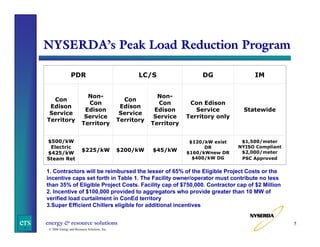
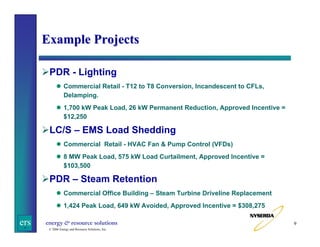
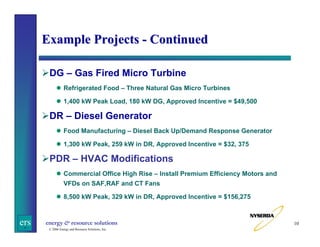
This document summarizes a presentation on challenges reviewing and inspecting demand response programs in New York. It provides background on NYSERDA's Peak Load Reduction Program and the roles of consultants in reviewing project applications and inspecting installations. Key challenges discussed include verifying large lighting projects, establishing load profiles, coordinating demand response generators, and ensuring all stakeholders are clear on requirements. The presentation emphasizes the importance of communication, scrutiny of projects, and involving all parties.