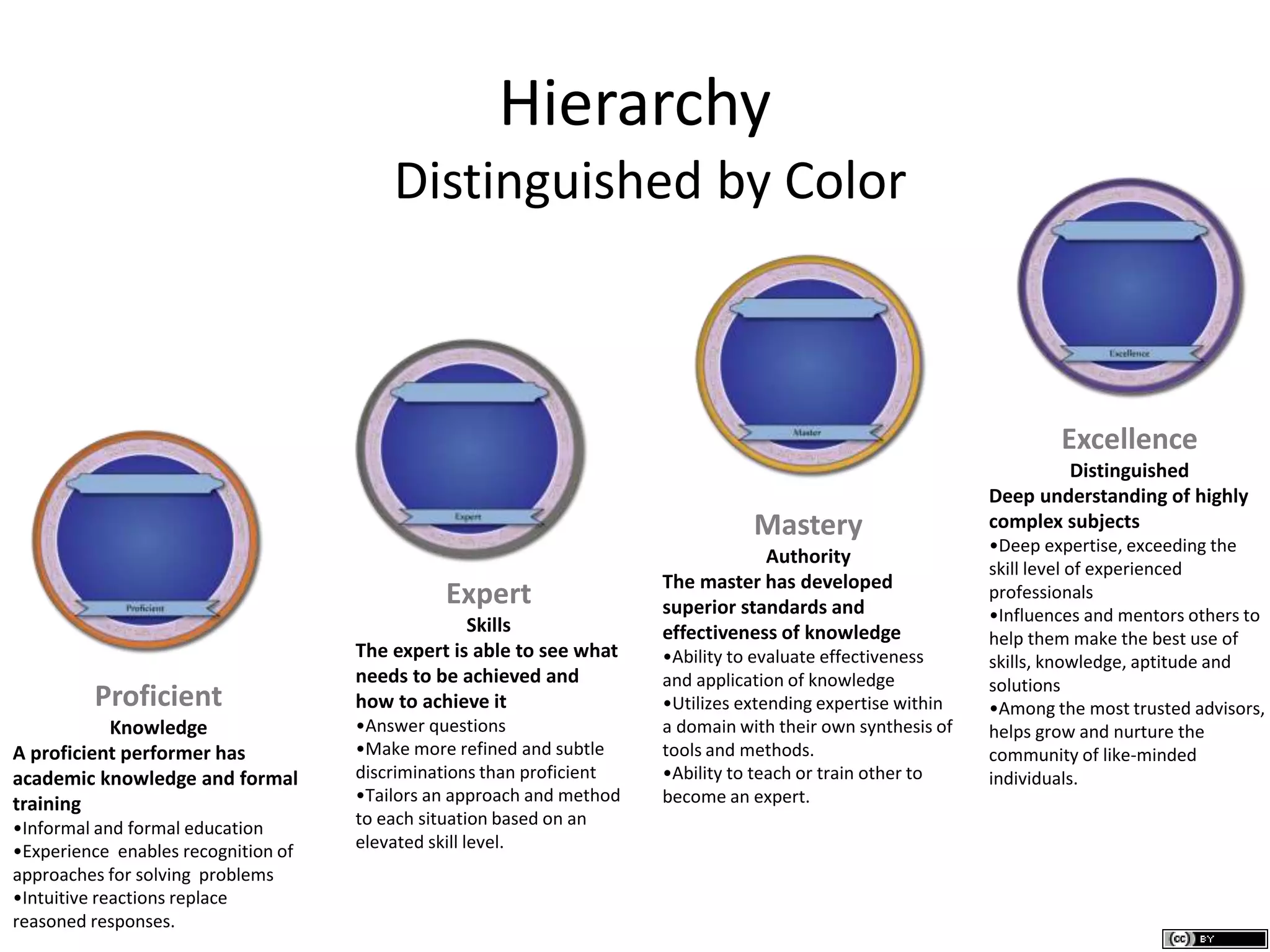
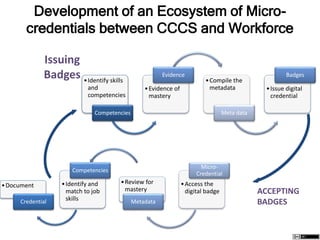
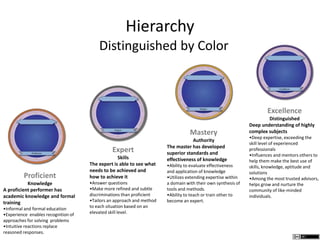
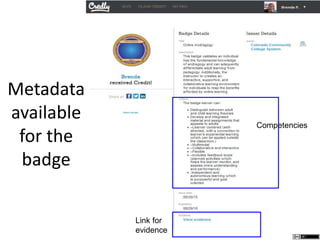
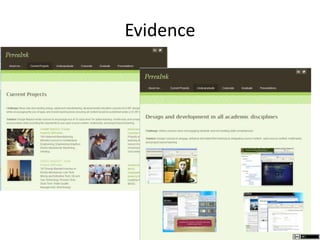
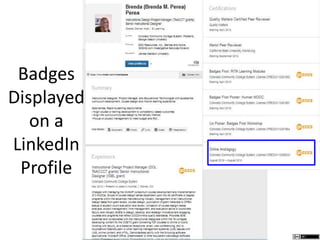
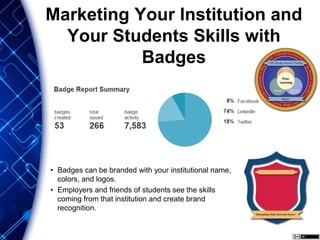
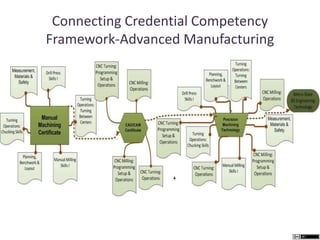
The document describes different levels of expertise - proficient, expert, mastery, and excellence. It provides descriptions of the characteristics associated with individuals at each level. A proficient performer has formal education and training, and can recognize approaches to solve problems. An expert can determine what needs to be achieved and how to achieve it, can make refined discriminations, and tailors their approach to each situation. A master has superior standards and knowledge application abilities, and can teach others. Those demonstrating excellence have deep understanding of complex subjects and influence and mentor others.