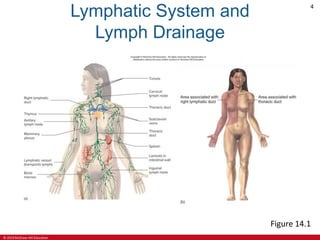
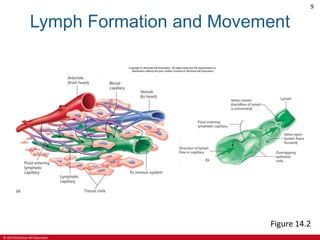
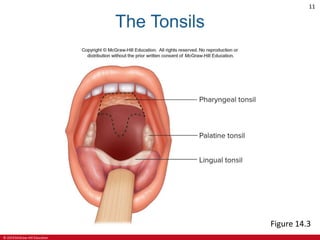
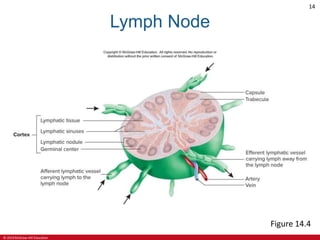
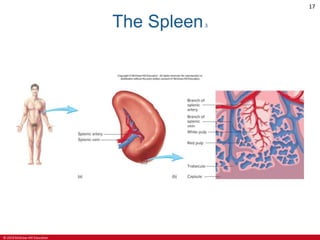
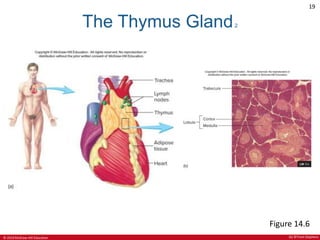
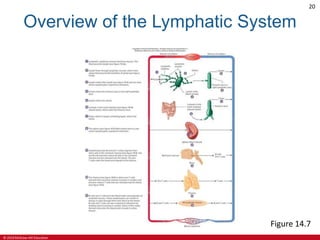
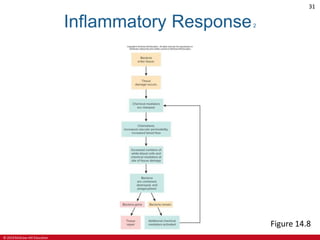
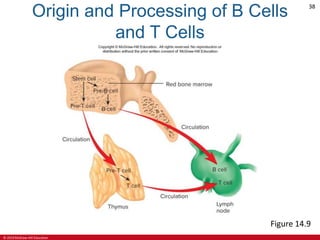
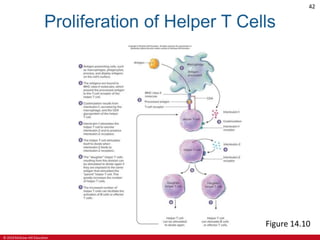
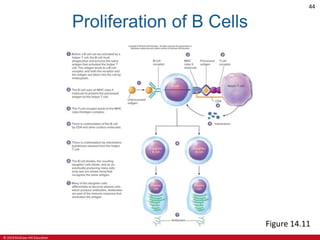
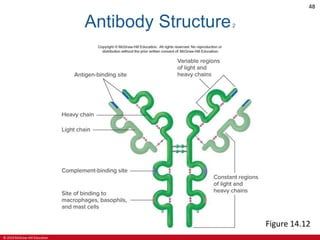
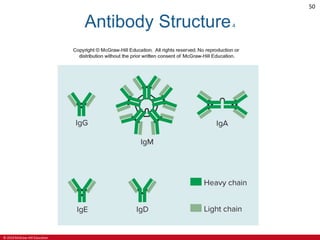
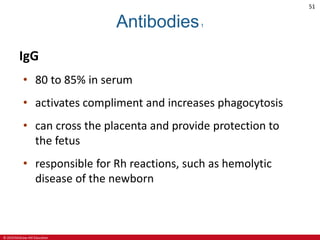
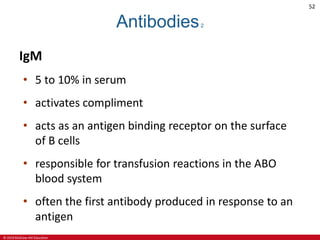
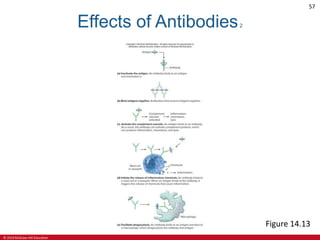
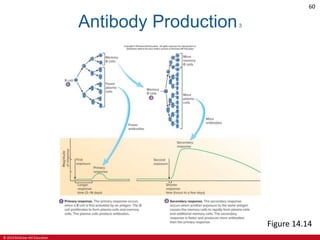
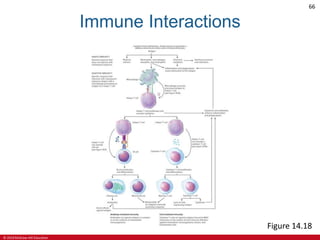
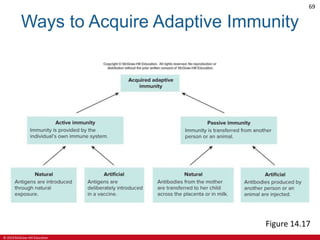
This document is a lecture outline on the lymphatic system and immunity from a textbook on anatomy and physiology. It covers the key components and functions of the lymphatic system including lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, the spleen, thymus gland, and tonsils. It also discusses the immune system, including innate immunity through physical barriers and chemical mediators, and adaptive immunity carried out by B and T lymphocytes through antibody-mediated and cell-mediated responses. Diagrams and figures are provided to illustrate these concepts.