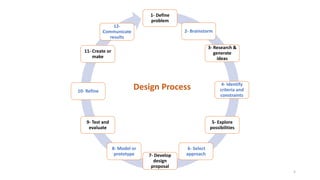
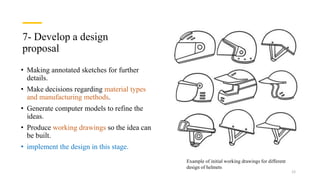
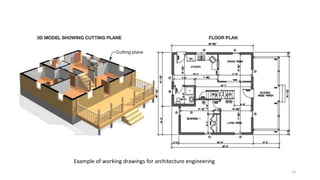
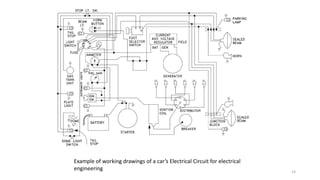
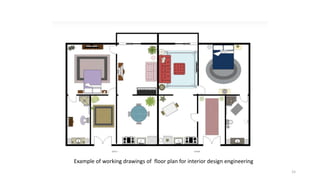
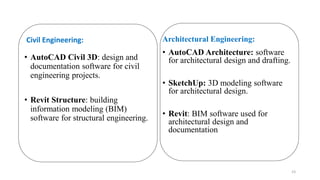
The document discusses the engineering design process and tools. It defines design as a problem-solving process used to systematically solve problems and create things people want. The engineering design process typically involves 12 steps: defining the problem, brainstorming, researching solutions, identifying criteria and constraints, exploring possibilities, selecting an approach, developing a design proposal, creating models/prototypes, testing and evaluating, refining the design, creating the final solution, and communicating results. The document also provides examples of common engineering design tools used in different fields like CAD software, simulation tools, and graphic design software.