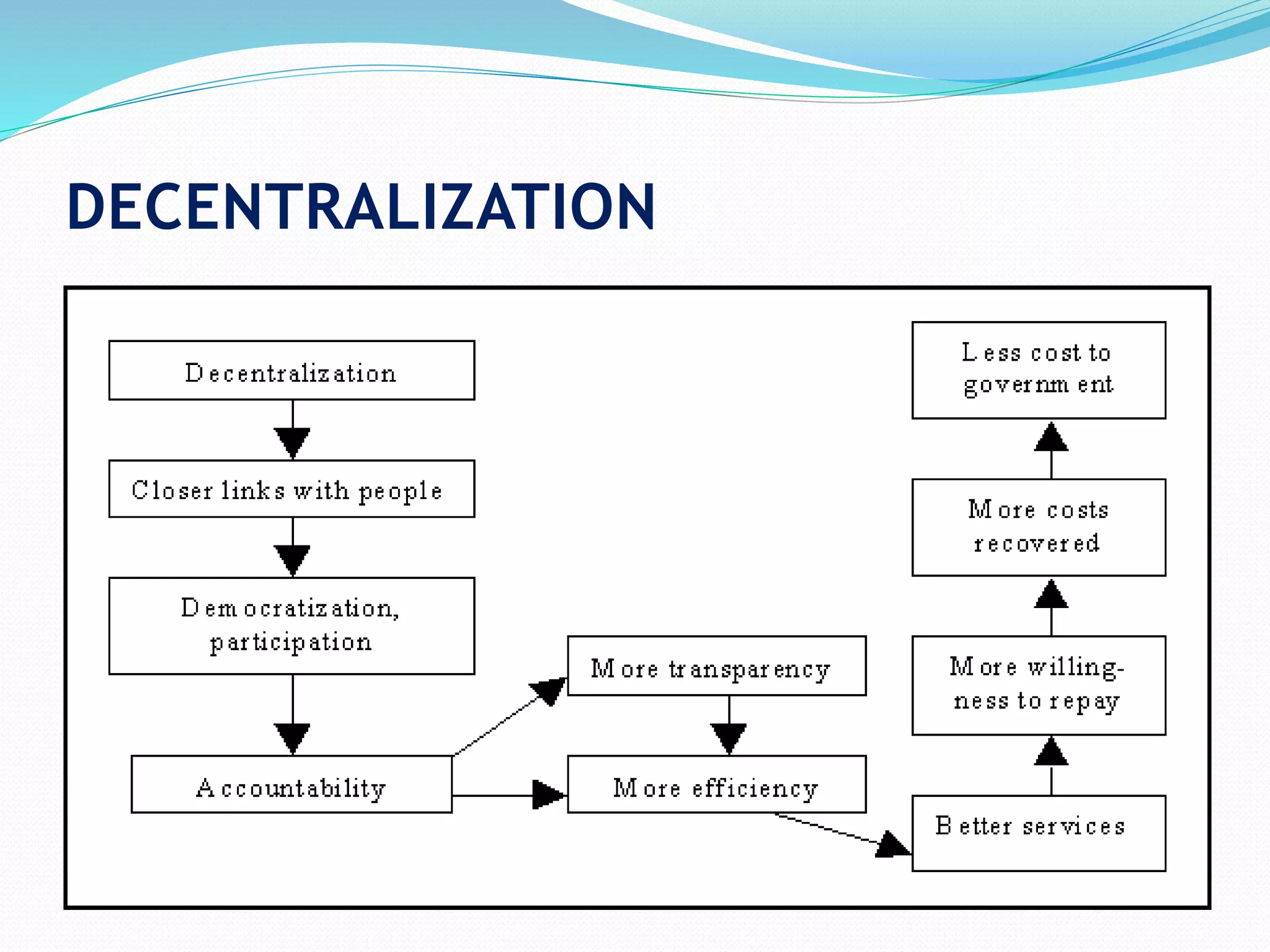
The document discusses the concepts of centralization and decentralization of authority as described by Henri Fayol, an influential figure in management theory. Centralization involves retaining decision-making power at higher management levels, while decentralization delegates authority throughout all levels of an organization. Advantages and disadvantages of both structures are outlined, along with factors influencing the decision to centralize or decentralize authority.