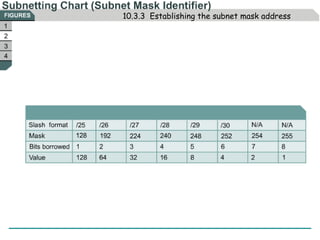
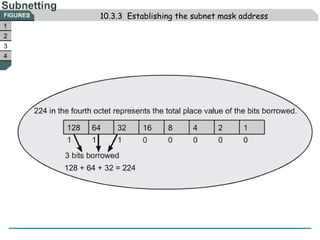
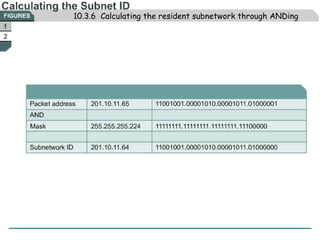
The document discusses subnetting IP addresses. It explains that subnetting provides benefits like smaller broadcast domains, low-level security, and increased address flexibility. Subnetting involves using host bits of an IP address as network bits, setting host bits of the network address to 0 and the broadcast address to 1. The document also notes how to establish the subnet mask address and apply it to classify IPs and calculate subnets through ANDing.