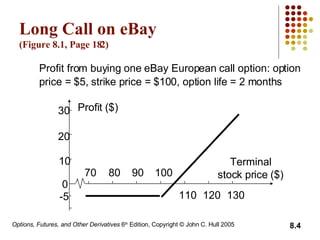
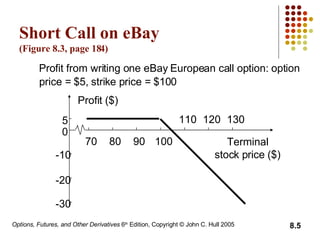
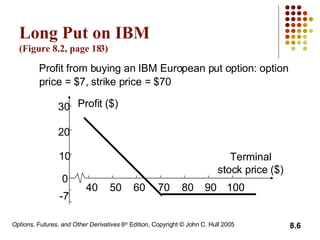
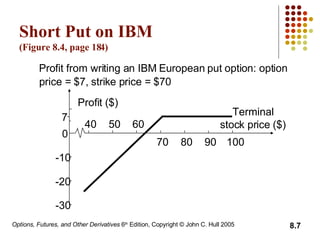
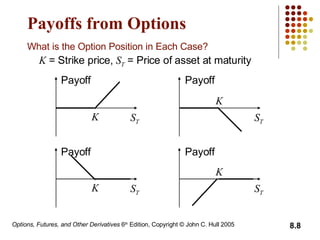
A call option gives the holder the right to buy the underlying asset, while a put option gives the holder the right to sell. European options can only be exercised at expiration, while American options can be exercised at any time before expiration. The document then discusses long and short positions in call and put options and provides examples of profit diagrams for different option positions. It also reviews the key terms, underlying assets, and specifications of exchange-traded options. The document concludes by discussing dividends and stock splits, market makers, margins, warrants, executive stock options, and convertible bonds.