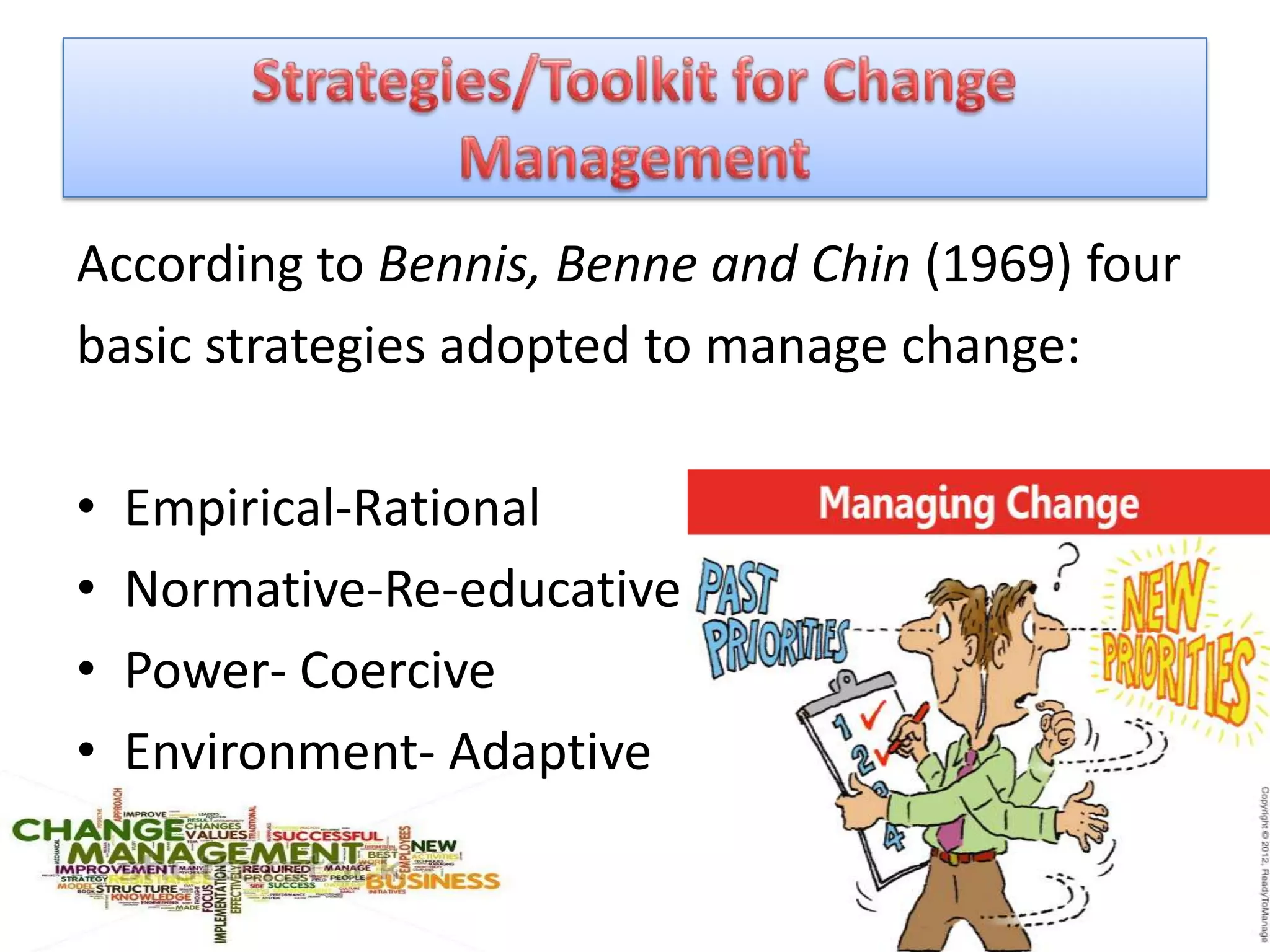
The document discusses change management, defining it as the organized and systematic application of knowledge, tools, and resources to help organizations achieve their business strategy through change. It notes that organizational change can be driven by factors like technology, business needs, the environment, and social changes. The document also outlines some common reasons for organizational change, the change process, and strategies for managing change effectively within an organization.