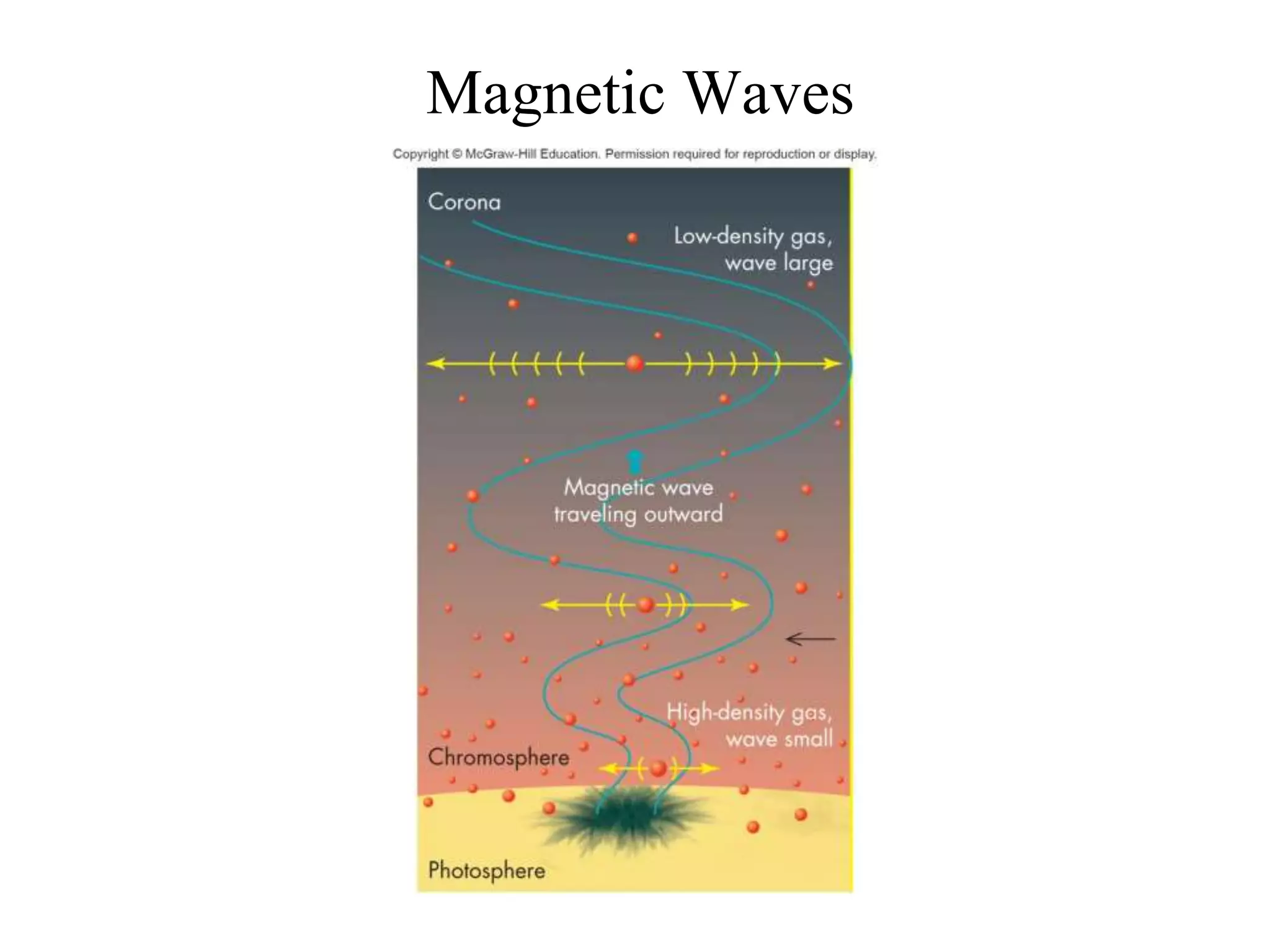
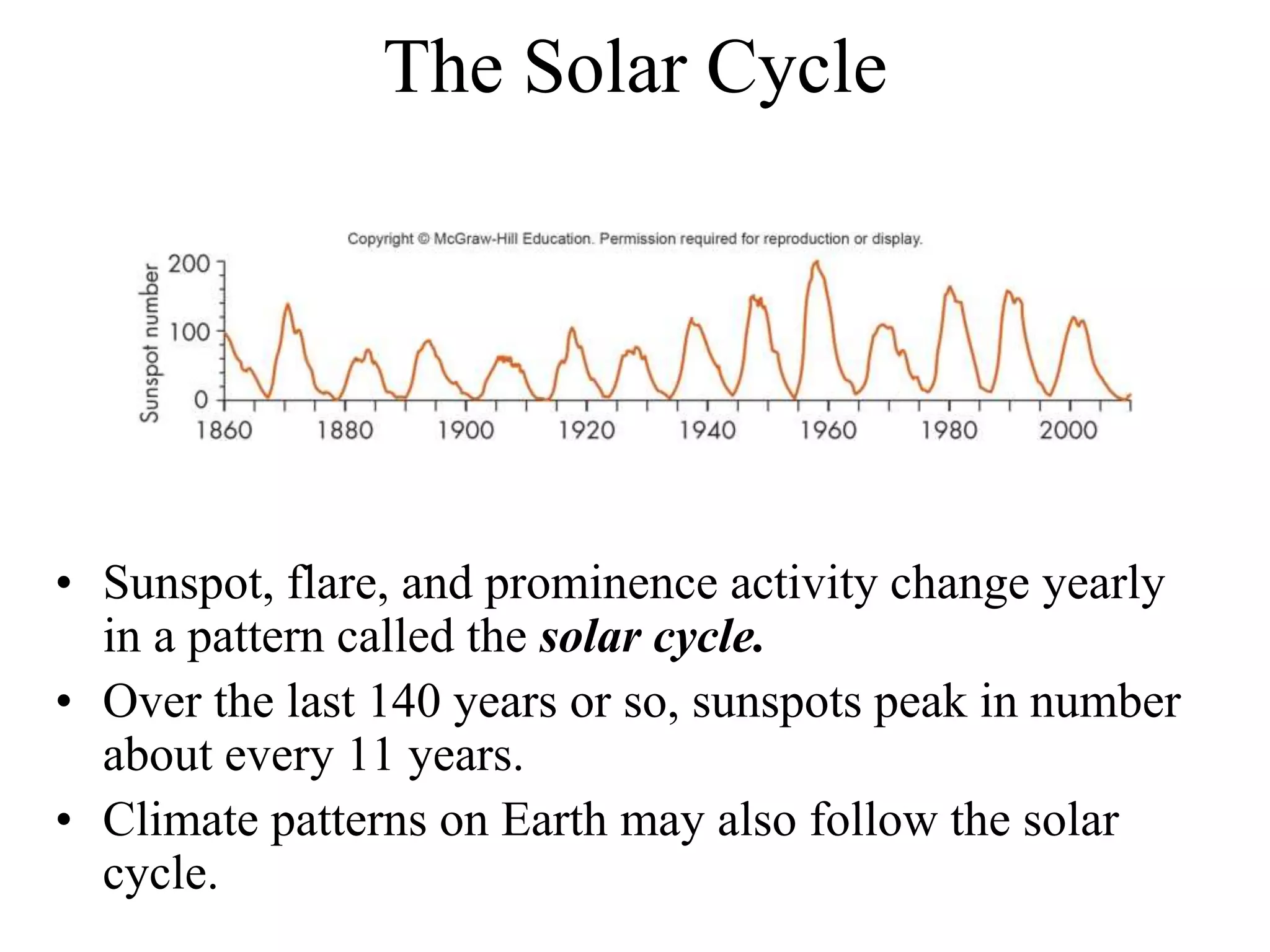
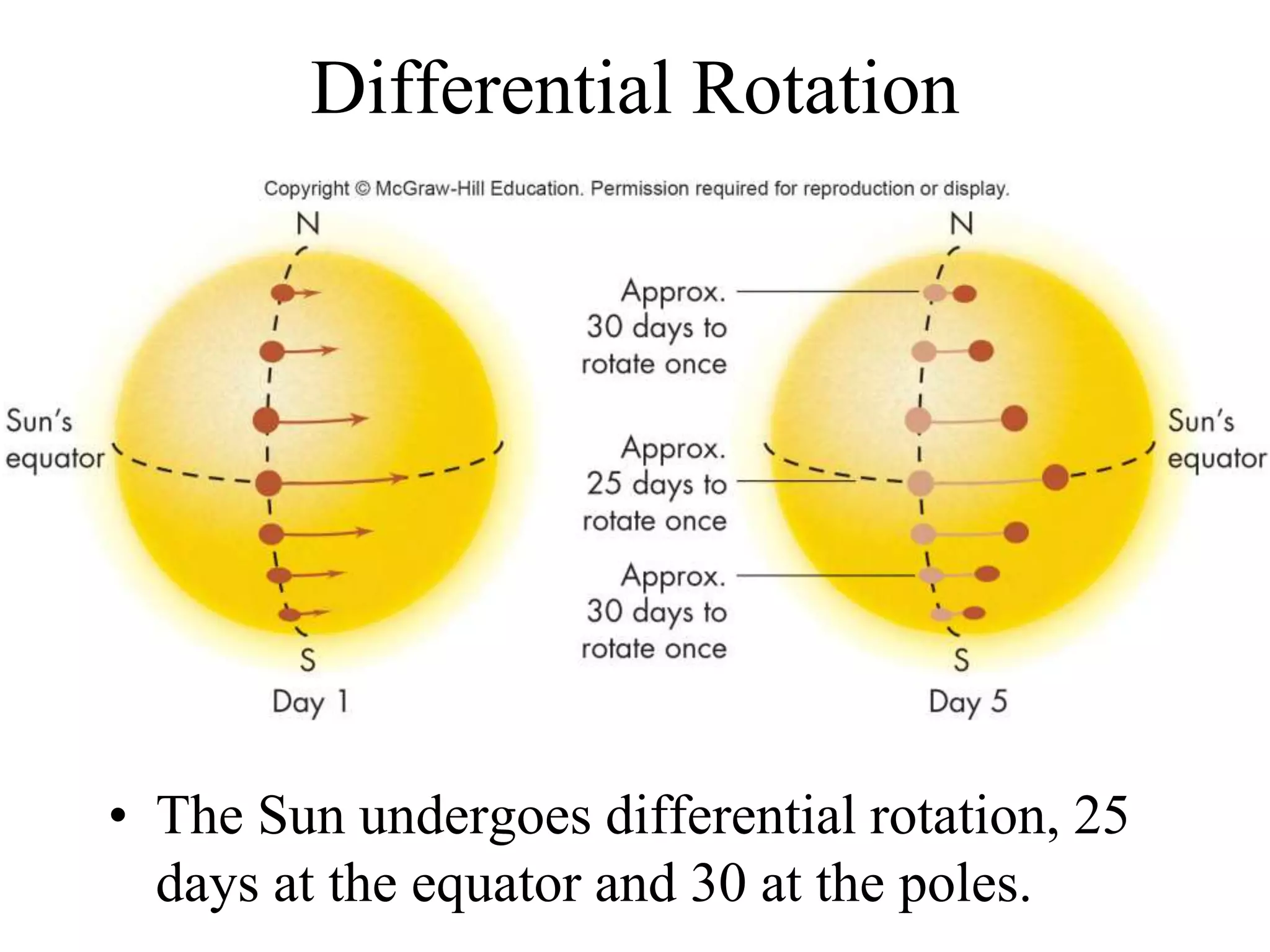
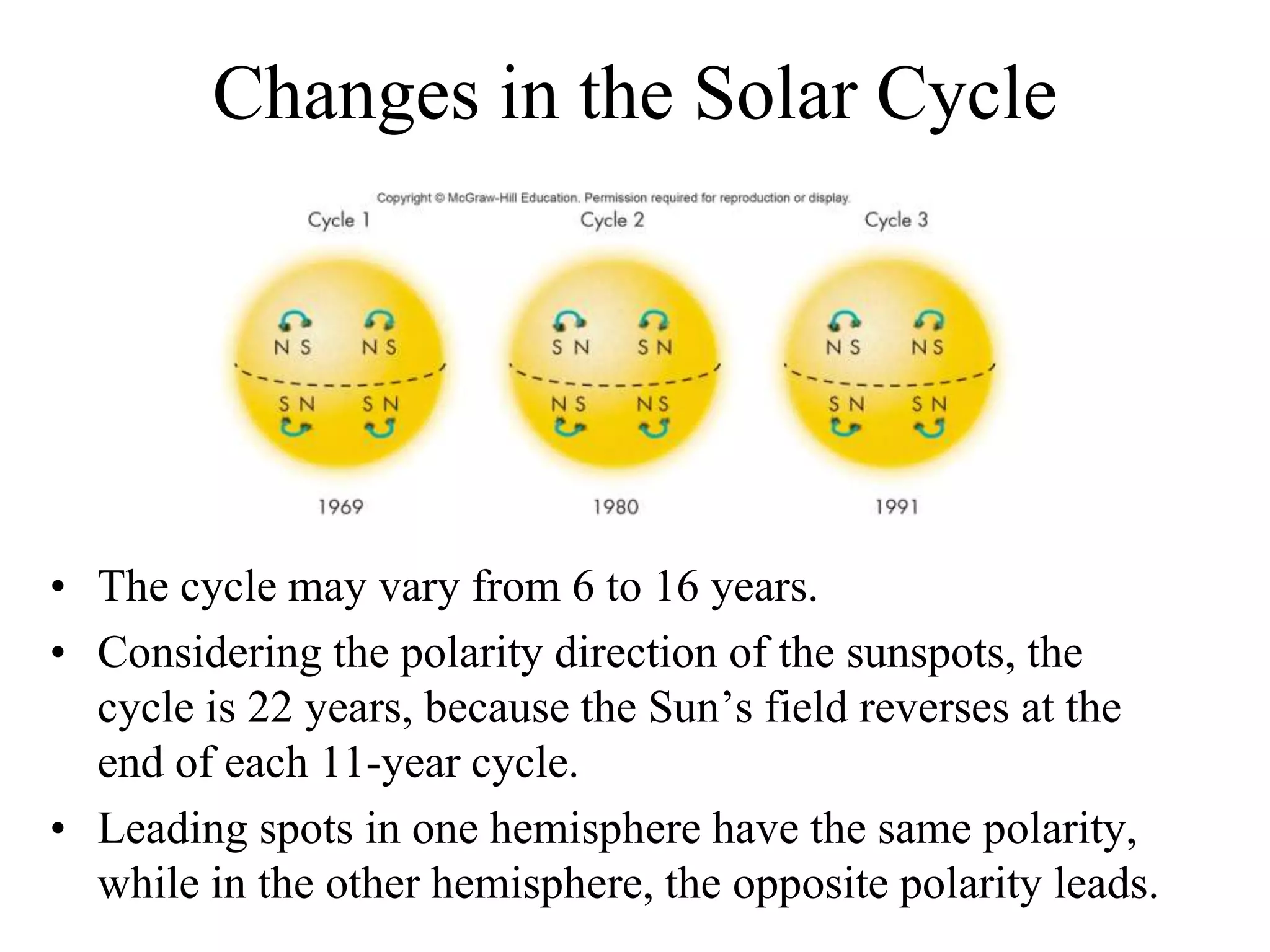
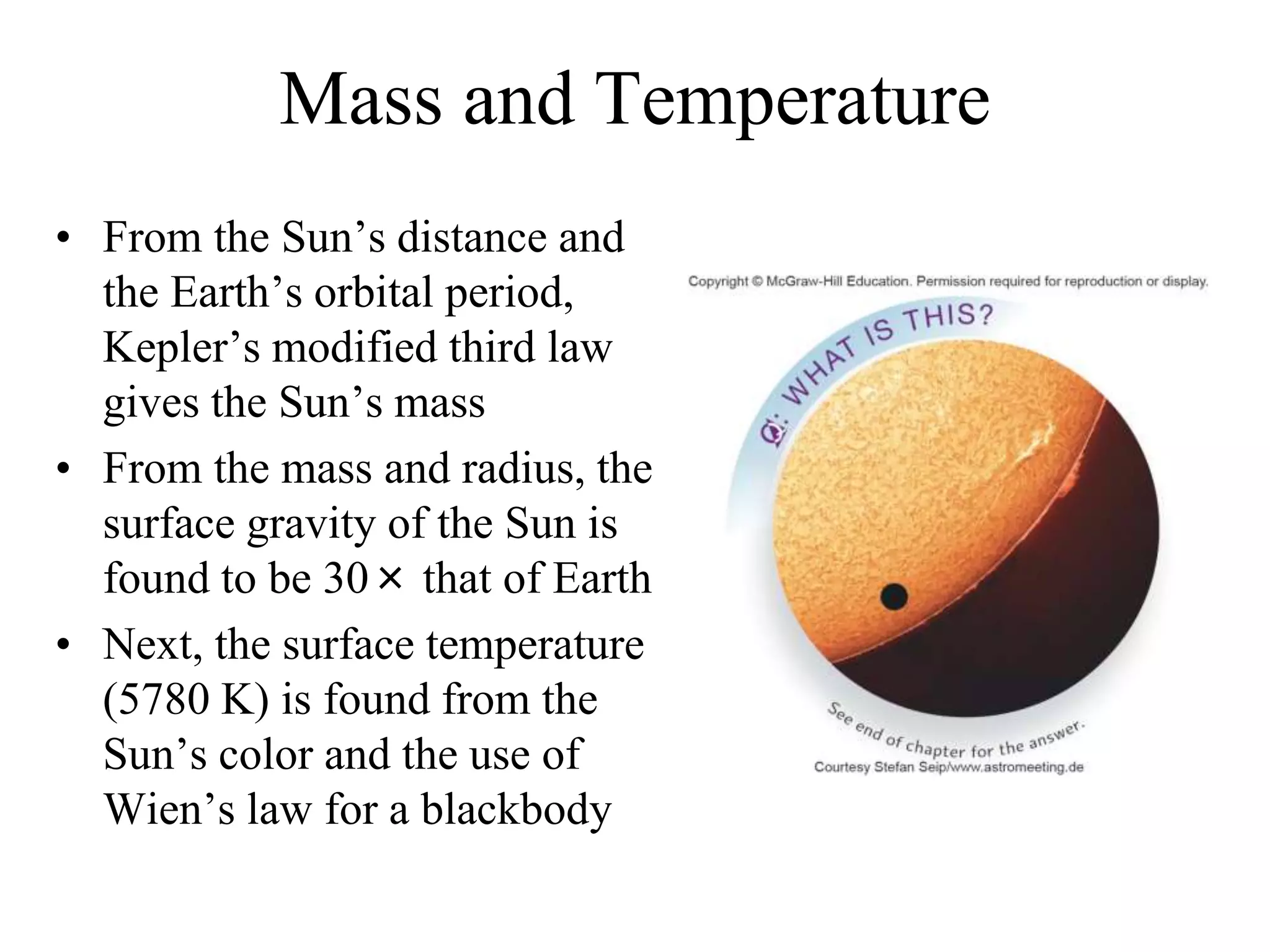
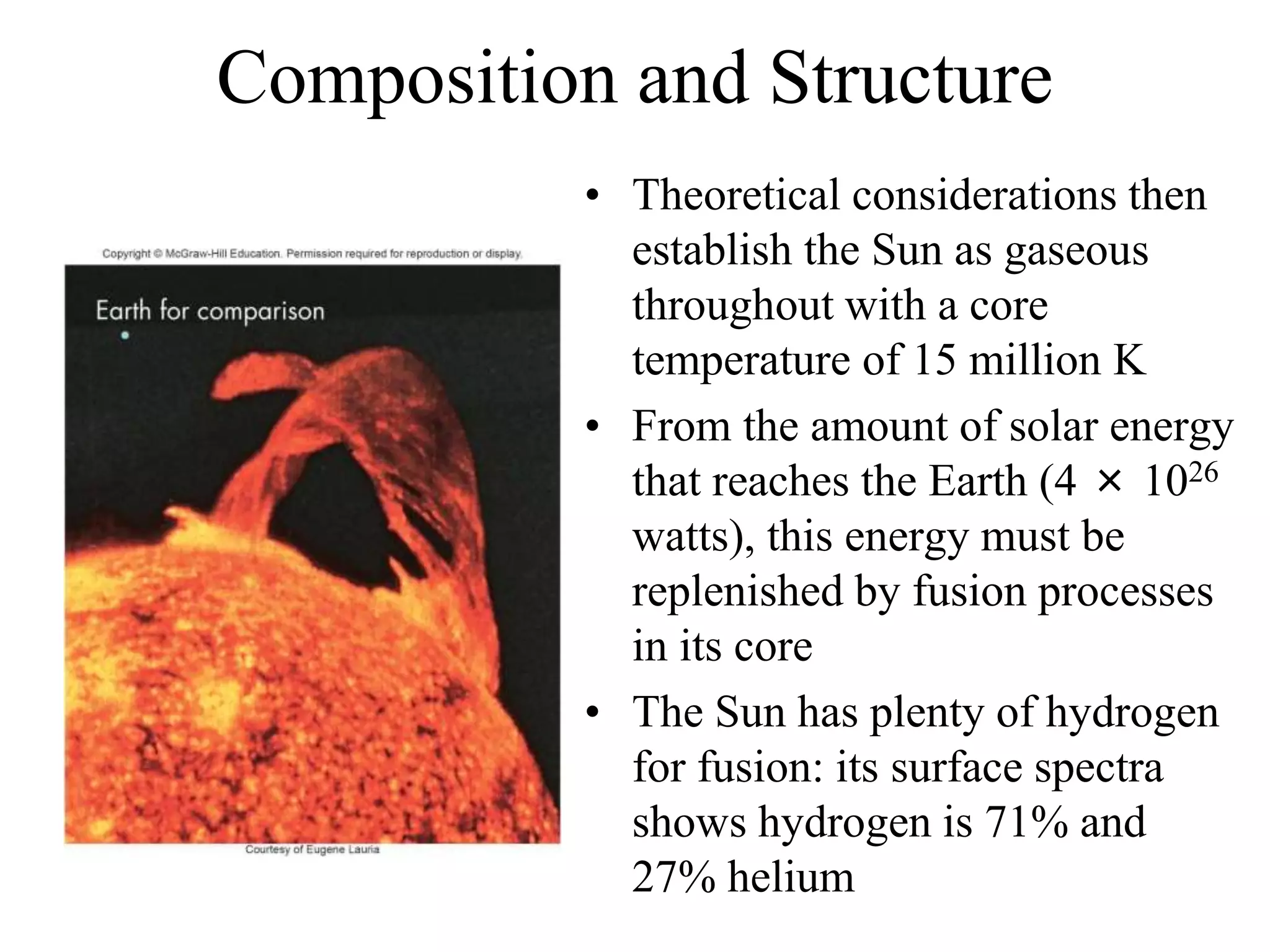
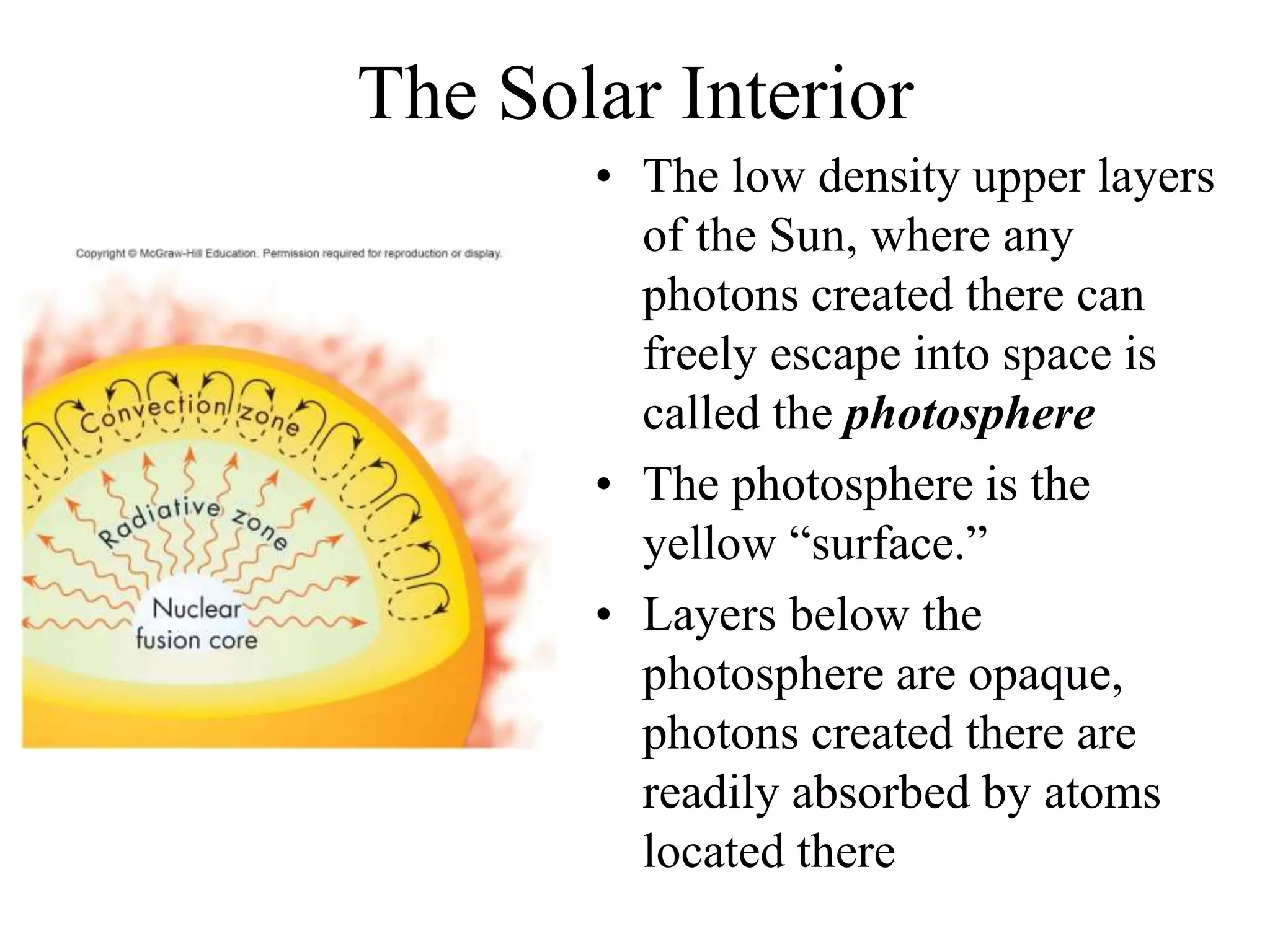
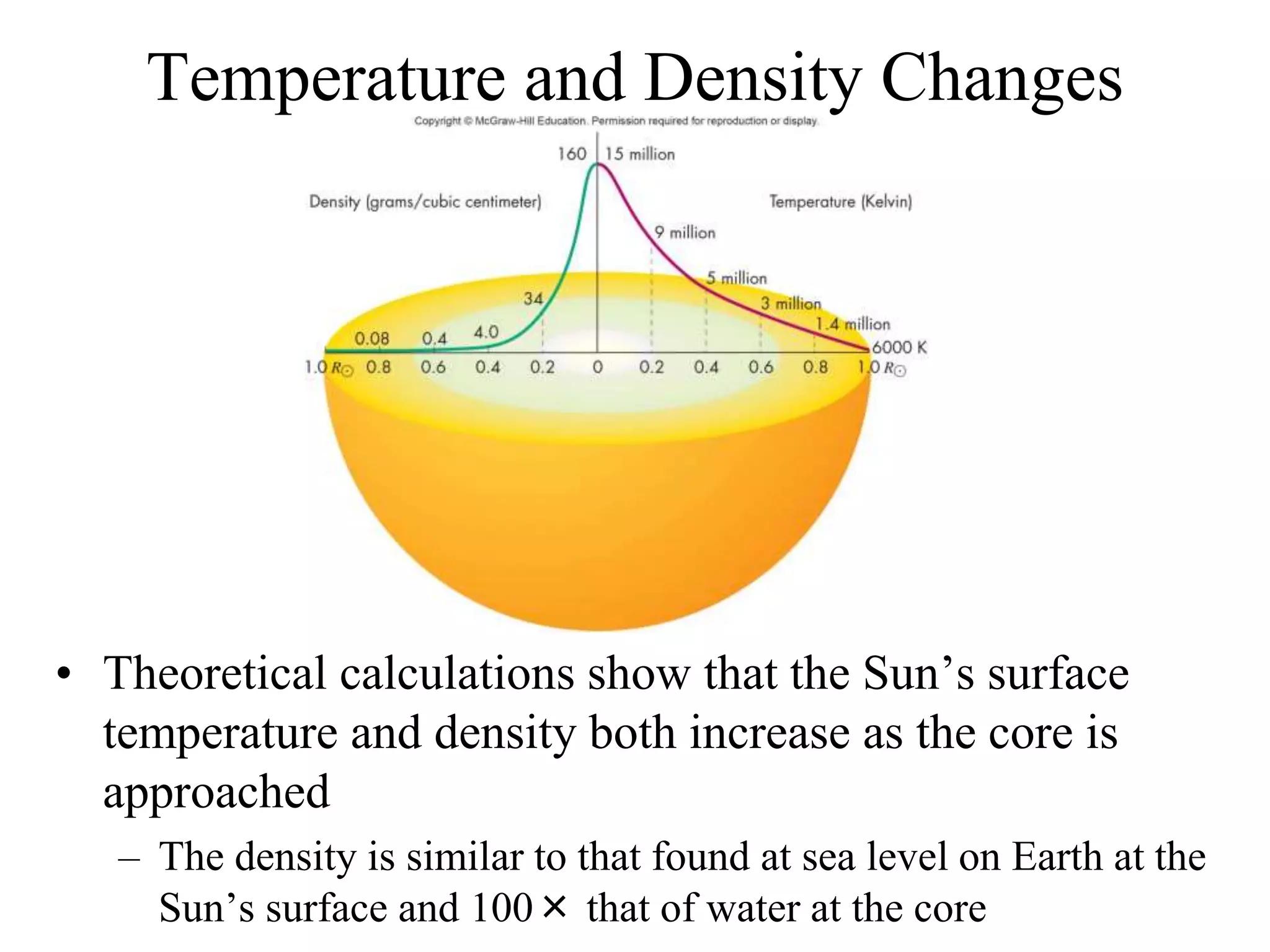
The Sun is a star composed of hot gas that powers itself through nuclear fusion in its core. It has several layers including the photosphere, chromosphere, and corona. The Sun's interior is divided into a radiative zone where heat transfers by radiation and a convection zone where heat rises and falls. Nuclear fusion in the core converts hydrogen to helium, releasing energy over billions of years. Magnetic activity on the surface includes sunspots, solar flares, and prominences. The solar wind carries the Sun's magnetic fields and particles into space.











![The Sun’s place on the H-R Diagram [Temperature
on the X-axis – Luminosity on the Y-axis]
The
Sun –
a G2V
star](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch12oursun1-201023145558/75/Ch12-our-sun-1-16-2048.jpg)






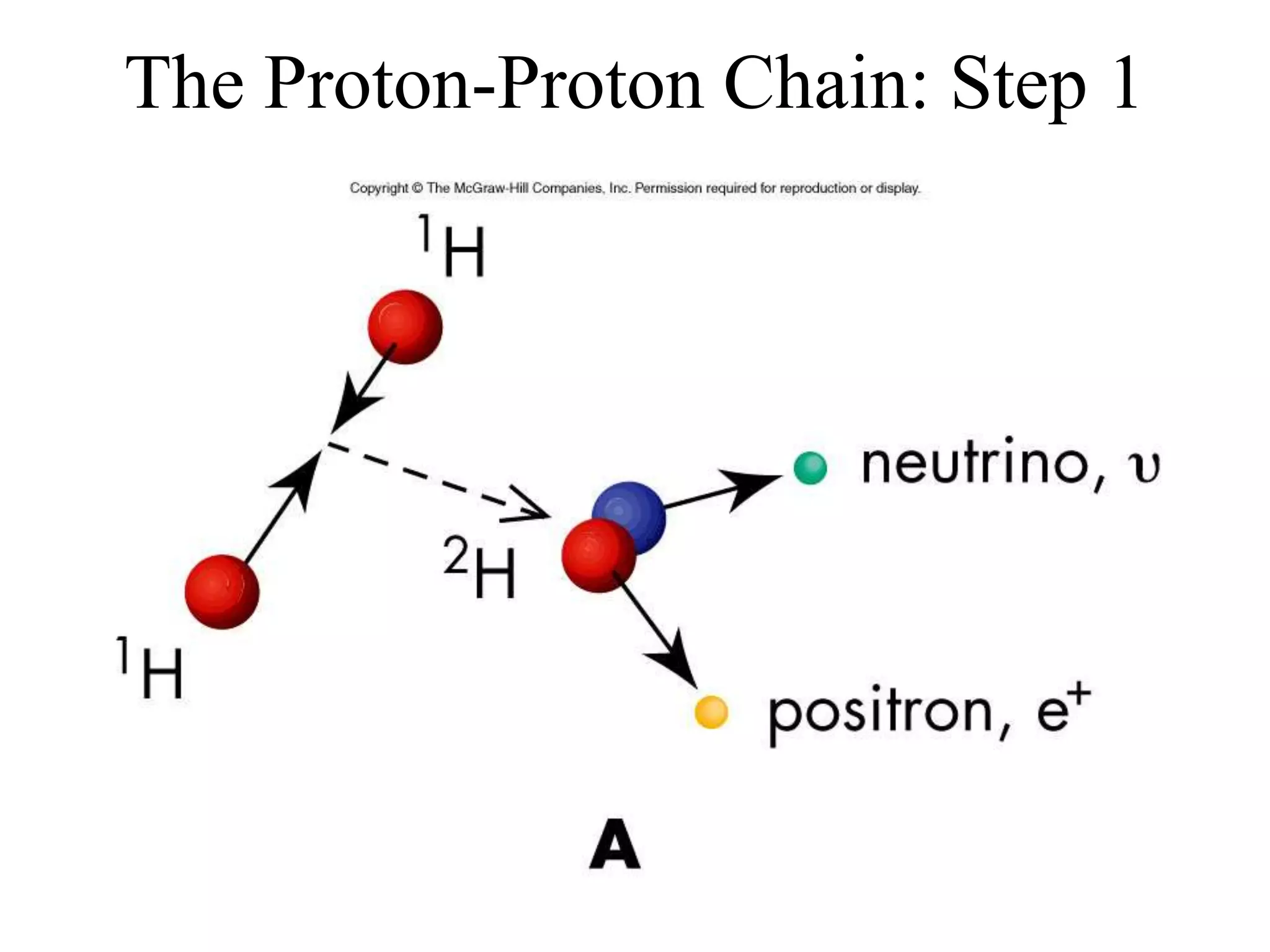
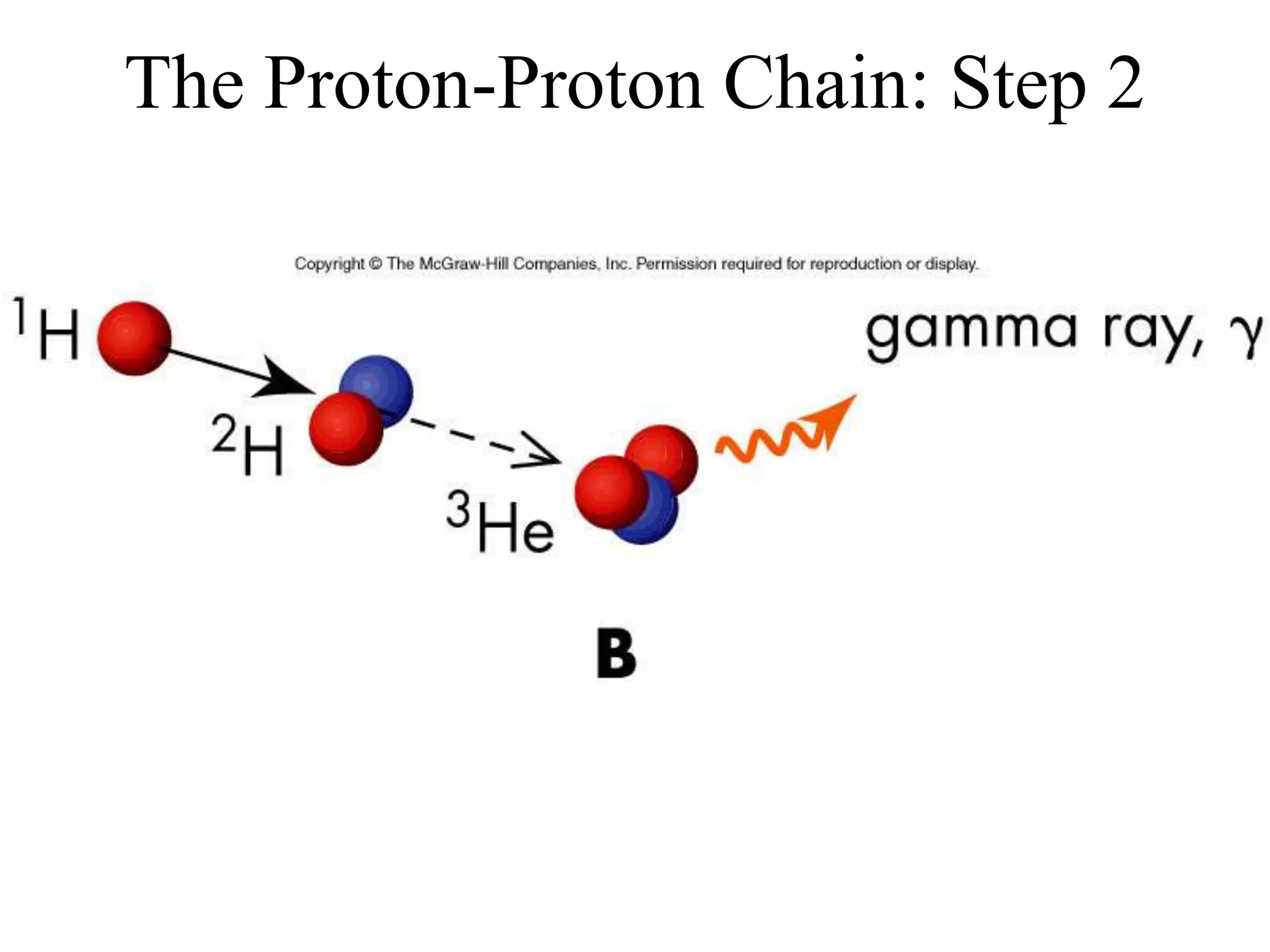
![Nuclear Fusion
• A detailed process for mass conversion in
the Sun called nuclear fusion was found:
– Sun’s core temperature is high enough to force
positively charged protons close enough
together to bind them together via the nuclear
or strong force [clip]
– The net effect is that four protons are converted
into a helium nucleus (plus other particles and
energy) in a three-step process called the
proton-proton chain](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch12oursun1-201023145558/75/Ch12-our-sun-1-23-2048.jpg)