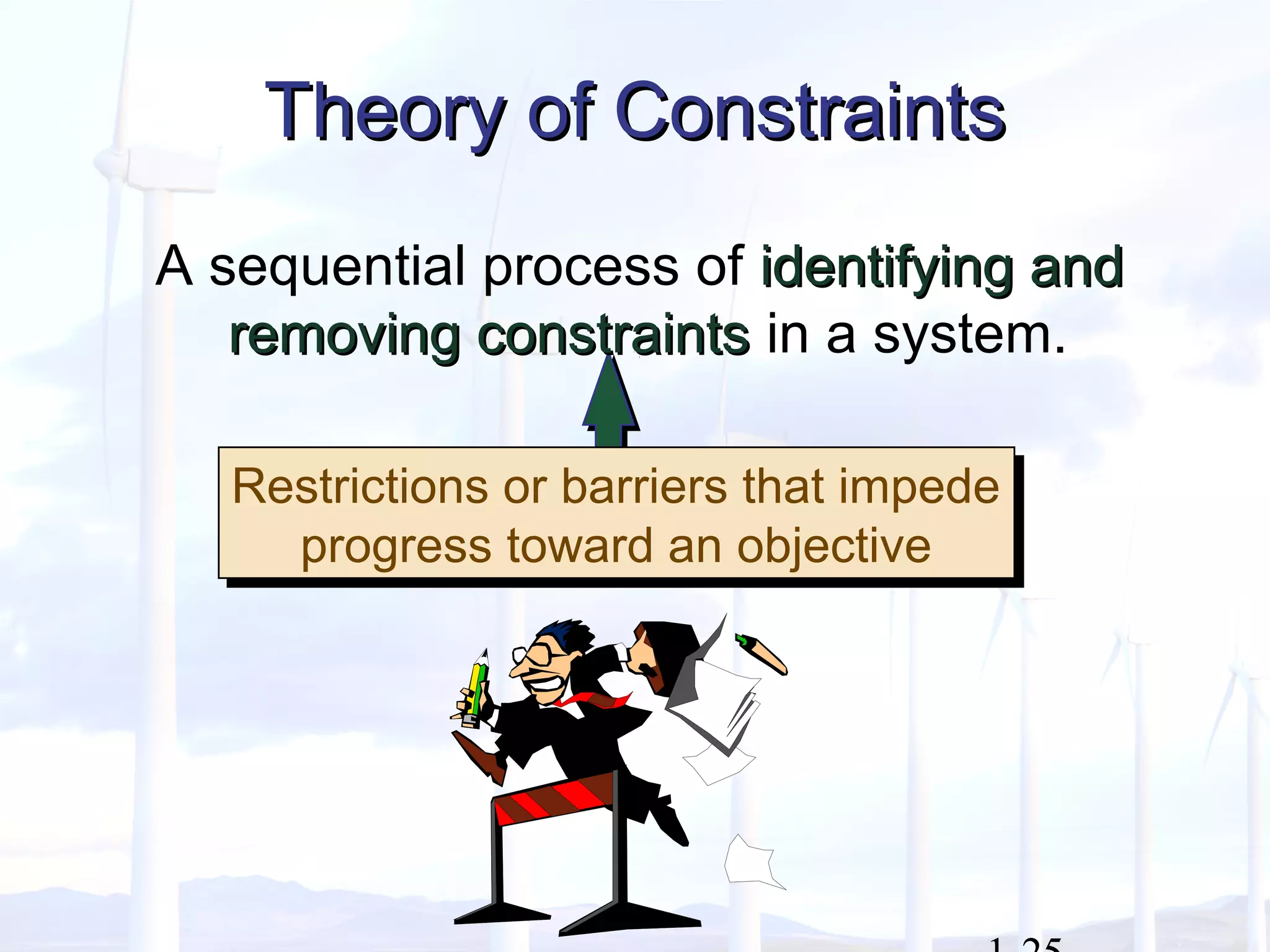
This document provides an overview of key concepts in managerial accounting. It defines managerial accounting as identifying, measuring, analyzing, interpreting, and communicating financial information to help managers plan, direct, and control organizational activities. The document discusses how managerial accounting adds value by providing information for decision-making, planning, controlling activities, motivating employees, measuring performance, and assessing competitiveness. It also distinguishes managerial from financial accounting and describes common roles in managerial accounting like the controller and treasurer. Major themes in managerial accounting discussed include information/incentives, costs/benefits, evolution/adaptation, and behavioral issues.