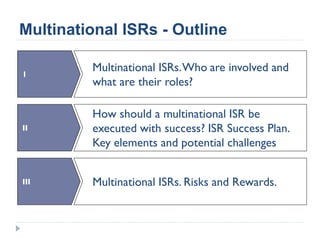
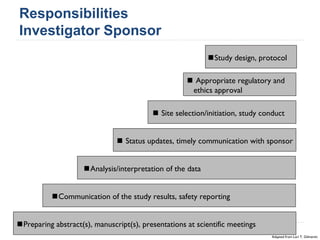
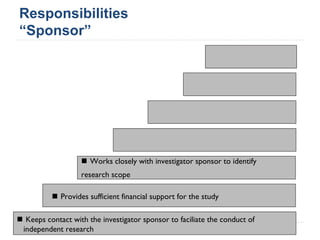
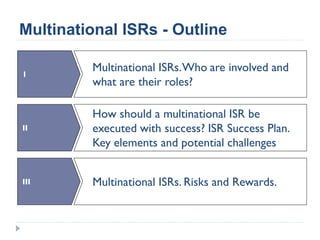
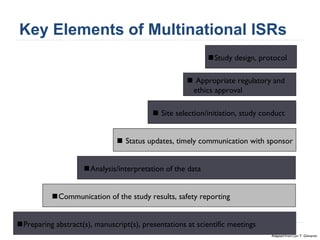
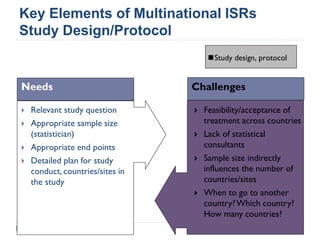
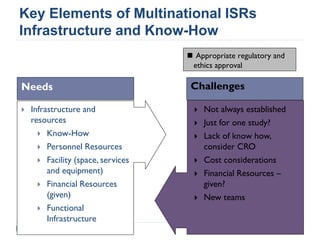
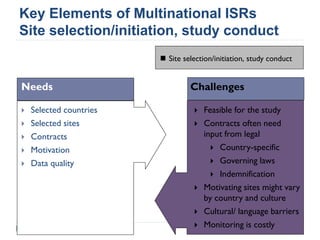
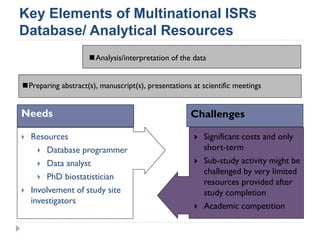
This document summarizes a presentation about challenges and experiences with multinational investigator-sponsored research (ISR) trials. It discusses the roles of investigators and sponsors in ISRs. It outlines key elements of a successful multinational ISR, including study design, infrastructure, site selection, and data analysis. Potential challenges include feasibility of treatment across countries, sample size, regulatory compliance, contractual issues, and limited resources. However, multinational ISRs also provide opportunities to expand medical knowledge through independent research and promote further studies.