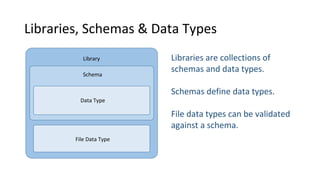
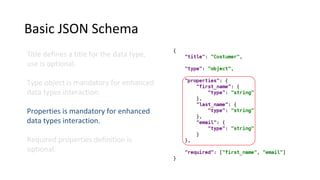
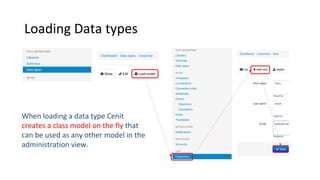
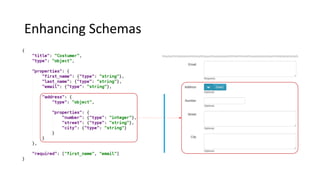
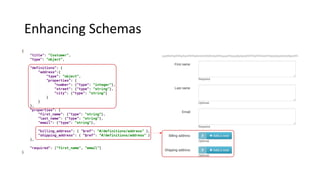
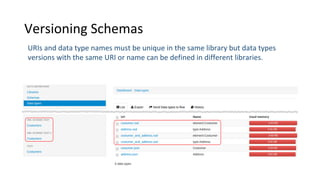
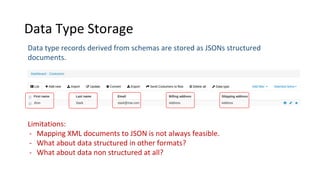
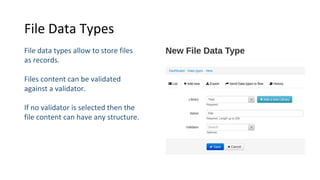
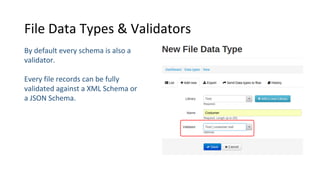
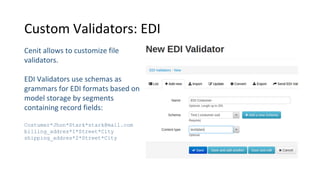
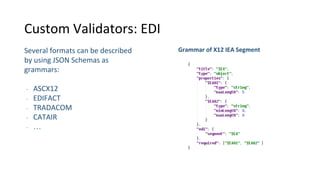
Libraries contain schemas and data types that define and validate file data types. Schemas can be defined using JSON schemas or XML schemas. When a data type is loaded, Cenit generates a class model for it. Data types can be enhanced, reused, and versioned. File data types allow files to be stored and validated against the associated schema. Custom validators like those for EDI formats can also be used to validate file contents.