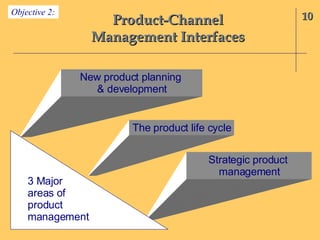
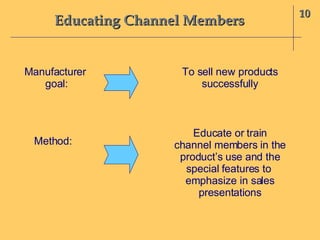
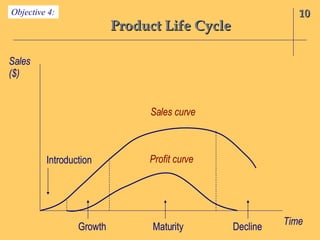
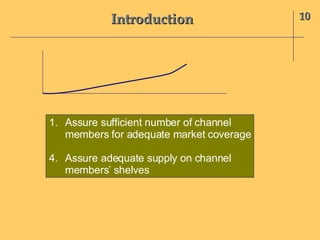
The document discusses the interface between product management and channel management. It outlines several key areas for coordination: soliciting channel member input on new product development; determining if new products are acceptable and can be effectively sold by channel members; educating members on new products; managing products through their lifecycle stages in relation to channel structure; and aligning channel members with product differentiation, positioning, and branding strategies. Successful product strategies depend on coordination with the capabilities and roles of channel members.