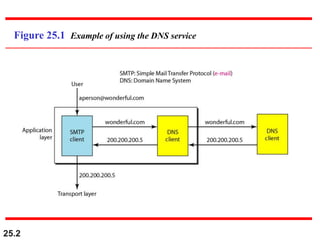
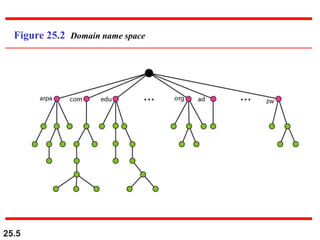
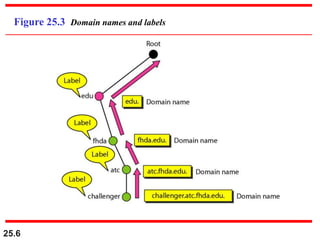
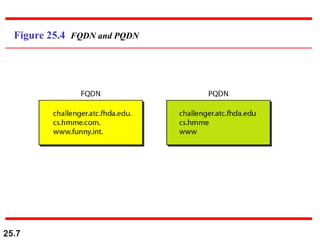
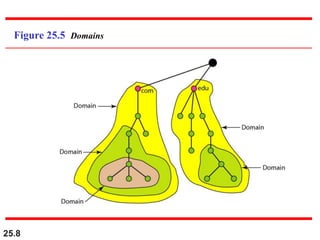
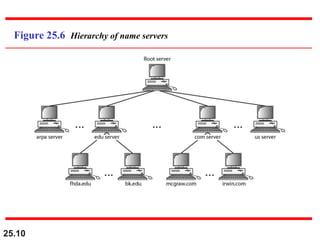
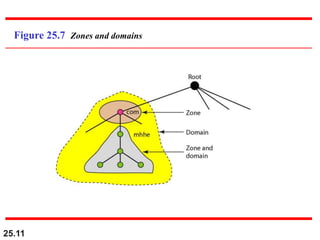
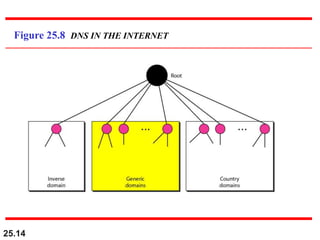
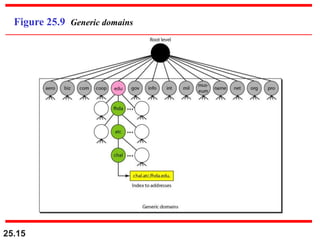
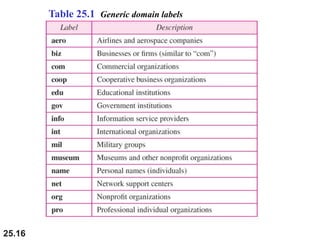
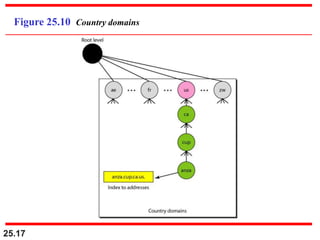
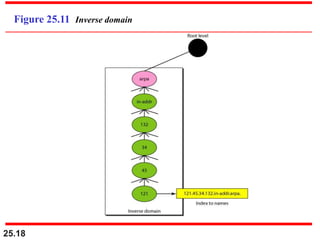
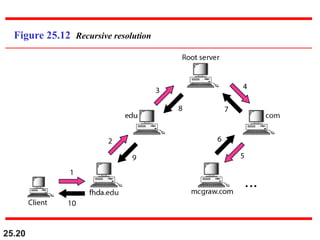
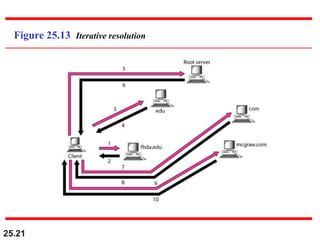
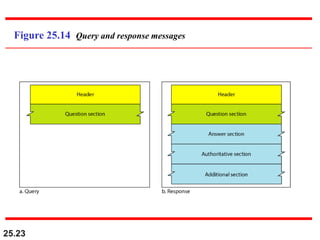
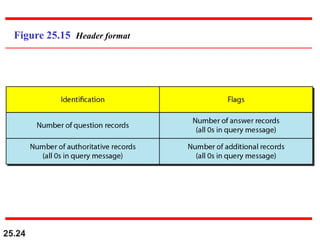
The document discusses the domain name system (DNS) which provides a hierarchical and distributed naming system that maps human-friendly domain names to computer-friendly IP addresses. It describes how DNS establishes a hierarchical domain name space with a root at the top level and up to 128 levels below. The domain name space is distributed across multiple name servers to avoid a single point of failure. DNS uses a client-server model where clients resolve names to addresses and vice versa through a recursive querying process with caching for performance.