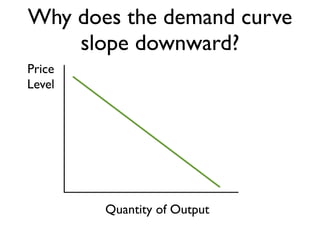
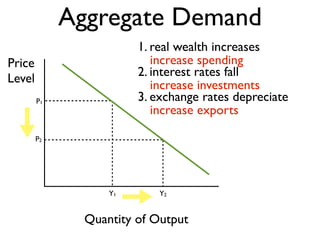
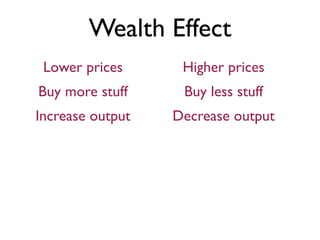
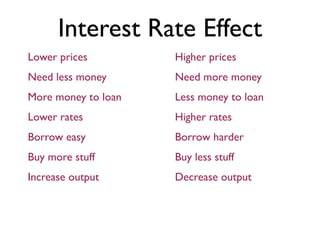
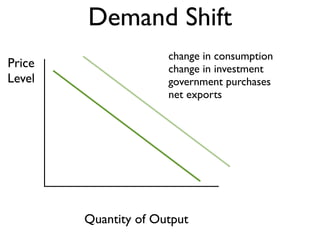
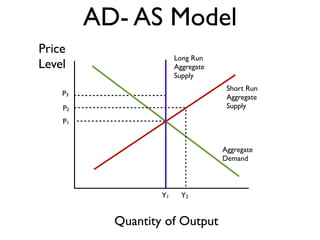
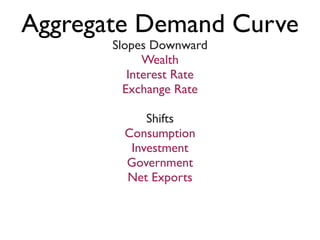
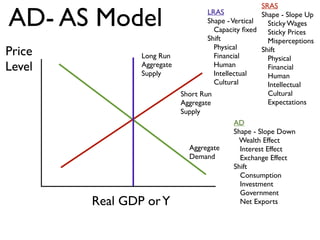
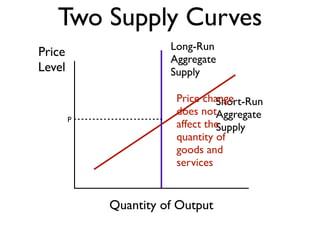
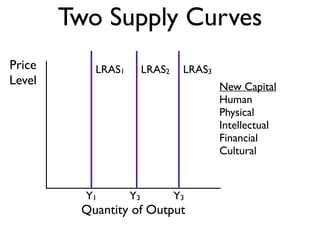
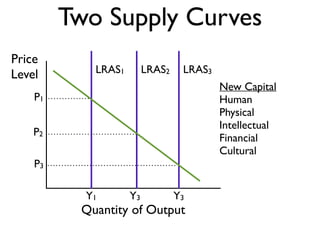
Exam 4 will take place on Tuesday May 12 and Wednesday May 13. It will cover Chapters 34, 35, and 36. The final exam is scheduled for Saturday May 23 from 9:00AM to 11:30AM. The document provides an overview of key economic concepts related to aggregate demand, aggregate supply, the economic cycle, and the AD-AS model. It defines important terms and outlines factors that can cause the aggregate demand curve, short-run aggregate supply curve, and long-run aggregate supply curve to shift.