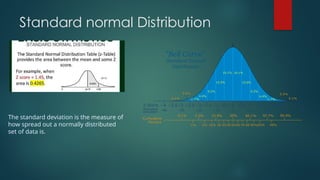
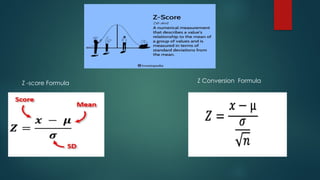
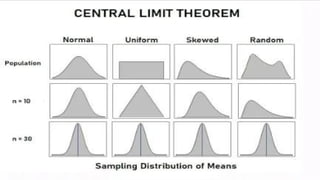
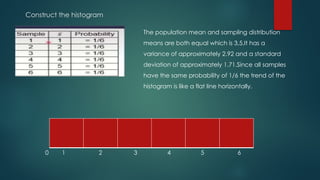
The Central Limit Theorem states that sample means will be normally distributed with sufficiently large samples, typically n ≥ 30, even if the population distribution is not normal. It discusses how to calculate probabilities using z-scores and provides examples involving high school students' exam completion times and a die's outcomes. The document also includes computations for population mean, variance, standard deviation, and illustrates a probability histogram for various sample sizes.