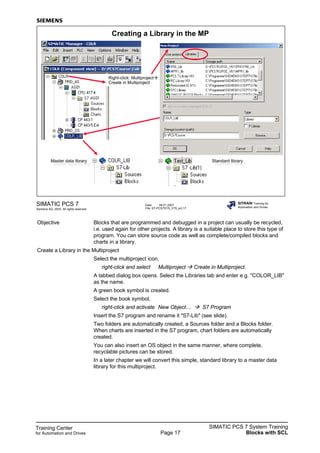
This document provides source code for a simulation block called Reactor that models a reactor process for a training course on PCS 7. The block contains input and output variables to control filling valves, a mixer motor, and monitor temperature and level values. The code defines the block attributes, declares the input, in-out, and output variables, and contains the algorithm to simulate the reactor process over time based on the input conditions and parameter values provided.




![Training Center
for Automation and Drives
SIMATIC PCS 7 System Training
Blocks with SCLPage 5
Date: 09.01.2007
File: ST-PCS7SYS_V70_scl.5
SIMATIC PCS 7
Siemens AG, 2003. All rights reserved.
SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Drives
Menu Insert
-> Block Template
OB
FB
FC
Comment
Constant
Parameters
DB
Instance DB
DB Referencing UDT
UDT
-> Control Structure
IF
CASE
FOR
WHILE
REPEAT
***** OB *****
ORGANIZATION_BLOCK OBxxx
VAR_TEMP
// Reserved
Info: ARRAY[0..19] OF BYTE;
// Temporary Variables
END_VAR
BEGIN
// Statements
;
END_ORGANIZATION_BLOCK
***** FB *****
FUNCTION_BLOCK FBxxx
VAR_TEMP
// Temporary Variables
END_VAR
VAR
// Static Variables
END_VAR
BEGIN
// Statement part
;
END_FUNCTION_BLOCK
***** FC *****
FUNCTION FCxxx : INT
VAR_TEMP
// Temporary Variables
END_VAR
BEGIN
// Statement part
;
FCxxx := 100;
END_FUNCTION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch7v70sclen-140422145011-phpapp02/85/Ch7-v70-scl_en-5-320.jpg)




![Training Center
for Automation and Drives
SIMATIC PCS 7 System Training
Blocks with SCLPage 11
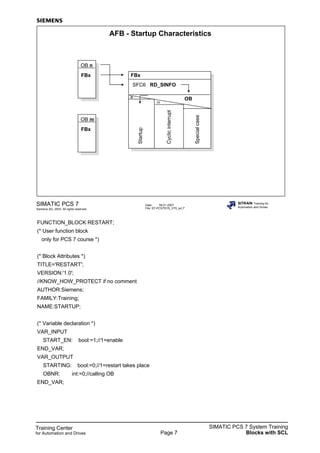
FUNCTION_BLOCK Reactor
(* Simulation block with feedback signals
for PCS 7 course only *)
(* Block Attributes *)
TITLE ='REAC';
VERSION:'5.0';
//KNOW_HOW_PROTECT if no comment
AUTHOR:Siemens;
FAMILY:Training;
NAME:PLANT;
(* Variable Declaration *)
VAR_IN_OUT
V1_OP_CL: BOOL; //Filling1
V2_OP_CL: BOOL; //Filling2
V3_OP_CL: BOOL; //Filling3
M1_ON_OF: BOOL; //Mixer motor
RS_COOL : BOOL; //Container empty and cold
SET_HOT : BOOL; //Container full and warm
V_RESET : BOOL; //Valves closed, motor off
END_VAR
VAR_INPUT
V1_FLOW: REAL := 100.0; //Flow V1 0..100%
V2_FLOW: REAL := 100.0; //Flow V2
V3_FLOW: REAL := 100.0; //Flow V3
CFV: REAL := 0.002; //Correction factor valves
V_HOT_FL: REAL := 0.0; //Flow heating 0..100%
TMP_ENV: REAL := 20.0; //Environment temperature
TMP_HOT: REAL := 120.0; //Heating medium temperature
T_LAG_SH: REAL := 10.0; //T_PT1-Shell[s]
T_LAG_IN: REAL := 30.0; //T_PT2-Inside[s] full reactor
SAMPLE_T: REAL := 1.0; //Sampling time[s]
END_VAR
Simulation block
REACTOR (FB600)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch7v70sclen-140422145011-phpapp02/85/Ch7-v70-scl_en-11-320.jpg)