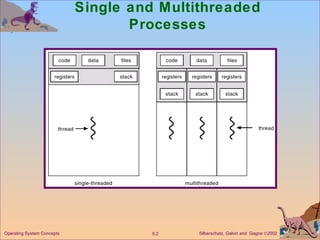
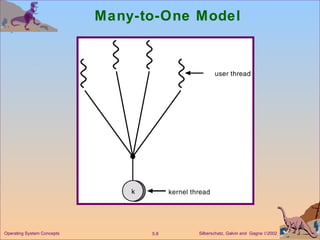
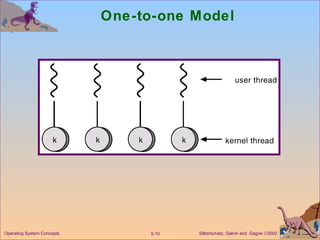
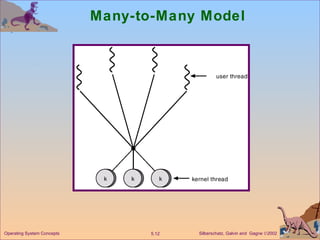
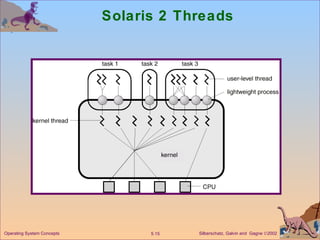
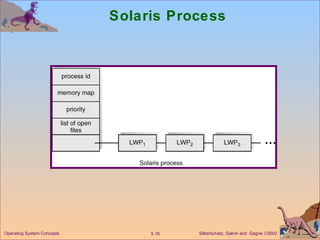
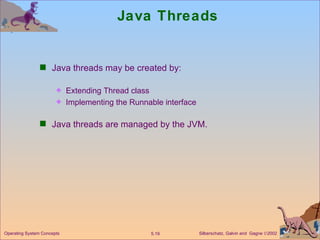
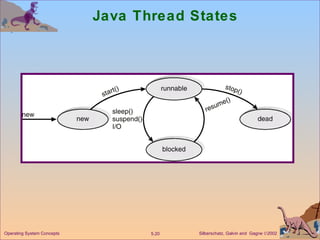
This document discusses different models of multithreading including many-to-one, one-to-one, and many-to-many. It also covers threading issues like signal handling and thread cancellation. Specific threading implementations are discussed for POSIX threads, Solaris threads, Windows 2000 threads, Linux threads, and Java threads.