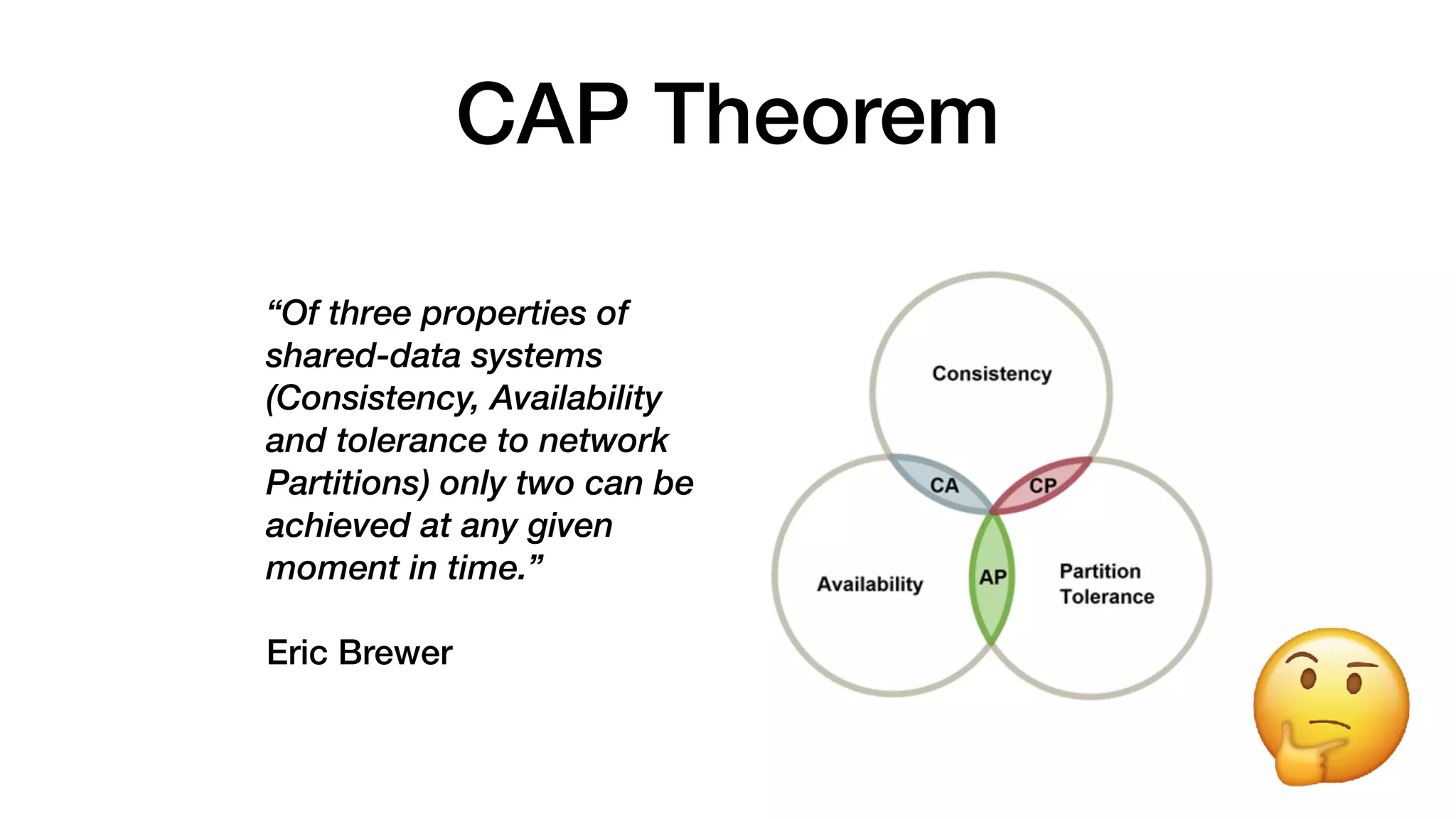
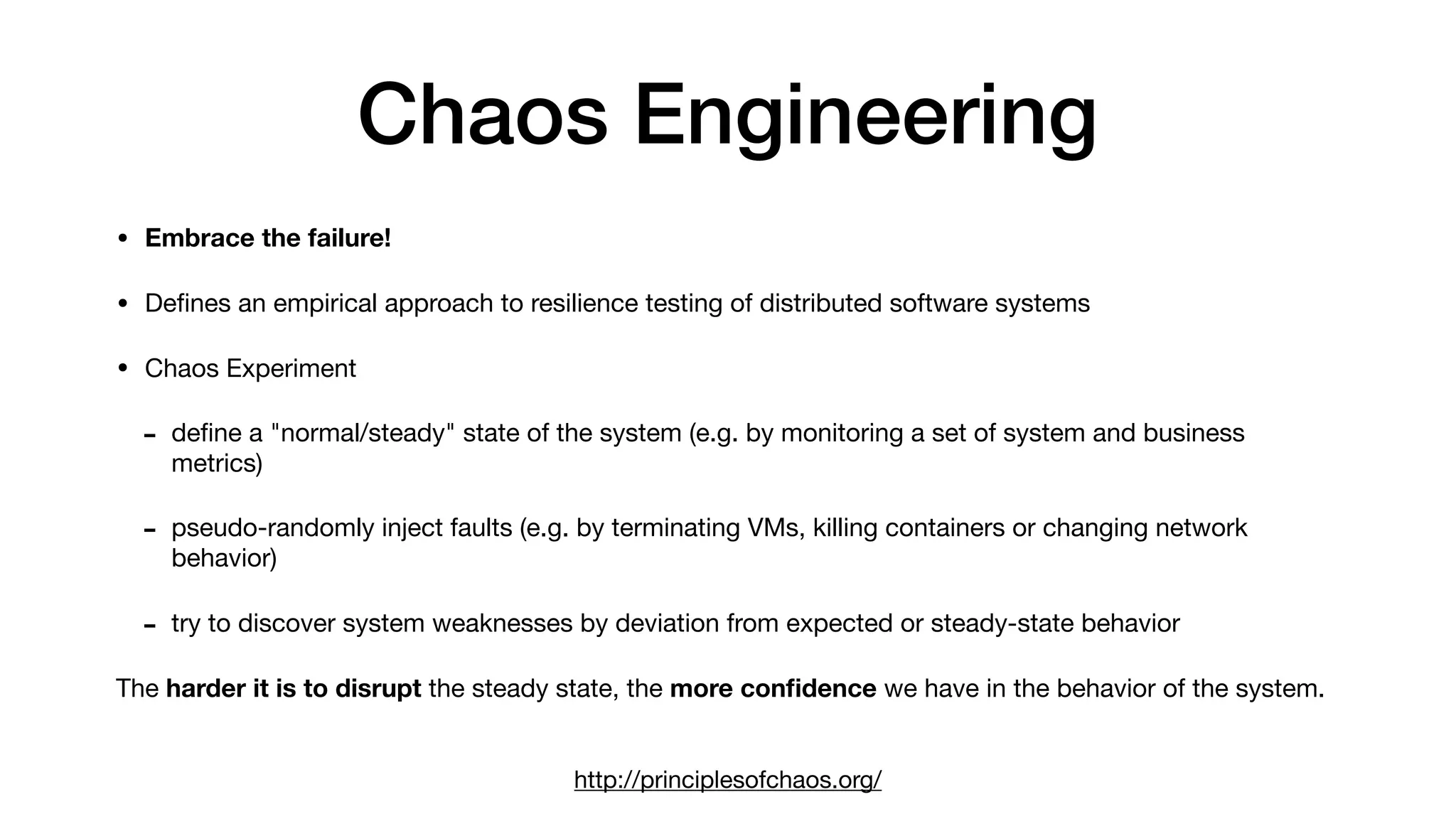
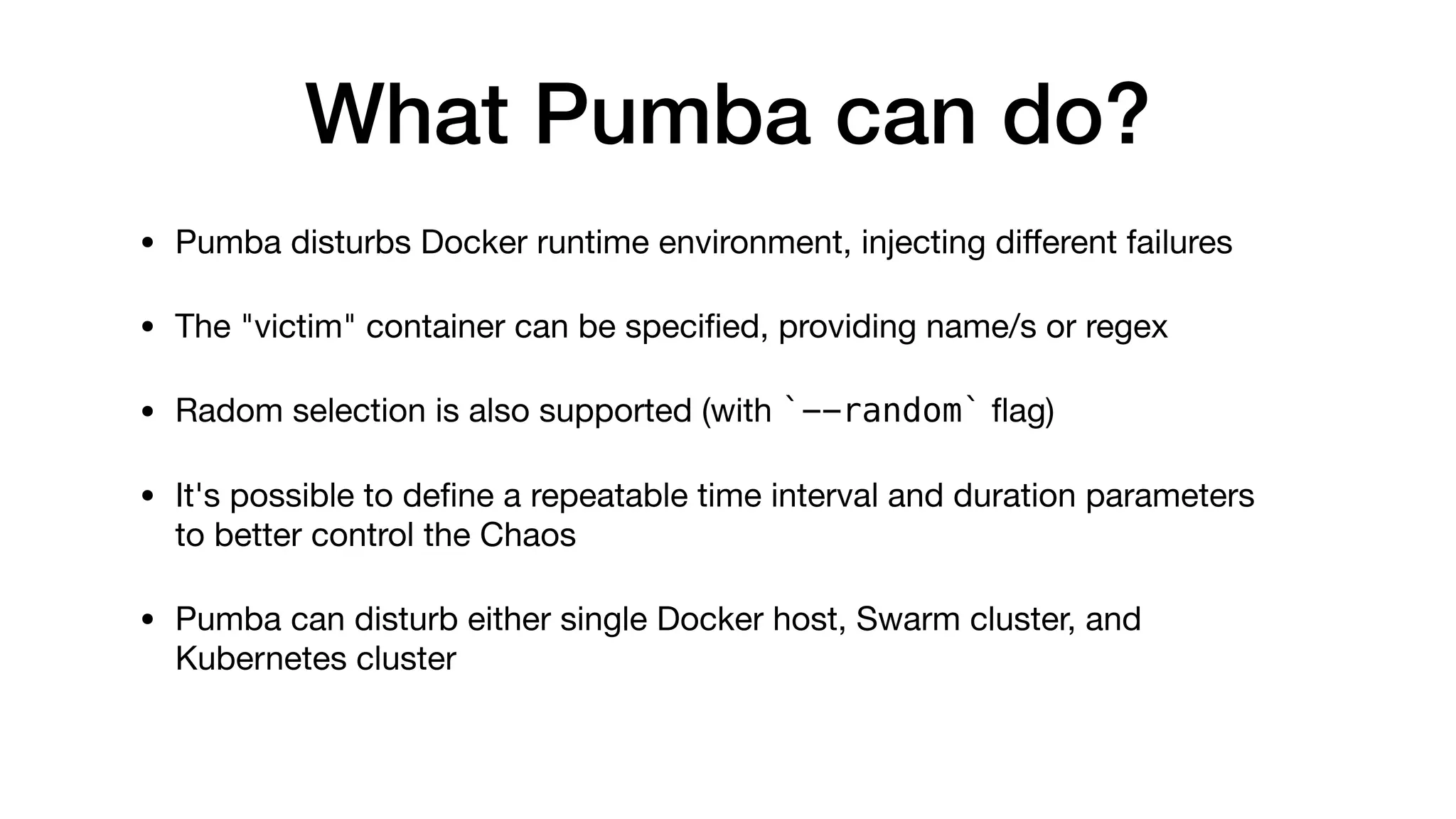
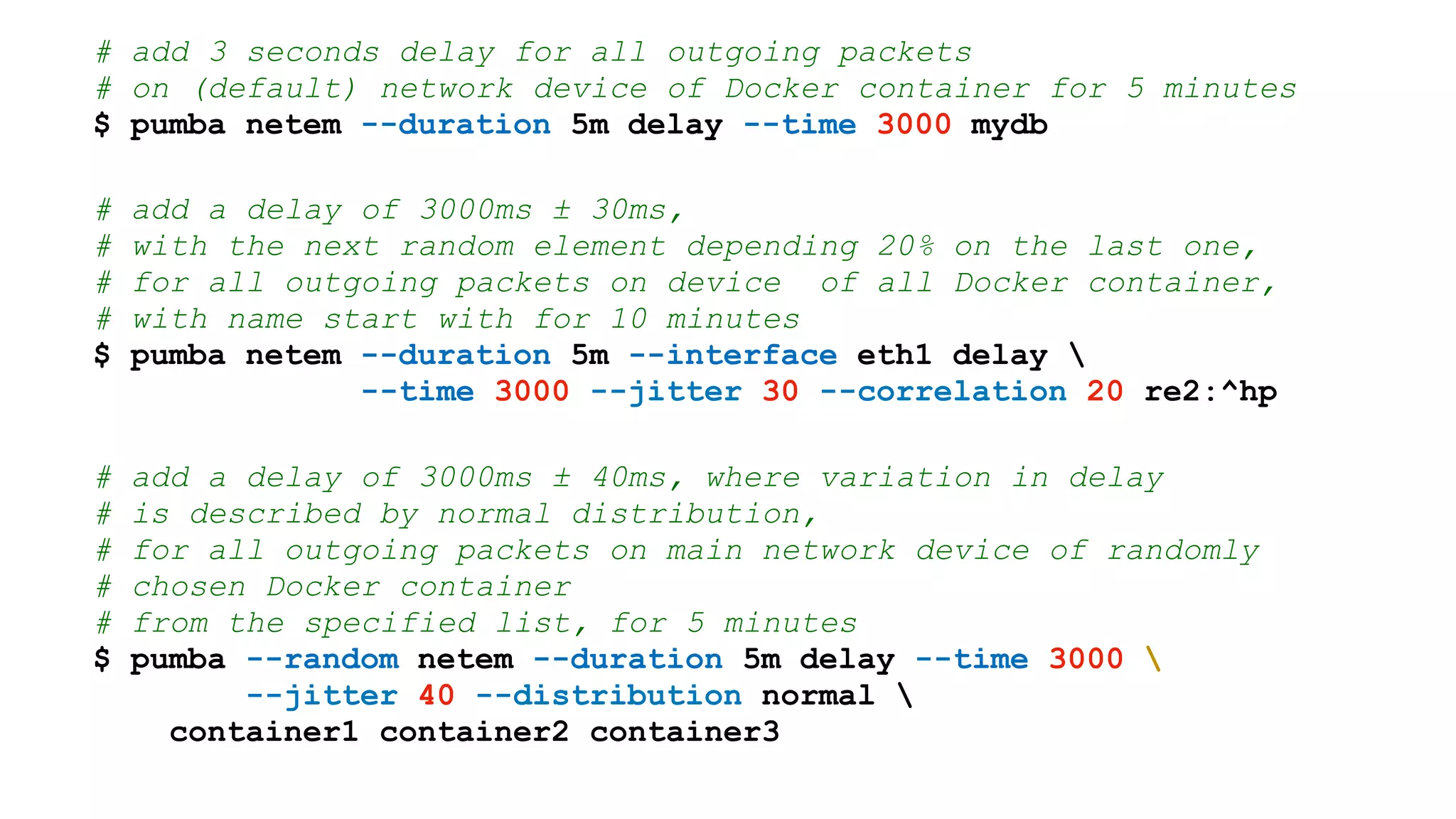
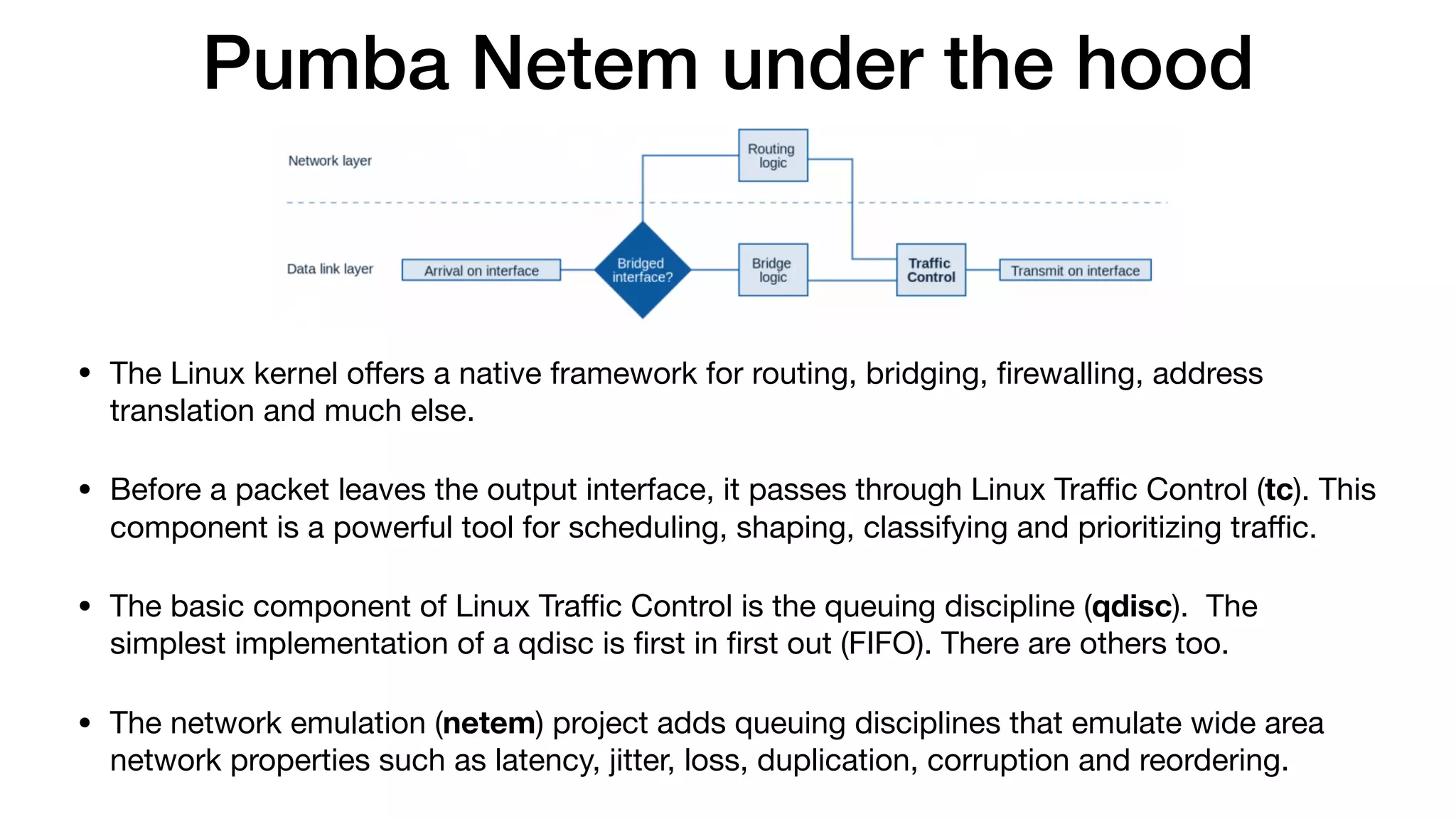
The document discusses chaos testing for Docker containers, highlighting the importance of resilience in complex software systems and the potential for failure. It introduces Pumba, an open-source tool for chaos testing that injects various types of failures into Docker environments, allowing users to test system weaknesses. The document also provides command examples for disrupting containers and emulating network failures using Pumba.