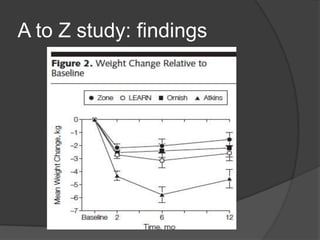
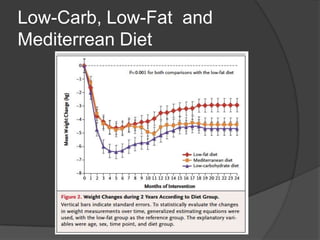
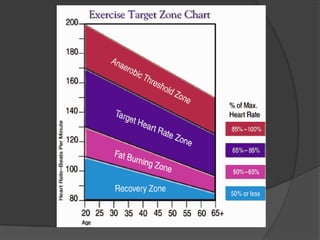
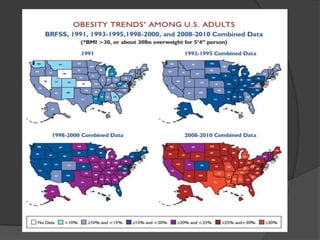
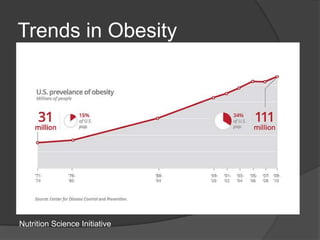
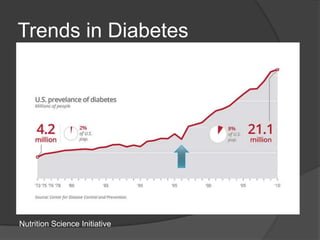
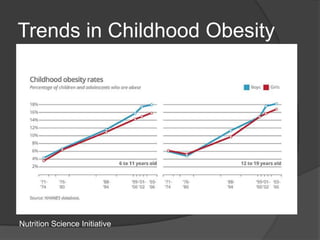
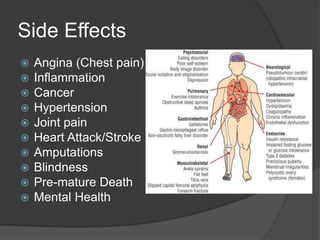
The document discusses changing nutrition guidelines and recommendations over the past 30 years as well as trends in obesity, diabetes, and childhood obesity in the United States. It notes that obesity rates have risen significantly in most states over the past decade and that obesity-related diseases continue to be highly prevalent. While current recommendations generally focus on reducing calorie intake and increasing exercise, some clinical studies have shown low-carbohydrate, high-fat diets can promote greater weight loss and improve health markers compared to low-fat diets. The document argues that lifestyle changes including adopting a paleo/low-carb diet, focusing on whole foods, sufficient sleep, and regular exercise are needed to lose weight and prevent obesity-related diseases.












![What are we currently told?
CDC: ―you must use up more calories
than you take in… since one pound [of
fat] equals 3,500 calories reduce 500-
1000 calories per day to lose 1 to 2
pounds per week.‖
Mayo Clinic: ―when it comes to weight
loss, it’s calories that count.‖](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cflweightlossseminar2012-130108154435-phpapp02/85/CFL-Nutrition-Weight-Loss-Seminar-20-320.jpg)